![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ethics |
• A set of rules or values that spell out appropriate human conduct •Rooted from Greek idea of Character |
|
|
|
Noble Cause Corruption (Unethical act) |
• A situation in which one commits an unethical act but for the greater good Example: A police officer violates the Constitution in order to capture a serious offender |
|
|
|
Police Corruption |
• Misconduct by police officers that can involve but not limited to illegal activities for economic gain, gratituities, favors, and so on |
|
|
|
"Slippery Slope" |
• The idea that a small first step can lead to more serious behaviors, such as the receipt of minor gratituities by police officers believed to eventually cause them desire or demand receipt of items of greater value |
|
|
|
Accepted Lying |
• Police activities intended to apprehend or entrap suspects. This type of lying is generally considered to be trickery. Example: Morally weakening the suspect so that the suspect voluntarily becomes involved. |
|
|
|
Deviant Lying |
• Occasions when officers commit perjury to convict suspects or are deceptive about some activity that is illegal or unacceptable to the department or public in general. Example: Lying that serves legitimate goals occurs when officer lie to secure a conviction, obtain a search warrant, or conceal omissions during an investigation |
|
|
|
Gratituities |
• The receipt of some benefit (a meal, gift, or some other favor) either for free or for a reduced price. - When officers accept minor gifts or gratituities, people often expect special service or accommodation |
|
|
|
Whistleblower Protection Act |
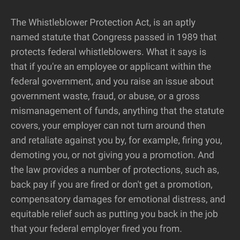
• A federal law prohibiting reprisal against employees who reveal information concerning a violation of law, rules, or regulations; waste of funds; an abuse of authority |
|
|
|
Discretion |
• Authority to make decisions in enforcing the law based on one's observations and judgement rather than the letter of the law. Example: The freedom to decide what should be done in a particular situation |
|
|
|
Ethical Decision-making Process (Looking at alternatives!) |
• A series of steps for addressing an ethical dilemma; includes looking at alternatives, considering stakeholders and consequences, and explaining to decision to others. |
|
|
|
"Bell, Book, and Candle" |
Bell: The Prima Facie test Book: Regulation or department procedure Candle: Scrutiny of others |
|
|
|
The Political Era (1840s-1930s) |
• The period of time when police were tied closely to politics and politicians, dependent on them for being hired and promoted, and for assignments- all of which raised the potential for corruption. |
|
|
|
The Reform Era (1930s-1980s) |
• Also the professional Era, from 1930s to 1980s when police sought to extricate themselves from the shackles of politicians, and leading to the crime- fighter era- with greater emphases being placed on numbers- arrests, citations, response times, etc. |
|
|
|
The Community Era (1980s-Now) |
• A time when police retrained to work with the community to solve problems by looking at their underlying causes and developing tailored responses to them. |
|
|
|
Private Police/Security |
• All nonpublic officers, including guards, watchmen, private detectives, and investigators; they have limited powers and only the same arrest powers as regular citizens. |
|
|
|
Proprietary |
• In-house security services, whose personnel are hired, trained, and supervised by the company or organization |
|
|
|
Kansas City Preventive Patrol |
• Conducted in Kansas, Missouri in 1973. • Researchers wanted to know if random patrol had only significant effect on crime- divided the city into 15 beats, five groups of three • Nothing changed |

|
|
|
Locard's Exchange Principle |
• The notion that offenders both leave something at the crime scene and take something from it; the crime scene analyst or investigators job is to locate that evidence and use it in the investigation |
|
|
|
DNA |
• Deoxyribonucleic acid, which is found in all cells; used in forensics to match evidence (hair, semen) left at a crime scene with a particular perpetrator. |
|

