![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Three Strike Law |
A crime control strategy where an offender commits 3 or more violent offenses will be sentenced to 25+ years in prison |
|
|
|
Consensus Theory of Justice |
Everyone has the same idea to create laws due to common interest |
Think the same |
|
|
Conflict theory of justice |
Explains how powerful groups create laws to protect their values and interest in diverse societies |
Large groups |
|
|
Crime control model |
A model that emphasizes law and order and argues that every effort must be made to suppress crime, and ty to convict and incarcerate offenders |
|
|
|
Due process model |
A model that advocates defendants presumption of innocence, protection of suspects rights, and limitations placed on police powers to avoid convicting innocent persons |
Innocent until proven guilty |
|
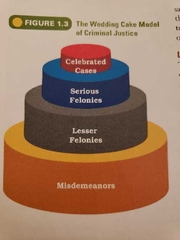
Wedding cake model |
A model of the criminal justice process whereby a four tiered hierarchy exists. Celebrated on top and lower tiers increasing in size as seriousness of cases |
|
|
|
Stare decisis |
"To stand by a decision" lower courts must follow and have the same decision of higher courts when the same legal issues and questions come to them |
|
|
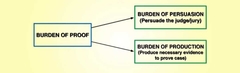
Burden of proof |
The requirement that the state must meet to introduce evidence or establish facts |
|
|
|
Criminal Law |
The body of law that defines criminal offenses and prescribes punishment for their infractions. All of society is wrong |
|
|
|
Civil law |

A generic term for all noncriminal law, usually related to settling disputes between private citizens, governmental, and/or business |
|
|
|
Mens rea |
"Guilty mind" the purposeful intention to commit a criminal act (they are aware of the consequences but still do it) |
|
|
|
Actus rea |
An act that accompanies ones intent to commit a crime, such as pulling out a knife and stabbing someone (proven guilty by DNA or evidence) |
|
|
|
Felony murder rule |
In the course of committing a crime someone dies, you will be charged with the death |
|
|
|
XYY chromosome |
The so-called criminal chromosome; criminal behavior is thought to be caused, in some offenders, by the extra Y chromosomes believed to cause agitations, agression, and greater criminal tendencies |
|
|
|
Social disorganization theory |
A theory maintaining that neighborhood characteristics, including poverty, racial heterogeneity, and resident transiency, break down social controls and lead to criminal behavior |
|
|
|
Strain theory |
A theory that argues criminal behavior is caused by feelings of strain, which occur when people believe that legitimate means of achieving success are not accessible to them. |
|
|
|
Learning theory |
A theory asserting that criminal behaviors are learned from associating with others and from social interactions and social experiences |
They learn and do from the people who they involve themselves with |
|
|
Labeling theory |
A theory contending that labeling a person as a deviant or criminal makes that person is more likely to engage in criminal behavior |
|
|
|
Social conflict theory |
A theory that explains crime as an outcome of conflicting interests between groups in society and the dominate groups attempts to control and exploit groups with less power. High status people commit as many crimes but it's the latter groups that get punished |
|
|
|
Feminist theory |
A theory that explains how gender inequality affects female offending and justice system responses to crimes committed by females. Explain why women commit fewer and different crimes than men, and why they might be subject to criminal justice sanctions for different reasons than men |
|
|
|
The classical school of criminology |
Criminal behavior is rational; people have free will to choose whether or not they will commit crime; that punishments should fit the crime; and that justice must be predictable |
|
|
|
Biological and trait theory |
Criminals are born and not made by their home or social environment. People are most likely to engage in crime if they possess criminogenic traits and are raised in environments that promote criminal behaviors |
|
|
|
National incident-based reporting system |
It was developed to collect information of crimes on a granular level to include detailed circumstances surrounding the crimes to gove law enforcement a better idea to what to look for in the future |
|
|
|
U.C.R: Uniform Crime Rate |
Published annually by the FBI, each report describes the nature of crime as reported by law enforcement agencies: includes analysis of Part 1 |
|
|
|
Hierarchy rule |
In the FBI uniform crime reports reporting scheme, the practice whereby only the most serious offense of several that are committed during a criminal act is reported by the police |
|
|
|
Duress |
threats, violence, constraints, or other action brought to bear on someone to do something against their will or better judgment. |
|
|
|
McNaughten Rule |
A test applied to determine whether a person accused of a crime was sane at the time of its commission and, therefore, criminally responsible for the wrongdoing. The M'Naghten rule is a test for criminal insanity. |
|
|
|
National crime victimization survey |
A random survey U.S. households that measures crimes committed against victims; includes crimes not reported to police |
|
|
|
"Heat of passion" |
Charge is considered as Voluntary manslaughter |
|

