![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Name this algae.
|
Spirogyra
Eukaryotic Protista |
|

Name this algae.
|
Ulothrix
Eukaryotic Protista |
|

Name this algae.
|
Oedogonium
Eukaryotic Protista |
|
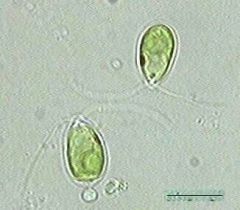
Name this organism.
|
Chlamydomonas
Eukaryotic Protista |
|
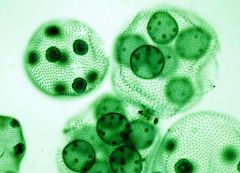
Name this organism.
|
Volvox
Eukaryotic Protista |
|
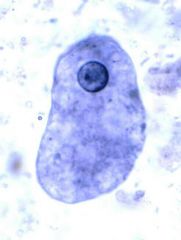
Name this organism, the disease it causes and it's classification based on motility.
|
Entamoeba histolytica
Amoebic dysentery Sarcodina |
|
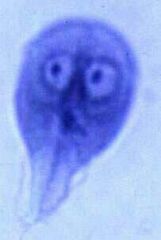
Name this organism, the disease it causes and it's classification based on motility.
|
Giardia lamblia
Water borne diarrhea Mastigophora |
|
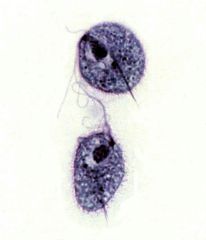
Name this organism, the disease it causes and it's classification based on motility.
|
Trichomonas vaginalis
Vaginitis Mastigophora |
|
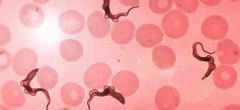
Name this organism, the disease it causes and it's classification based on motility.
|
Trypanosoma gambiensa
African sleeping sickness Mastigophora |
|
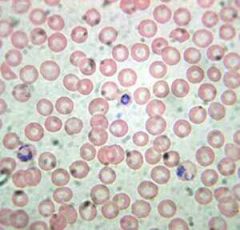
Name this organism, the disease it causes and it's classification based on motility.
|
Plasmodium vivax
Malaria Sporozoa |
|

Name this organism.
|
Stentor
Ciliata |
|
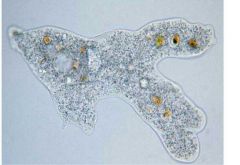
Name this organism.
|
Chaos chaos
Sarcodina |
|
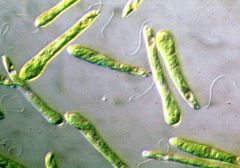
Name this organism.
|
Euglena
Mastigophora |
|
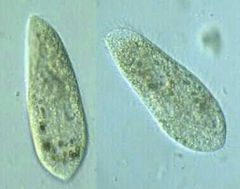
Name this organism.
|
Paramecium
Ciliata |
|
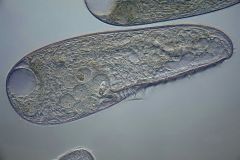
Name this organism.
|
Blepharisma
Ciliata |
|
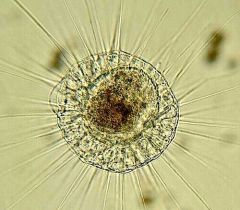
Name this organism.
|
Actinosphaerium
Sarcodina |
|
|
Name the three morphologies of bacteria.
|
Bacilli
Cocci Spiral |
|
|
Five arrangements of bacteria.
|
Diplo - two
Staphylo - grape like clusters Strepto - chains of Tetrad - four Sarcinae - group of eight, cube |
|
|
Name five eukaryotic algae of the kingdom protista.
|
Spirogyra
Ulothrix Oedogonium Chlamydomonas Volvox |
|
|
What is movement toward or away from a chemical?
|
Chemotaxis
|
|
|
What is movement toward or away from light?
|
Phototaxis
|
|
|
What is movement toward or away from oxygen?
|
Aerotaxis
|
|
|
What are characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
|
No nucleus
No organelles Peptidoglycan Binary fission 1 circular chromosome |
|
|
What are characteristics of eukaryotic cells?
|
Nucleus
Organelles If cell wall cellulose chitin Mitosis & meiosis Linear chromosomes |
|
|
Name four prokaryotic cyanobacteria of the monera kingdom.
|
Oscillatoria
Anabaena Nostoc Gleocapsa |
|
|
What is a nitrogen fixation called?
|
Heterocyst
|
|
|
A structure used for flotation is called what?
|
Gas vacuoles
|
|
|
What bacteria causes syphillis?
|
Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
What bacteria causes Gonorrhea?
|
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
What bacteria causes tetanus?
|
Clostridium tetani
|
|
|
What bacteria causes botulism?
|
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
What bacteria causes gas gangrene?
|
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
What bacteria causes antibiotic associated diarrhea (AAD)?
|
Clostridium difficle
|
|
|
What is amoeboid motion (pseudopod)?
|
Sarcodina
|
|
|
What is motion by flagella?
|
Mastigophora
|
|
|
What is motion by cilia?
|
Ciliata
|
|
|
Living protozoans that are non motile are classified as what?
|
Sporozoa
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of protozoans?
|
Lack a cell wall
Mostly motile Use phagocytosis & pinocytosis Unicellular Eukaryotic Reproduce sexually & asexually |
|
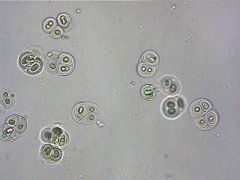
Name this organism.
|
Gleocapsa
Prokaryotic Monera |
|

Name this organism.
|
Oscillatoria
Prokaryotic Monera |
|
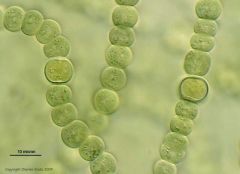
Name this organism.
|
Nostoc
Prokaryotic Monera |
|
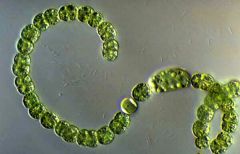
Name this organism.
|
Anabaena
Prokaryotic Monera |

