![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
270 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Acceptance Criteria |
A list of minimum requirements that a server or service component must meet for it to be acceptable to key stakeholders |
|
|
Agile |
An umbrella term for a collection of frameworks and techniques that together enable teams and individuals to work in a way that is typified by collaboration, prioritization, iterative, and incremental delivery, and time boxing. There are several specific methods (or framework) that are classed as Agile, such as Scrum, Lean, and Kanban. |
|
|
Architecture management practice |
The practice of providing an understanding of all the different elements that make up an organization and how those elements relate to one another. |
|
|
Asset register |
A database or list of assets, capturing key attributes such as ownership and financial values. |
|
|
CSFs |
Critical Success Factors |
|
|
Critical Success Factors |
Measures of success, agreement of what constitutes success, definition of done |
|
|
Availability |
The ability of an IT Service or other configuration item to perform its agreed function when required. |
|
|
Baseline |
A report or metrics that serves as a starting point against which progress or change can be assessed |
|
|
Best Practice |
A way of working that has been proven to be successful by multiple organizations. |
|
|
Big Data |
The use of very large volumes of structure and unstructured data from a variety of sources to gain new insights. |
|
|
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) |
A key activity in the practice of service continuity management that identifies vital business functions and their dependencies. |
|
|
Business Relationship Manager (BRM) |
A role responsible for maintaining good relationships with one or more customers. |
|
|
Call |
An interaction (e.g. a telephone call) with the service desk. A call could result in an incident or a service request being logged. |
|
|
Call/Contact Center |
An organization or business unit that handles large numbers of incoming and outgoing calls and other interactions. |
|
|
Capability |
Thr ability of an organization, person, process, application, configuration item, or IT Service to carry out an activity. |
|
|
Capacity and Performance Management Practice |
The practice of ensuring that services achieve agreed and expected performance levels, satisfying current and future demand in a cost effective way |
|
|
Warranty of a service |
Availability, capacity, continuity, and security are key elements of Warranty that make a service fit for use or how a service is delivered: offers assurance |
|
|
Capacity Planning |
The activity of creating a plan that manages resources to meet demand for services. |
|
|
Change |
The addition, modification, or removal of anything that could have a direct or indirect effect of services. |
|
|
Change Authority |
A person or group responsible for authorizing a change. |
|
|
Products |
Configuration if resources create products and services |
|
|
Service |
A means of enabling value co-creation by facilitating outcomes that customers want to achieve without the customer having to manage specific cost or risk. |
|
|
Change Enablement Practice |
The practice of ensuring that risks are properly assessed, authorizing changes to proceed and managing a change schedule in order to maximize thr number of successful service and product changes. |
|
|
Change Model |
A repeatable approach to the management of a particular type of change. |
|
|
Change Schedule |
A calendar that shows planned and historical changes |
|
|
Charging |
An activity that assigns a price for service |
|
|
Cloud Computing |
A model for enabling on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources that can be rapidly provided with minimal management effort or provider interactions |
|
|
Compliance |
The act of ensuring that a standard or set of guidelines is followed, or that proper, consistent accounting or other practices are being employed |
|
|
The ultimate value of a service is determined by whom? |
The Customer determines the ultimate value of a service |
|
|
A service provider suggests that they provide recovery of a service in 24 hours in the event of a disaster. This is an example of what? |
A warranty |
|
|
A set of specialized organizational capabilities for enabling value for customers in the form of services is the ITIL definition of what? |
Service Management |
|
|
Configuration |
An arrangement of configuration items (CIs) or other resources that work together to deliver a product or service. Can also be used to describe the parameter settings for one or more CIs. |
|
|
Which service management dimension is focused on third parties and how they are managed? |
Partners and suppliers - third party is an alternate word for vendor, outsourcer, or external provider; are all part of the Partner and Supplier dimension |
|
|
What is a key focus of the "value streams and processes" dimension? |
Activity Workflows - Steps, activities, procedures, work instructions, and models are in the Value Streams and Processes dimension |
|
|
What are the Four Dimensions? |
Organizations and People, Information and Technology, Value Streams and Processes, and Partners and Suppliers |
|
|
What is a focus of the "Suppliers and Partners" Dimension? |
Internal IT must manage external provider relationships in order to work together in the provisioning of products and services |
|
|
Which Guiding Principle recommends an investigation of existing capabilities before starting a practice over? |
Start Where You Are - Before starting, or starting over, you should know where you are - - create a current state baseline through assessments, audits, benchmarks, and SWOT Analysis |
|
|
What is the Focus on Value Principle all about? |
Investigating why the customer uses the services and how the service helps them meet their goals -- examine how to co-create valuable customer and user experiences to realize value |
|
|
Which guiding principles begins with assessing who the customers and stakeholders are? |
The Guiding Principle, "Focus on Value," will allow you to know who the customers and other stakeholders are, which is essential to co-creation of Value |
|
|
In which guiding principle is the theory of constraints highlighted? |
Think and Work Holistically - Theory of Constraint identifies bottlenecks and issues |
|
|
Which value chain activity provides information about service improvements to all value chain activities? |
Improve |
|
|
Which value chain activity uses service components to fulfill service requests? |
Deliver and support - fulfilling all requests is delivering solutions or support for the products and services |
|
|
Which value chain activity includes communications with customers and users? |
Engage - is interacting with all stakeholders |
|
|
Which value chain activity includes service performance with customers? |
Engage - engage interacts with stakeholders to review service performance in service reviews, during which improvements may be identified for Improve |
|
|
Which value chain activity includes establishing enterprise architecture? |
Plan - produces strategic, tactically and operational plans that includes establishing architectures. |
|
|
Which value chain activity includes the introduction of new or changed services? |
Design and Transition - Introduction of products and services is a transition activity into the production environment. |
|
|
Which value chain activity includes providing components? |
Obtain/Build - focuses on components of products and service |
|
|
Which value chain activity provides stakeholder feedback for improvements? |
Engage - interacts with stakeholders to gather requirements, demand, and feedback |
|
|
Which value chain activity produces requirements and specifications? |
Design and Transition does not usually gather requirements from stakeholders, it acquires them from engage; from which D/T creates technical requirements and specifications for Obtain/Build |
|
|
What does a value chain do? |
Converts inputs into outputs - by combining SVC activities, we create value chains, value streams, practices, and or processes that convert inputs to outputs |
|
|
What are Standard Changes? |
Low risk, preauthorized, routine changes: Well understood and fully documented; Implemented without needing additional authorization; Risk assessment repeated only if there is a modification to thr way it is carried out. |
|
|
Normal Changes are... |
Use the standard process to schedule, assess, and authorize change; Change models determine the roles for assessment and authorization; Initiation of a normal change is triggered by the creation of a change request; Organizations that have an automated pipeline for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) often automate most steps of the Change Enablement process. |
|
|
Emergency Changes are changes that... |
Must be implemented as soon as possible to prevent a major incident or resolve one; Not typically included in a change schedule; Assessment and authorization is expedited; May be acceptable to defer some documentation and reduce testing; May also be a separate change authority. |
|
|
For what is a change schedule used? |
It is used to plan changes, assist in communication, avoid conflicts, and align resources |
|
|
What is a change freeze? |
Change freezes mean that changes are stopped immediately and no new changes are allowed. |
|
|
What is the purpose of incident management? |
To minimize the negative impact of incidents by restoring normal service operation as quickly as possible. |
|
|
Configuration Item (CI) |
Any components that needs to be managed in order to deliver an IT service. |
|
|
Configuration Management Database (CMDB) |
A database used to store configuration records throughout their life cycle. The CMBD also maintains the relationships between configuration records. |
|
|
Configuration Maintenence System (CMS) |
A set of tools, data, and information that is used to support service configuration management. |
|
|
Configuration Record |
A record containing the details of a configuration item (CI). Each configuration record documents the life cycle of a single CI. Configuration records are stored in a configuration management database. |
|
|
Continual Improvement Practice |
The practice of aligning an organization’s practices and services with changing business needs through the ongoing identification and improvement of all elements involves in the effective management of products and services. |
|
|
Services Request |
A request from a user or a user's authorized representative that initiates a service action that has been agreed as a normal part of a service delivery. |
|
|
What is the purpose of Relationship Management? |
To establish and nurture the links between the organization and its stakeholders at strategic and tactical levels. |
|
|
Continuous Deployment |
An integrated set of practices and tools used to deploy software changes into the production environment. These software changes have already passed pre-defined automated tests. |
|
|
Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery |
An integrated set of practices and tools used to merge developers' code, build and test the resulting software, and package it so that it is ready for deployment. |
|
|
Control |
The means of managing a risk, ensuring that a business objective is achieved, or that a process is followed. |
|
|
IT Asset |
Any financially valuable component that can contribute to the delivery of an IT product or service. |
|
|
Event |
Any change of state that has significance for thr management of an IT Service or other Configuration Item (CI). |
|
|
Cost |
The amount of money spent on a specific activity or resource. |
|
|
Cost Centre |
A business unit or project to which costs are assigned. |
|
|
Critical Success Factor (CSF) |
A necessary precondition for the achievement of intended results. |
|
|
Culture |
A set of values that is shared by a group of people, including expectations about how people should behave, ideas, beliefs, and practices. |
|
|
What are the Seven Guiding Principles? |
1. Focus on Value 2. Start Where You Are 3. Progress Iteratively with Feedback 4. Collaborate and Promote Visibility 5. Think and Work Holistically 6. Keep It Simple and Practical 7. Optimize and Automate |
|
|
What does it mean to Focus on Value? |
Everything that the organization does needs to map, directly or indirectly, to value for the stakeholders. The focus encompasses the experience of customers and users. |
|
|
What does it mean to Start Where You Are? |
Do not start from scratch and build something new without considering what is already available to be leveraged. The current state should be investigated and observed directly to be understood. |
|
|
What does Progressing Iteratively with Feedback entail? |
Do not attempt to do everything at once. Smaller sections can be executed in a timely manner with sharper focus. Use feedback before, during, and after to ensure focus. |
|
|
What would Collaborating and Promoting Visibility look like? |
Working together across boundaries produces results that have greater buy in, more relevance to objectives, and better likelihoods of long term success. Share information to the greatest degree possible. |
|
|
What are the Three Governance Activities? |
Evaluate, Direct, Monitor (EDM - Electronic Dance Music) |
|
|
What happens during Evaluate? |
Reviewing portfolios, strategies, policies |
|
|
Who are possible stakeholders? |
--Service consumers: customer, user, sponsor; --Service Providers - internal and external - funding from consumer - business development - image improvement --Service Provider employees - financial and nonfinancial incentives, career and professional development, sense of purpose --Governing bodies - Country, state, county, city village, town, association, etc --Society and community - employment, taxes, organizations' contribution to the social and community development --Charity organizations - financial and non-financial contributions from other organizations --Shareholders - financial benefits, such as dividends, sense of assurance and stability |
|
|
Users |
Consume Services |
|
|
Customers |
Define services and ensure outcomes |
|
|
Sponsor |
Financially liable for things, responsible for service continuation |
|
|
Service Offerings are... |
A formal description of one or more services designed to address the needs of a target consumer group. |
|
|
Service Value Chain Activities include: |
Plan, Improve, Engage, Design and Transition, Obtain/Build, Deliver and Support |
|
|
The service value chain (SVC) exists... |
--inside the Service Value System (SVS) --using Value Streams that describe activities an organization takes int he creation of value --converts inputs to outputs |
|
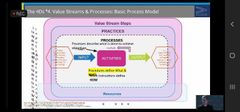
Explain this slide |
Inputs are taken Used in activities To produce outputs Ensure proper procedures Remember that the output of one activity could be an input to another activity |
|
|
What are the 34 practices? |
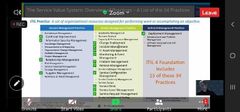
|
|
|
Service Level Management... |
Sets clear business-based targets for service performance, so that the delivery of a service can be properly assessed, monitored, and managed against these targets. Major activities are Customer Engagement and Customer Feedback |
|
|
Incident Management |
Maximized the number of successful IT changes by ensuring that risks have been properly assessed, authorizing changes to proceed, and managing the change schedule |
|
|
Service Request Management |
Support the agreed-upon quality of a service by handling all predefined, user-initiated service request in an effective and user friendly manner |
|
|
Change Enablement |
Maximized the number of successful IT changes by ensuring that risks have been properly assessed, authorizing changes to proceed, and managing the change schedule |
|
|
Continual Improvement |
Align the organization's practices and services with changing business needs through the ongoing identification and improvement of services, service components, practices, or any element involved in the efficient and effective management of products and services |
|
|
Service Desk |
Capture demand for incident resolution and service requests. It should also be the entry point and single point of contact for the service provider with all of its users. Service desk models/types include local, central, and virtual |
|
|
Problem Management |
Reduce the likelihood and impact of incidents by identifying actual and potential causes of incidents and managing workarounds and known errors. Phases are Problem Identification, Problem Control, and Error Control |
|
|
Relationship Management |
Establish and nurture the links between the organization and its stakeholders at strategic and tactical levels including the identification, analysis, monitoring, and continual improvement of relationships with and between stakeholders. |
|
|
Information Security Management |
Protect the information needed by the organization to conduct its business. this includes understanding and managing risks to the confidentiality , integrity, and availability of information, as well as other aspects of information security |
|
|
Supplier Management |
Ensure that the organization's suppliers and their performances are managed appropriately to support the seamless provision of quality products and services |
|
|
Service Configuration Management |
Ensure that accurate and reliable information about the configuration of services and the CIs that support them are available when and where they are needed |
|
|
IT Asset Management |
Plan and manage the full lifecycle of IT assets, to help the organization maximize value; control cost, manage risk, support decision making about purchases, reuse and retirement of assets; meet regulatory and contractual obligations |
|
|
What are the Seven Steps of the Continual Improvement Mode? |
How do we keep the momentum Going? What is the Vision? - Business Vision, goals and objectives Where are we now? Perform baseline assessments Where do we want to be? Define measurable targets How do we get there? Define improvement plan Take Action Execute improvement actions Did we get there? KPIs and evaluations |
|
|
Customer |
The role that defines the requirements for a service and takes responsibility for the outcomes of service consumption |
|
|
Customer Experience (CX) |
The sum of functional and emotional interactions with a service and service provider as perceived by a service customer |
|
|
Dashboard |
A real-time graphical representation of data |
|
|
Deliver and Support |
The value chain activity that ensures services are delivered and supported according to agreed specifications and stakeholders' expectations |
|
|
Demand |
Input to the service value system based on opportunities and needs form internal and external stakeholders |
|
|
Deployment |
The movement of any service component into any environment |
|
|
Deployment management practice |
The practice of moving new or changed hardware, software, documentation, processes, or any other service component to live environments |
|
|
Design and transition |
The value chain activity that ensures products and services continually meet stakeholder expectations for quality, costs, and time to market |
|
|
Design thinking |
A practical and human-centered approach used by product and service designers to solve complex problems and find practical and creative solutions that meet the needs of an organization and its customers |
|
|
Development Environment |
An environment used to create or modify IT services or applications |
|
|
DevOps |
An organizational culture that aims to improve the flow of value to customers. DevOps focuses on culture, automation, Lean, measurement, and sharing (CALMS) |
|
|
Digital Transformation |
The evolution of traditional business models to meet the needs of highly empowered customers, with technology playing an enabling role |
|
|
Disaster |
A sudden unplanned event that causes great damage or serious loss to an organization. A disaster results in an organization failing to provide critical business functions for some predetermined minimum of time |
|
|
Disaster Recovery Plans |
A set of clearly defined plans related to how an organization will recover from a disaster as well as return to a pre-disaster condition, considering the four dimensions of service management |
|
|
Driver |
Something that influences strategy, objectives, or requirements |
|
|
Effectiveness |
A measure of whether the objectives of a practice, service, or activity have been achieved. |
|
|
Efficiency |
A measure of whether the objectives of a practice, service, or activity have been achieved |
|
|
Emergency Change |
A change that must be introduced as soon as possible |
|
|
Engage |
The value chain activity that provides a good understanding of stakeholder needs, transparency, continual engagement, and good relationships with all stakeholders |
|
|
What is the purpose of the "monitoring and event management" practice? |
To systematically observe services and service components, and record and report selected changes of state. The purpose of the monitoring and event management practice is to systematically observe services and service comments, and record and report selected changes of state identified as events. |
|
|
The purpose of the _____________ is to ensure that the organization continually co-creates value with all stakeholders in line with the organization's objectives. |
Service Value System (SVS) Why? The purpose of the service value system is to ensure that the organization continually co-creates value with all stakeholders through the use and management of products and services. |
|
|
What practice provides support for managing feedback, compliments, and complaints from users? |
Service Request Management Why? The purpose of the service request management practice is to support the agreed quality of a service by handling all pre-defined, user-initiated service requests in an effective and user friendly manner. Also: Each service request may include one or more of the following: ...feedback, compliments, and complaints (for example, complaints about anew interface or compliments to a support team). |
|
|
What guiding principle emphasizes the need to understand the flow of work in progress, identify bottlenecks, and uncover waste? |
Collaborate and Promote Visibility Why? Collaborate and promote visibility states: Insufficient visibility of work leads to poor decision making, wich in turn impacts the organization's ability to improve internal capabilities. It will then become difficult to drive improvements as it will not be clear which ones are likely to have the greatest positive impact on results. To avoid this, the organization needs to perform such critical analysis activities as: understanding the flow of work in progress; identifying bottlenecks, as well as excess capacity and uncovering waste |
|
|
What does the Service Desk practice entail? |
One aspect of a good service desk is its practical understanding of the wider organization, the business processes, and the users. Service desks provide a clear path for users to report issues, queries, and request, and have them acknowledged, classified, owned, and actioned. |
|
|
Change enablement as a practice includes the assessment and authorization of __________. |
Changes |
|
|
Investigating the cause of incidents is a purpose of ____________________ practice. |
Problem Management |
|
|
Relationship management is supposed to... |
establish and nurture the links between the organization and its stakeholders at strategic and tactical levels. |
|
|
Which practice ensures that accurate and reliable information is available about configuration items and the relationships between them? |
Service Configuration Management Practice Why? The purpose of the service configuration management practice is to ensure that accurate and reliable information about the configuration of services and the CIs that support them are available when and where needed. This includes information on how CIs are configured and the relationships between them. |
|
|
The purpose of the ________________________ practice is to systematically observe services and service components, and record and report selected changes of state identified as events. |
Monitoring and Event Management |
|
|
The purpose of the ____________ practice is to capture demand for incident resolution and service requests. |
Service desk |
|
|
The purpose of the ______________________________ is to plan and manage the full lifecycle of all IT assets, to help the organization: maximize value, control costs, manage risks, support decision making about purchase, reuse, and disposal of assets. |
IT Asset Management Practice |
|
|
Which guiding principle describes the importance of doing something instead of spending a long time analyzing different options? |
Progress iteratively with feedback guiding principle Why? Progress iteratively with feedback recommends comprehending the whole, but doing something. Sometimes the greatest enemy to progressing iteratively is the desire to understand and account for everything. This can lead to what has sometimes been called "analysis paralysis, in which so much time is spent analyzing the situation that nothing ever gets done about it. |
|
|
What is the main crux of the Optimize and Automate Guiding Principle? |
Optimize and automate says that you should understand and optimize something before you automate it. Attempting to automate something that is complex or suboptimal is unlikely to achieve the desired outcome. |
|
|
What does it mean to say we will be following the Start Where You Are Guiding Principle? |
This means that you should understand the current situation before making changes. services and methods already in place should be measured and or observed directly to properly understand their current state and what can be reused form them. Decisions on how to proceed should be based on information that is as accurate as possible. |
|
|
If you're using the guiding principle Focus on Value, then you'd be... |
realizing that each improvement iteration should create value for stakeholders. All activities conducted by the organization should link back, directly or indirectly, to value for itself, its customers, and other stakeholders |
|
|
What should be done for every problem? |
It should be prioritized based on its potential impact and probability. Why? Problems are prioritized for analysis based on the risk that they pose. They are managed as risks based on their potential impact and probability. |
|
|
When should a workaround be used for a problem to reduce the impact of the problem? |
When a problem cannot be resolved quickly, it is often useful to find and document a workaround for future incidents, based on an understanding of the problem. |
|
|
What considerations influence the supplier strategy of an organization? |
Corporate culture of the organization. Why? Some organizations have a historical preference for one approach over another. Longstanding cultural bias is difficult to change without compelling reasons. |
|
|
The ______________________________ dimension encompasses an organization's relationships with other organizations that are involved in the design, development, deployment, delivery, support, and or continual improvement of services. It also incorporates contracts and other agreements between the organization and its partners or suppliers. These considerations depend on the supplier strategy rather than influence it. |
Partners and Suppliers dimension |
|
|
The type of cooperation with suppliers depends on the ____________________________. |
Supplier strategy. Why? The forms of cooperation are not fixed but exist as a spectrum. An organization acting as a service provider will have a position on this spectrum, which will vary depending on the strategy and objectives for customer relationships. |
|
|
Which practice provides visibility of the organization's services by capturing and reporting on service performance? |
Service Level Management Practice Why? Service level management provides the end-to-end visibility of the organization's services. To achieve this, service level management: ...captures and reports on service issues, including performance against defined service levels. |
|
|
Service desks... |
...provide a clear path for users to report issues, queries, and requests and have those reports acknowledged, classified, owned, and actioned. |
|
|
A request from a __________ or ______________ that initiates a service action is part of service request management. |
User or Authorized reperesentative |
|
|
Which practices is responsible for moving components to live environments? |
Deployment Management Why? The purpose of the deployment management practice is to move new or changed hardware, software, documentation, processes, or any other component to live environments. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the release management practice? |
The purpose of the release management practice is to make new and changed services and features available for use. This could possibly not be in a live environment according to the book. |
|
|
What practice identifies metrics that reflect the customer's experience of a service? |
Service Level management Why? Service level managment identifies metrics and measures that are a truthful reflection of the customer's actual experience and level of satisfaction with the whole service. Also: Engagement is needed to understand and confirm the actual ongoing needs and requirements of customers, not simply what is interpreted by the service provider or has been agreed several years before. |
|
|
______________is needed to understand and confirm the actual ongoing needs and requirements of customers, not simply what is interpreted by the service provider or has been agreed several years before. |
Engagement How will you know what the customer wants and needs without engaging, aka talking to, communicating with them? |
|
|
The purpose of ______________________________ is to capture demand for incident resolution and service requests. It should also be the entry point and single point of contact for the service provider with all of its users. |
Service Desk |
|
|
________________________ as part of the incident management practice helps direct the incident to the correct support area. |
Categorization of Incidents Why? More complex incidents will likely be escalated to a support team for resolution. Typically, the routing is based on the incident category, which should help to identify the correct team. |
|
|
The category is concerned with the type of incident whereas ______________________ is determined by business impact. |
Incidents are prioritized based on agreed classification to ensure that indigents with the highest business impact are resolved first. |
|
|
Which role submits service requests? |
The user or their authorized representative Why? The purpose of the service request management practice is to support the agreed quality of a service by handling all pre-defined, user-initiated service requests. A service request is defined as a request from a user or a user's authorized representative that initiates a service action |
|
|
The customer is.... |
... the role that defines the requirements for a service and takes responsibility for the outcomes of service consumption. Note: A customer could also be a user, and in that role, they may submit a service request. A service request is always submitted by someone in their role as user. |
|
|
What are different items often included as part of incident management? |
--There may be scripts for collecting information from users during initial contact. --There should be a formal process for logging and managing incidents. --Investigation of more complicated incidents often requires knowledge and expertise rather than procedural steps |
|
|
The __________________________ process does NOT usually include formalized, detailed procedures for how to diagnose, investigate, and resolve incidents. |
The Incident Management Process |
|
|
True or false. A single change authority should be assigned to authorize all types of change and change models. |
false. Why? It is essential that the correct change authority is assigned to each type of change to ensure that change enablement is both efficient and effective. For normal changes, change models based on the type of change determine the roles for assessment and authorization. A single change authority is inadequate. |
|
|
A ________________________ should be assigned for each type of change and change model. |
Change authority Why? It is essential that the correct change authority is assigned to each type of change to ensure that change enablement is both efficient and effective. For normal changes, change models based on the type of change determine the roles for assessment and authorization. |
|
|
Normal changes are... |
...changes that need to be scheduled, assessed, and authorized following a process. Thus, all normal changes will be authorized by a change authority. |
|
|
__________________________ can be preauthorized because they are low risk, preauthorized changes that are well understood and fully documented, and can be implemented without needing additional authorization. |
Standard changes |
|
|
________________________ are not typically included in a change schedule, and the process for assessment and authorization is expedited to ensure that they can be implemented quickly. These types of changes should be authorized by a change authority. |
Emergency Changes |
|
|
_______________________________ represent the steps an organization takes in the creation of value. Each activity transforms inputs into outputs. These inputs can be demanded from outside the value chain or outputs from other activities. All the activities are interconnected, with each activity receiving and providing triggers for further action |
Value chain activities |
|
|
Because of the fact that _________________ are specific combinations of activities and practices, and each one is designed for a particular scenario, there can be multiple ________________________ within one service value chain. |
service value streams |
|
|
What is the purpose of the service desk practice? |
The purpose of the service desk practice is to capture demand for incident resolution and service requests. It should also be the entry point and single point of contact for the service provider with all of its users. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the problem management practice? |
The purpose of the problem management practice is to reduce the likelihood and impact of incidents by identifying actual and potential causes of incidents, and managing workarounds and known errors. |
|
|
Which ITIL concept describes governance? |
The service value system (SVS) Why? The components of the service value system (SVS) are: -guiding principles -governance -service value chain -practices -continual improvment |
|
|
What are the seven guiding principles? |
-focus on value -start where you are -progress iteratively with feedback -collaborate and promote visibility -think and work holistically -keep it simple and practical -optimize and automate |
|
|
What are the four dimensions? |
-organizations and people -information and technology -partners and suppliers -value streams and processes |
|
|
What are the activities of the service value chain (SVC)? |
-plan -improve -engage -design and transition -obtain/build -deliver and support |
|
|
What is a standard change? |
A change that is well understood, fully documented, and pre-authorized |
|
|
What happens if a workaround becomes the permanent way of dealing with a problem that cannot be resolved in a cost effective manner? |
The problem remains in the known error status |
|
|
The ___________________________ dimension of a service covers roles and responsibilities, formal organizational structures, culture, and required staffing and competencies, all of which are related to the creation, delivery, and improvement of a service. |
organizations and people dimension |
|
|
The guiding principle of keep it simple and practical has as a key consideration to |
understand how each element contributes to value creation. Why? When analyzing a practice, process, service, metric, or other improvement target, always ask whether it contributes to value creation |
|
|
Environment |
A subset of the It infrastructure that is used for a particular purpose, for example, a live environment or test environment. Can also mean the external conditions that influence or affect something. |
|
|
Error |
A flaw or vulnerability that may cause incidents |
|
|
Error control |
Problem management activities used to manage known errors |
|
|
Escalation |
The act of sharing awareness or transferring ownership of an issue or work item |
|
|
Event |
Any change of state that has significance for the management of a service or other configuration item. |
|
|
External customer |
a customer who works for an organization other than that of the service provider |
|
|
failure |
the loss of ability to operate to specification or deliver the required output or outcome |
|
|
feedback loop |
a technique whereby the outputs of one part of system are used as inputs to the same part of the system |
|
|
Four Dimensions of Service Management are |
the four perspectives that are critical to the effective and efficient facilitation of value for customers and other stakeholders in the form of products and services: -Organizations and people -Information and technology -Partners and suppliers -Value streams and processes |
|
|
goods |
tangible resources that are transferred or available for transfer from a service provider to a service consumer, together with ownership and associated rights and responsibilities |
|
|
governance |
the means by which an organization is directed and controlled |
|
|
identity |
a unique name that is used to identify and grant system access rights to a user, person, or role |
|
|
improve |
is the value chain activity that ensures continual improvement of products, services, and practices across all value chain activities and the four dimensions of service management |
|
|
incident |
an unplanned interruption to a service or reduction in the quality of a service |
|
|
incident management |
the practices of minimizing the negative impact of incidents by restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible |
|
|
information and technology |
one of the four dimensions of service management. It includes the information and knowledge used to deliver services and the information and technologies used to mange all aspects of the service value system. |
|
|
information security management practice |
The practice of protecting an organization by understanding and managing the risks to the confidentiality integrity, and availability of information. |
|
|
information security policy |
the policy that governs an organization's approach to information security management |
|
|
infrastructure and platform management practice |
the practice of overseeing the infrastructure and platforms used by an organization. This enables the monitoring of technology solutions available, including solutions from third parties. |
|
|
Integrity |
a security objective that ensures information is only modified by authorized personnel and activities. |
|
|
internal customer |
a customer who works for the same organization as the service provider |
|
|
internet of things |
the interconnection of devices via the internet that were not traditionally thought of as IT assets, but now include embedded computing capability and network connectivity |
|
|
IT Asset |
Any financially valuable components that can contribute to the delivery of an IT product or service |
|
|
IT infrastructure |
All of the hardware, software, networks, and facilities that are required to develop, test, deliver, monitor, manage, and support IT services |
|
|
IT Service |
A service based on the use of information technology |
|
|
ITIL |
Best practice guidance for IT service management |
|
|
ITIL Guiding Principles |
Recommendations that can guide an organization in all circumstances, regardless of changes in its goals, strategies, type of work, or management structure. Focus on Value Start Where You Are Progress Iteratively with Feedback Collaborate and Promote Visibility Think and Work Holistically Keep it Simple and Practical Optimize and Automate |
|
|
ITIL service value chain |
An operating model for service providers that covers all the key activities required to effectively mange products and services. Plan - creating a plan Engagement - communication with all ppl necessary Design and Transition - design something, then you send it to the obtain build people, and then you deliver and support Obtain build - make it Deliver and Support - work together with production Production and services - delivered and supported Improve whenever needed Value is generated through demand |
|
|
KANBAN |
A method for visualizing work, identifying potential blockages, and resource conflicts, and managing work in progress |
|
|
Key Performance Indicator (KPI) |
An important metric used to evaluate the success in meeting an objective |
|
|
knowledge management practice |
the practices of maintaining and improving the effective, efficient, and convenient use of information and knowledge across an organization |
|
|
known error |
A problem that has been analyzed but has not been resolved |
|
|
Lean |
An approach that focuses on improving workflows by maximizing value through the elimination of waste |
|
|
lifecycle |
the full set of stages, transitions, and associated statuses in the life of a service, product, practice, or other entity |
|
|
live environment |
A controlled environment used in the delivery of IT services to service consumers |
|
|
Maintainability |
The ease with which a service or other entity can be repaired or modified |
|
|
Major incident |
An incident with significant business impact, requiring an immediate coordinated resolution |
|
|
management system |
interrelated or interacting elements that establish policy and objectives and enable the achievement of those objectives |
|
|
maturity |
A measure of the reliability, efficiency, and effectiveness of an organization, practice, or process |
|
|
mean time between failures (MTBF) |
A metric of how frequently a service or other configuration item fails |
|
|
mean time to restore service (MTRS) |
a metric of how frequently a service or other configuration item fails |
|
|
measurement and reporting |
the practice of supporting good decision making and continual improvement by decreasing levels of uncertainty |
|
|
metric |
a measurement or calculation that is monitored or reported for management and improvement. |
|
|
minimum viable product (MVP) |
a product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and to provide feedback for future product development |
|
|
mission |
a short but complete description of the overall purpose and intentions of an organization |
|
|
model |
a representation of a system, practice, process, service, or other entity that is used to understand and predict its behavior and relationships |
|
|
modelling |
the activity of creating, maintaining, and utilizing models |
|
|
monitoring |
repeated observation of a system, practice, process, service, or other entity to detect events and to ensure that the current status is known |
|
|
Monitoring and Event Management Practice |
The practice of systematically observing service and service components, and recording and reporting selected changes of state identified as events. |
|
|
obtain/ build |
the value chain activity that ensures service components are available when and where they are needed, and that they meet agreed specifications |
|
|
operation |
the routine running and management of an activity, product, service, or other configuration item. |
|
|
operational technology |
the hardware and software solutions that detect or cause changes in physical process through direct monitoring and or control of physical devices such as valves, pump's, etc. |
|
|
What are the components of the Service Value System? |
Governance, Practices, Continual Improvement, the Service Value Chain, Guiding Principles |
|
|
Is the onboarding of a new employee an example of a service request? |
Yes |
|
|
Does applying the Collaborate and Promote visibility guiding principle require reaching consensus? |
No |
|
|
What are the main points of the Collaboration and Promote Visibility Principle? |
Collaboration does not mean consensus (communication). Communicate in a way the audience can hear (stakeholder identification) Good decisions can only be made on visible data (make work visible). |
|
|
True or false Deployment moves a CI to a live environment. |
true |
|
|
True or False Deployment makes a configuration Item available for use, and release moves a service to a live environment |
false |
|
|
When a configuration item is released, it is... |
made available for use. This may or may not be in a live environment. The important thing is that it is USEABLE. |
|
|
Is the request for a workaround a service request? |
No, it is part of incident management. |
|
|
Which service concept describes a service consumer taking resources and becoming the service provider when offering those services downstream to their customers? A. Service Relationship Model B. Service Management Model C. Service Consumption D. Service Model |
A. Service relationships model |
|
|
Is there such a thing as the Service Management Model in ITIL? |
No. It is a total fake out. |
|
|
What are these concepts categorized in ITIL and what do they do? Focus on Value Start Where you Are Progress Iteratively with Feedback Collaborate and Promote Visibility Think and work Holistically Keep it Simple and Practical Optimize and Automate |
They are Guiding Principles. The Seven Guiding Principles are recommendations that can guide an organization in all circumstances, regardless of changes in its goals, strategies, type of work, or management structure. They are universal and enduring; helping make decisions in all actions, initiatives & relationships |
|
|
What are the similarities and differences between Deployment and Release? |
They are both practices of ITIL. Deployment moves the CI to a live environment; Release makes a service available for use. Sometimes Deployment and Release can happen at the same time. However, usually release happens first so that testing can occur and then deployment comes afterward. |
|
|
Organization |
a person or a group of people that has its own functions with responsibilities, authorities, and relationships to achieve its objectives |
|
|
organizational change management practice |
the practice of ensuring that changes in an organization are smoothly and successfully implemented and that lasting benefits are achieved by managing the human aspects of the changes. |
|
|
Organizational resilisience |
the ability of an organization to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and adapt to unplanned external influences |
|
|
organizational velocity |
the speed, effectiveness, and efficiency with which a organization operates. Organizational velocity influences time to market, quality, safety, costs, and risks |
|
|
organizations and people |
one of the four dimensions of service management. it ensures that the way an organization is structured and managed, as well as its roles, responsibilities, and systems of authority and communication, are well defined and support its overall strategy and operating model. |
|
|
outcome |
a result for a stakeholder enabled by one or more outputs |
|
|
Output |
A tangible or intangible deliverable of an activity |
|
|
outsourcing |
the process of having external suppliers provide products and services that were previously provided internally |
|
|
partners and suppliers |
one of the four dimensions of service management. It encompasses the relationships an organization has with other organizations that are involved in the design, development, deployment, delivery, support, and or continual improvement of services. |
|
|
partnership |
a relationships between two organizations that involves working closely together to achieve common goals and objectives |
|
|
performance |
a measure of what is achieved or delivered by a system, person, team, practice, or service |
|
|
pilot |
a test implementation of a service with a limited scope in a live environment |
|
|
plan |
the value chain activity that ensures a shared understanding of the vision, current status, and improvement direction for all four dimensions and all products and services across an organization |
|
|
policy |
formally documented management expectations and intentions, used to direct decisions and activities |
|
|
portfolio management practice |
the practice of ensuring that an organization has the right mixed of programmes, projects, products, and services to execute its strategy within its funding and resource constraints |
|
|
post-implementation review (PIR) |
a review after the implementation of a change to evaluate success and identify opportunities for improvement |
|
|
problem |
a cause, or potential cause, of one or more incidents |
|
|
problem management practice |
the practice of reducing the likelihood and impact of incidents by identifying actual and potential cause of incidents, and managing workarounds and known errors |
|
|
Procedure |
a documented way to carry out an activity or a process |
|
|
process |
a set of interrelated or interacting activities that transform inputs into outputs |
|
|
product |
a configuration of an organization's resources designed to offer value for a consumer |
|
|
production environment |
see live environment |
|
|
programme |
a set of related projects and activities , and an organization structure created to direct and oversee them |
|
|
project |
a temporary structure that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more outputs or products according to an agreed business case. |
|
|
project management practice |
the practice of ensuring that all an organization's projects are successfully delivered |
|
|
quick win |
an improvement that is expected to provide a return on investment in a short period of time with relatively small cost and effort |
|
|
record |
a document stating results achieved and providing evidence of activities performed |
|
|
recovery |
the act of returning a configuration item to normal operation after a failure |
|
|
recovery point objective (RPO) |
the point to which information used by an activity must be restored to enable the activity to operate on resumption |
|
|
recovery time objective (RTO) |
the maximum acceptable period of time following a service disruption that can elapse before the lack of business functionality severely impacts the organization |
|
|
relationship management practice |
the practice of establishing and nurturing links between an organization and its stakeholders at strategic and tactical levels |
|
|
release |
a version of a service or other configuration item, or a collection of configuration items, that is made available for use. |
|
|
release management practice |
the practice of making new and changed service and features available for use |
|
|
reliability |
the ability of a product, service, or other configuration item to perform its intended function for a specified period of time or number of cycles |

