![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the 5 phases of the Service Lifecycle?
|
1. Service Strategy
2. Service Design 3. Service Transition 4. Service Operation 5. Continual Service Improvement Page 47, ITIL Foundation |
SDTO(CS)
|
|
|
Is it possible to be "ITIL Compliant"
|
No.
ITIL is a set of best practices that are to be adapted to specific environments. |
|
|
|
Adoption of best practice needs to consider which things?
|
1. Sources
2. Enablers 3. Drivers 4. Scenarios Page 15, ITIL Foundation |
4 areas
|
|
|
Give some examples of Best Practice Sources
|
– Standards
– Industry Practices – Academic Research – Training & Education – Internal Experience Page 15, ITIL Foundation |
Sources generate choices of best practice to choose from.
|
|
|
Give some examples of Best Practice Enablers
|
– Employees
– Customers – Suppliers – Advisors – Technology Page 15, ITIL Foundation |
Enablers aggregate the ability to carry out selected best practices.
|
|
|
Give some examples of Best Practice Drivers
|
– Substitutes
– Regulators – Customers Page 15, ITIL Foundation |
Events or activities that create the need to adopt a practice
|
|
|
Give some examples of Best Practice Scenarios
|
– Competition
– Compliance – Commitment Page 15, ITIL Foundation |
The situation(s) which cause(s) an organisation to focus on specific practices
|
|
|
What are some of the reasons that ITIL is successful?
|
– Vendor Neutral
– Non–Prescriptive – Best Practice ITIL is successful because it is practical, structured guidance that has been proven to work in organisations everywhere. Page 16, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a Service?
|
A means of delivering value to customers by facilitating outcomes customers want to achieve without the ownership of specific costs and risks
Value Outcomes Costs Risks Page 18, ITIL Foundation |
VOCR
|
|
|
What is an Outcome?
|
The result of carrying out an activity, following a process, or delivering an IT service; intended and actual.
Page 18, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is an IT Service?
|
A service provided by an IT service provider. An IT service is made up of a combination of IT, people and processes:
– Customer–facing – Supporting Page 18, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
How are customer outcomes accomplished?
|
By the performance of tasks.
Page 19, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Are services analogous to systems, or components of technology?
|
No!
Services are perceived by the customer as an end–to–end comprehensive entity comprised of technology, people, processes, suppliers, funding, facilities, regulatory compliance, etc Page 19, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Which 3 ways can services be classified?
|
1. Core – deliver basic outcomes
2. Enabling – Required for delivery of Core, may or may not be visible to customers. 3. Enhancing – Not essential to delivery of core service Page 20, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
In which 3 areas is value defined? |
1. Business outcomes achieved 2. Customer's preferences 3. Customer's perception of what was delivered
Page 23, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are the two primary elements of Value? |
1. Utility: Fit for purpose. What the service does.
2. Warranty: How the service is delivered to the customer.
Both of these are necessary for the service to have value.
Page 25, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are two types of assets?
|
1. Capabilities
2. Resources Capabilities are developed over time, and represent an organisation's ability to control, coordinate, and deploy resources in order to produce value. Resources are the direct inputs required for production. Page 27, ITIL Foundation |
Tangible and Intangible...
|
|
|
What is Service Management? |
A set of specialised organisational capabilities for providing value to customers in the form of services.
(Service Management transforms capabilities and resources into valuable services)
Page 28, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Who are the stakeholders in IT Service Management?
|
– Customers
– Users – Suppliers Customers – Those who buy goods or services. An IT service provider's customer defines and agrees the service level targets. Users – Those who use the service on a day–to–day basis Suppliers – Third parties responsible for supplying goods and/or services that are required to deliver IT Services. |
|
|
|
What is a process? |
A structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective Page 28, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
4 Characteristics of a process? |
1. Measurable 2. Delivers Specific Results 3. Has Customers or Stakeholders 4. Responds to a specific trigger
Page 37, ITIL Foundation
|
|
|
|
What is a function? |
A team or group of people, and the tools or other resources they use to carry out one or more processes or activities Page 39, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a group? |
In ITIL, groups refer to people who perform similar activities. They're usually not formal organisational structures. Page 39, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a team? |
A team is a more formal type of group. These are people who work together to achieve a common objective, not necessarily in the same organisational structure. Page 39, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a role? |
A role, defined in a process or function, is used to assign activities and grant responsibilities and authorities to a person or team Page 40, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
The Service Owner |
Is accountable for the delivery of a specific IT service, and is a primary stakeholder in all of the underlying IT processes - Represents the service - Provides input - Escalation Point - Represents the service at CAB meetings - Provides input/priorities for CSI efforts Page 42, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is CSI? |
Continual Service Improvement |
|
|
|
The Process Owner |
Is accountable for ensuring a process is fit for purpose. - Documenting and publicising the process - Defining/reviewing/actioning KPIs - Ultimately responsible for the design of the process - Improving process efficiency - Training - Resourcing Page 43, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
The Process Practitioner |
Is responsible for carrying out one or more process activities Page 40, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What does RACI stand for? |
Responsible Accountable Consulted Informed The RACI Model is an authority matric used to allocate roles and responsibilities in relation to processes and activities. Page 44, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Service Strategy... |
Provides guidance for developing abilities that enable the organisation to function in a more strategic manner.
(Fundamental questions; who, what, how.) Page 47, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Service Design... |
Focuses on creating service integrity through the design and development of services and serviced management practices in a holistic, consistent, and effective manner.
(Realise strategic intent)
Page 47, ITIL Foundation
|
|
|
|
Service Transition... |
Aids in developing and improving capabilities for effectively transitioning new or changed services into operation. (Does the design make sense? Test, get acceptance) Page 47, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Service Operation... |
Guidance for the day-to-day processes required for the delivery and management of services (Longest phase of the lifecycle, where the customer reaps the value) Page 47, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Continual Service Improvement... |
Is guidance aimed at the evaluation and improvement of the quality of services, processes, and the Service Lifecycle. Page 47, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of metrics? |
1. Technology Metrics 2. Service Metrics 3. Process Metrics Page 50, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a Critical Success Factor (CSF)? |
Something that must happen if an IT service, process, plan, project, or other activity is to succeed.
Page 51, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI)? |
KPIs are used to measure the achievement of Critical Success Factors. Eg. "10% increase in customer satisfaction for handling Incidents over the next 6 months" Page 51, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of KPI? |
1. Qualitative 2. Quantitative Page 51, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are the 4 categories of KPI? |
1. Compliance 2. Quality 3. Performance 4. Value Page 52, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is the Deming Cycle? |
PLAN DO CHECK ACT Page 54, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
3 Service Provider types |
Type 1 - Internal service provider Type 2 - Shared services unit Type 3 - External service provider Page 60, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Which 3 areas make up the Service Portfolio? |
1. Service Pipeline 2. Service Catalog 3. Retired Services Page 61, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What are the four Ps? |
1. People 2. Processes 3. Products (Technology) 4. Partners (Suppliers) Page 78, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is a Service Design Package? |
It represents documents which define all aspects of an IT service and its requirements through each stage of its lifecycle Page 79, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is S.T.A.M.P? |
Service Solutions Tools and systems for management information Architectures Measurement systems Processes Page 80, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is an SLA? |
A written agreement between an IT service provider and the IT customer(s) Page 87, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
What is an OLA? |
An agreement between an IT service provider and another part of the same organisation that assists with the provision of services Page 87, ITIL Foundation |
|
|
|
Service Transition... |
Ensures that new, modified, or retired services meet the expectations of the business as documented in the Service Strategy and Service Design stages of the lifecycle.
Page 119, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is a model? |
Another name for a workflow
Sets of predefined steps that can be followed.
Page 123, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is a CI? |
A service asset that needs to be managed in order to deliver services. (Service Asset: Capability/Resources) Page 129, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What does SACM (Service Asset & Configuration Management) do? |
Ensures that CIs are identified, baselined, maintained, and changes to them are controlled. Page 129, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is a DML? |
A definitive media library. Page 132, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Change Management? |
To control the lifecycle of all changes, enabling beneficial changes to be made with minimum disruption to IT services. Page 133, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of Change? |
1. Standard Change: Pre-authorised, low risk 2. Emergency Change: Time critical. Consequences of waiting are unacceptable 3. Normal Change: Any service change that is not standard or emergency Page 135, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Release & Deployment Management? |
Plan, Schedule, and control the build, test, and deployment of releases. Page 143, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What are the 4 phases of Release & Deployment? |
1. Release & Deployment Planning 2. Release Build & Test 3. Deployment 4. Review & Close Page 148, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Knowledge Management? |
To share perspectives, ideas, experience, and information Page 149, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is an SKMS? |
Service Knowledge Management System Page 150, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is DIKW? |
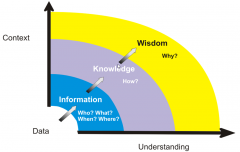
Data Information Knowledge Wisdom Pg 152 |
|
|
|
What is the relationship of CMDB, CMS, and SKMS? |
SKMS -> CMS -> CMDB (1 or more) Page 153, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What does SKMS stand for? |
Service Knowledge Management System |
|
|
|
What does CMS stand for? |
Configuration Management System |
|
|
|
What is an Event? |
Any change of state that has significance for the management of a CI or IT Service Page 157, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is an Alert? |
A notification that: - A threshold has been reached - Something has changed - A failure has occurred Page 158, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is an Incident? |
An unplanned interruption to an IT service or reduction in the quality of an IT service. Failure of a Configuration Item that has not yet impaced service. Page 159, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define Impact |
A measure of the effect of an incident, problem or change on business processes. Impact is often based on how service levels will be affected. Page 160, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define Urgency |
A measure of how long it will be until an incident, problem or change has a significant impact on the business. Page 160, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define Priority |
Priority is used to identify the relative importance of an incident, problem, or change, and is used to identify required times for actions to be taken Page 160, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is a Service Request? |
A request from a user for information or for small changes that are low risk, frequently performed, low cost, etc Page 161, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define Problem |
The underlying cause of one or more incidents Page 162, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define Workaround |
A technique which reduces or eliminates the impact of an incident or problem for which a full resolution is not yet available. Page 163, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
Define 'Known Error' |
A Problem that has a documented root cause and a workaround Page 164, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is 'KEDB'? |
Known Error Database Page 164, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is the goal of Incident Management? |
To restore normal service operation as quickly as possible. Minimise the adverse impact on business operations Ensure the best possible levels of service quality and availability are maintained Page 169, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
What is a Major Incident? |
An incident that results in significant disruption to the business. Page 173, ITIL Foundations |
|
|
|
2 Types of Problem Management |
1. Reactive 2. Proactive Page 185, ITIL Foundations |
|

