![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Effector CD4+ T cells
|
- Secretion of cytokines
- Thp = naive CD4+ cells |
|
|
Where?
|
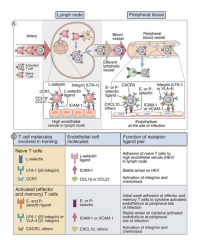
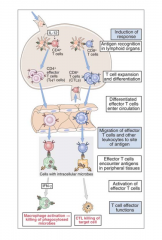
Primary immune responses occur in secondary lymphoid tissues and lead to the generation of T cell subsets that secrete distinct patterns of cytokines
|
|
|
Antigen Recognition and Molecular Interactions
|
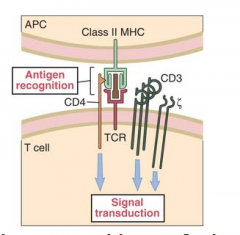
T-cells requires that the antigen be displayed on the surface of an antigen presenting cell in association with class II MHC (peptide/class II MHC)
|
|
|
Dendritic cell
|
- Most efficient antigen-presenting cell
- Expresses both class II MHC and various costimulatory molecules |
|
|
Signals for CD4+ Activation
|
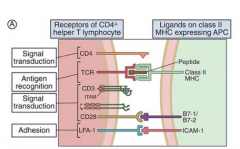
1. Peptide/class II MHC with TCR
2. Class II MHC with CD4 3. B7 family of costimulatory molecules with their counter ligands, CD28/CTLA4 4. CD40 with its counter ligand CD40L/CD154 5. Adhesion molecules |
|
|
Primary Response: Progression from CD4+ Naive T cell (Thp) to T cell Subsets:
|
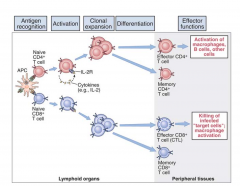
- TCR interaction with peptide/MHC II - naïve CD4+ T cells, Thp, express IL-2 receptors, and secrete the cytokine, interleukin-2 (IL-2)
- Interaction of IL-2 induces clonal expansion of antigen stimulated T cells, increasing # of T cells peptide/class II MHC - Costimulatory signals from ligation of CD4 (or CD8) with class II MHC (or class I MHC) are also required for optimal T cell activation |
|
|
CD28 with CD80/CD86
|
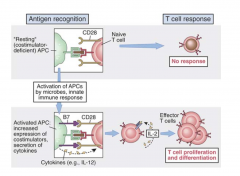
- Critical signal in T cell activation leading to clonal expansion
- T cell activation expression of CD28 initially increases, then is transiently down regulated |
|
|
CD80 (B7)
|
- Ligand for CD28 exists in two distinct forms = CD80 and CD86/B7-1 and B7-2
- Both are constitutively expressed on dendritic cells and peritoneal macrophages - Induced on activated B cells, monocytes, and Langerhans cells |
|
|
Classic Model of Thp cell Activation
|
- Th0 cells secrete cytokines common to both subsets (IL-4, IL-2, and IFNγ)
|
|
|
Th1 or Th2 cell phenotype
|
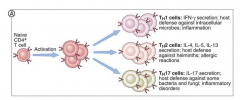
Depends on several factors:
1. If IFNy = high, Th1 2. If IL-4 = high, Th2 |
|
|
Source and Role of IL-4 (Non-T cell Derived Source)
|
- Th0 populations are driven towards the Th2 and Type-2 cytokine secretion
- Type-2 cytokine = IL-5, IL-6, IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, TGF-B |
|
|
Source and Role of IFNγ (NK cell Derived)
|
- Th0 cells to Th1 and Type-1 cytokine secretion
- Type-1 cytokines = IL-2, IFN-y, TNF |
|
|
IL-12
|
- Produces IFNγ - indirectly increases Th1 and Type 1 cytokine secretion
|
|
|
Type 1 cytokines vs. Type 2 cytokines
|
- Type 1 cytokines = IL-2, TNF, IFNγ
- Type 2 cytokines = IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, TGFβ, and IL-13 |
|
|
Type 1
|
- Macrophages, NK cells and CD8+ T cells
- Responsible for delayed type hypersensitivity responses that are manifestation of activation of memory CD4+Th1 cells (clinical section). - Required for viruses, parasites, fungi, and intracellular bacteria. |
|
|
Type 2
|
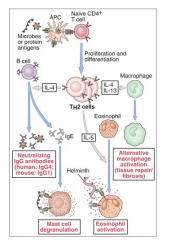
- B-cell induced activation and support antigen
- B-cell differentiation to plasma cells - Support isotype switching to IgG1 and IgE (IL-4) |
|
|
IL-10
|
- Down regulation of Th1 (cells/cytokines) via inhibition of IL-12 secretion
|
|
|
T cell Regulation
|
1. Peptide/MHC complexes are no longer being presented to T cells
2. Reciprocal regulation of cytokine secretion by Th1 and Th2 cells 3. CTLA-4/CD152 interaction 4. CD200-CD200R interaction 5. Apoptosis 6. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) |
|
|
Role of CTLA-4/CD152
|
- Binds the B7 family members
- Apoptotic stimulus |
|
|
CD200
|
- Ligand for CD200R1 and its isoforms
- Leads to suppression of T-cell-mediated immune responses - CD200 expression on tumor cells suppresses anti-tumor cytotoxic immune responses |
|
|
CD200R
|
- CD200R is expressed primarily on cells of the myeloid lineage (some T cells)
- C4+ T cells, memory cells express higher amounts of CD200R - CD200R expression is up-regulated on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after stimulation. - Interaction of CD200 with CD200R leads to suppression of the cell expressing CD200R |
|
|
Adaptive-Induced T Regulatory cells (a/iTregs)
|
- a/i Tregs arise in the periphery following activation of Thp cells in the presence of TGFβ
- CD4+, CD25+, and FOXP3+ |
|
|
CD4+ Th17 cells
|
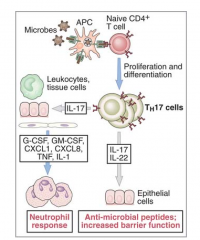
- Arise from Th0 cells in the presence of TGFβ and IL-6
- TGFβ and IL-1 may also induce the differentiation |
|
|
Summary of differentiation of Th17
|
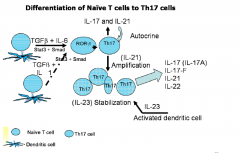
- NOTE: FINAL stage requires IL-23
|
|
|
Secondary Response (Memory) T cell activation
|
- Memory cells can serve an immunosurveillance role, having been pre-sensitized to the immunizing agent that induced their differentiation
- Memory CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines |
|
|
CD8+ T cell Activation (Antigen Induced differentiation)
|
IL-2 and IFNγ induces differentiation of pCTL to CTL
|
|
|
Costimulatory molecules for T-cell activation
|
- CD2 and LFA-3, LFA-1 and ICAM (1-3)
- These are necessary |
|
|
Presentation of Peptide-Class I MHC
|
- CD8+ T cells recognize peptide-MHC class I on the surface of any nucleated cell
- TAP-1 and TAP-2 - complex with Class I MHC in the endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Sequence of Events in Development of pCTL to CTL
|
- Requires IL-2
- Differentiation of most pre-CTLs requires auxiliary activation of Th1 cells to provide a source of IFNγ and IL-2 - IL-2 functions in a paracrine manner to induce proliferation and clonal expansion of those pCTLs that express IL-2 receptors - CTLs (hereafter termed CTLs) function in immune surveillance |
|
|
CTL cytotoxicity and delivery of lethal hit
|
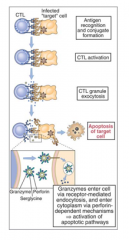
1. Formation of mature CTL with the target cell
2. Triggers the localization of lytic granules to the CTL membrane where the two cells are in contact 3. Polarization of granule release directed towards the target cell -ensures specificity of killing 4. Death of the target cell occurs by either osmotic lysis or apoptosis |
|
|
Perforin
|
- Pore forming protein whose insertion into the target cell membrane leads to colloidal swelling and osmotic lysis
- Release of perforin dependent on calcium |
|
|
CD8+ T cell activation: Secondary Response (Memory)
|
- After infection, some T cells become dormant = memory cells
- CD8+ T cells requires less costimulation than for primary responses - Memory CD8+ T cells can occur anywhere that the T cell encounters a cell expressing the same Class I MHC-peptide that triggered its activation |
|
|
Activators of Lymphocytes
|
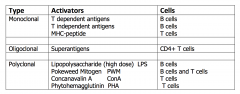
|
|
|
Superantigens
|
- Superantigens crosslink the CD4+ T cell variable region, at a site that is independent of the peptide binding site, with class II MHC proteins
- Do not undergo processing and presentation by MHC molecules |

