![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Describe suture and list Types of Sutures |
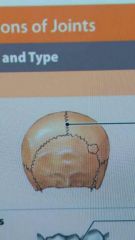
A synarthrosis joint. It is classified as Fibrous. Types: Serrate, Squamous, Synostosis and Plane |
3 start with S and one starts with P |
|
|
Describe a squamos suture |
one bone overlaps another |
|
|
|
Which is the most common suture? |
serrate suture |
|
|
|
Describe a plane suture |
margins of bone are fairly smooth and line up next to each other (maxillary suture) |
|
|
|
describe synostosis |
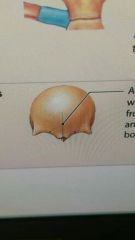
A bony synarthrosis joint. present during growth of the skull |
|
|
|
Describe the diarthrosis joint |

3rd type of functional classification. Only synovial joints are classified like this. It is freely movable, stable, complex always synovial joint, hip/shoulder have labrum |
|
|
|
What is labrum |
an extension of the articular cartilages that enalrges the joint surface area and is present in the hip and shoulder |
|
|
|
describe a synarthrosis joint |

1st type of functional classification. immovable. Includes sutures, gomphosis, synchondrosis and synostosis |
|
|
|
describe synchondrosis |
A synarthrosis joint. The connecting material is hyaline cartilage, immovable |
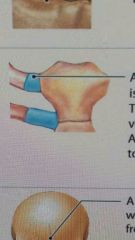
examples are the epiphyseal plate and costal cartilages |
|
|
characteristics fibrous joints |
This is a structural classification. Includes suture, gomphosis, and syndesmosis. No synovial cavity, Connected by dense fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
|
characteristics of cartilaginous joints |
This is a structural classification. Includes synchondrosis & symphysis type. Has no synovial cavity, cartilage bridges articulating bone, are synarthrosis or amphiarthrosis |
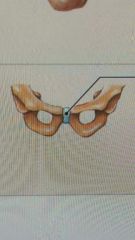
in synchondrosis and symphisis |
|
|
what is gomphosis |
A synarthrosis joint. Classified as Fibrous. Immovable, periodontal ligament, holds teeth in bony socket (alveoli) |
|
|
|
what is syndesmosis |
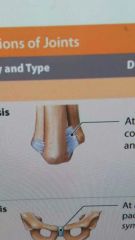
A amphiarthrosis classified joint. It is fibrous. United by ligament |
|
|
|
What is amphiarthrosis? |

2nd type of functional joint classification. Slightly movable under compession, twisting or tension. Includes syndesmosis & symphysis. |
examples are symphyses and syndesmoses |
|
|
characteristics of symphysis |

A amphiarthrosis joint. Slightly movable. Cartilaginous. made of fibrocartilage |
examples are intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis |
|
|
Characteristics of a synovial joint |
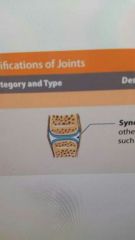
A diarthrosis classified joint. Most complex. Has joint cavity and ligaments to support articulating bone. |
|
|
|
Synovial Joint Features |
1. joint capsule with 2 layers 2. joint cavity inside of joint capsule 3. synovial membrane (inner layer of capsule) produced hyaluronic acid 4. synovial forms film over joint surface 5. articular covers joint surface |
There are 5 features |
|
|
What are the joint points of contact? |
Between 2 bones, between cartilage and bone, and between teeth and bone |
3 different points of contact |
|
|
Characteristics of the joint capsule |
has 2 layers, thickness varies in body, may be reinforced by or incorporate tendons and ligaments |
|
|
|
What are the joint capsule layers |
outer: dense fibrous connective tissue, stratum fibrosum, poor blood supply, good nerve supply inner: synovial membrane, makes hyaluronic acid for synovial fluid, good blood supply, poor nerve supply |
|
|
|
What is synovial fluid like? |
clear, yellow, viscous, reduces friction between articulations, provides nourishment for articular cartilage, contains hyaluronic acid and lubricin |
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage like? |
lacks blood vessels and nerve, transmits and distributes high loads, maintence of contact stress at low levels, reduces friction,shock absorber |
Found on the articular surfaces of bones, aKA hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Extra scapular versus intrascapular |
Describes location of ligaments. Outside of joint capsule vs. within joint capsule |
|
|
|
Characteristics of articular discs of synovial joints |
made of fibrocartilage , allows articular bones to fit tightly together, increases knee stability, reduces friction, shock absorber |
|
|
|
What are bursae? |
Flat sacs filled with synovial fluid located between 2 structures |
|
|
|
What are tendon sheaths |
tube like bursae that wrap around tendons in wrist and ankle |
|
|
|
Bursitis |
Chronic inflammation caused by excessive stress , the bursa swells and muscles become sore and stiff |
|
|
|
Factors of range of motion in synovial joints |
1. shape of articulating bones 2. tension & strength of joint ligaments arrangement 3. activity of muscles around joints 4. hormones and disuse |
There are 4 |
|
|
joint cavity |
space that separates the articulating surfaces of bone in synovial joint |
|
|
|
uniaxial joints |
bones are free to move in one place, around one axis |
example is a hinge joint ( flexion/extension, pivot joint) |
|
|
Biaxial Joint |
bones are free to move in 3 directions around three axes |
examples are ball and socket , flexion/extension, adduction/abduction & rotation |
|
|
Functions of Synovial fluid |
1. Lubrication 2. Nutrient distribution 3. Shock absorption |
3 functions |
|
|
Accessory Structures |
1. Cartilages 2. Fat pads 3. Ligaments 4. Tendons 5. Bursae |
There are 5 |
|
|
What is a fibrocartilage pad called? |
Meniscus |
|
|
|
Where are fat pads located? |
Superficial to the joint capsule. |
|
|
|
What is a sprain? |
Ligaments with torn collagen fibers |
|
|
|
Ligaments attach ___ to _____. And do what? |
Bone to bone. Support and strengthen joint. |
|
|
|
Tendons attach ____ to ____. And do what? |
Muscle to bone. Help support joint. |
|
|
|
What is subluxation? |
A partial dislocation |
|
|
|
Three types of dynamic movement |
1. Linear movement 2. Angular movement 3. Rotation |

|
|
|
Types of angular movement |
Flexión Extension Hyperextension Abduction Adduction Circumduction
|
There are 6 |
|
|
Types of Rotation |
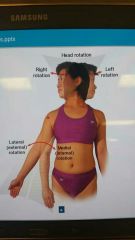
Left & right Medial & lateral Pronation & supination |
|
|
|
Special movements |

Inversión Eversion Dorsi flexión Plantar flexión Opposition Reposition Protraction Retraction Elevation Depression Lateral flexion |
|
|
|
Functional classification of Synovial joints |
Gliding Hinge Pivot Condylar Saddle Ball-socket |
6 of them |
|
|
Movement of gliding joint |
Gliding, Slight nonaxial or multi axial |
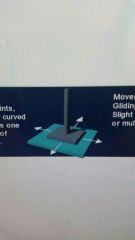
|
|
|
Movement of hinge joint |

Angular, mono axial |
|
|
|
Movement of Condylar joint |

Angular, biaxial |
|
|
|
Movement of saddle joint |

Angular, biaxial |
|
|
|
Movement of pivot joint |

Rotation , monoaxial |
|
|
|
Movement of ball and socket joint |
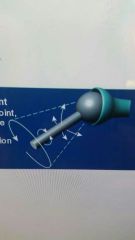
Angular, Circumduction, rotation, triaxial |
|
|
|
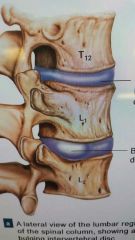
Outside and inside of intervertebral discs |
Outside : anulus fibrosus Inside: nucleus pulposus |
|
|
|
Vertebral joints are also called ____. |
Symphyseal joints |
|
|
|
Slipped disc |
Bulge in anulus fibrosis. |
|
|
|
Herniated disc |
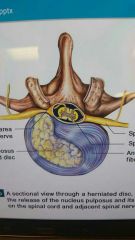
Nucleus pulposus breaks through anulus fibrosus. |
|
|
|
Shoulder joint is also called the ____. |
Glenohumeral joint |
|
|
|
What is the socket of the shoulder joint? |
Glenoid labrum |
|
|
|
Shoulder muscles |
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Subscapularis Teres Minor |
|
|
|
What is the larger joint of the arm? |
Humeroulnar joint (Trochlea of humerus and Trochlear notch of ulna) |
|
|
|
Location of patellar ligament |
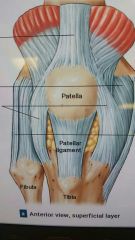
|
|
|
|
Rheumatism |
Pain and stiffness of skeletal and muscular systems. |
|
|
|
Arthritis |
All forms of rheumatism that damage articular cartilages of Synovial joints |
|
|
|
How is joint immobilization treated? |
Continuous passive motion (Cpm) |
|
|
|
Factors affecting bone strength |
1. Age 2. Physical stress 3. Hormone levels 4. Calcium and phosphorus uptake and excretion 5. Genetic and environmental factors |
|
|
|
Movements in the frontal plane are _____ such as _____ and _____. |
Sideways; Adduction , abduction |
|
|
|
Movements in the sagittal plane are __ and ___ such as ____ and ____. |
Up and down; Flexion and extension |
|
|
|
Movements in the transverse plane are _____. |
Rotational |
|

