![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
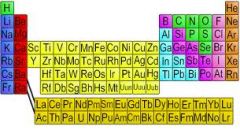
Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Element
|
An element is a pure substance that can't be separated into a simpler substance by physical or chemical means.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Pure Substance
|
Substance which contains only 1 type of particle called an atom.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Characteristic Property
|
Properties which don't depend upon the amount of the element. Some examples are boiling point, melting point, reactivity with acid or density.
In the picture, the Helium in the balloon makes is rise because Helium's characteristic property is that it is lighter than air. |
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Metal
|
An element that is shiny and able to conduct heat and electricity well. Some examples are Lead, Copper and Tin. The picture is of Copper Pipes
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Nonmetal
|
An element that conducts heat and electricity poorly. Examples are Sulfur, Iodine and Neon. The picture is of a piece of Sulfur.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 1 Vocabulary: Metalloid
|
An element that has the properties of both metals and nonmetals. The picture shows two different metalloids.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Vocabulary: Compound
|
A substance composed of two or more different elements chemically combined to create something new. They can only be separated by chemical means. Salt in the picture is a compound.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 3 Vocabulary: Mixture
|
A combination of two or more elements, compounds or both. They don't form specific ratios of compounds and may be separated by physical means. When mixed, original parts maintain characteristic properties. Think about pizza, you can separate cheese from the bread.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 4 Vocabulary: Solution
|
A solution is composed of the particles of two or more substances spread evenly among each other. One part is the solute (what is being dissolved) and the other is the solvent (what is doing the dissolving).
|
|
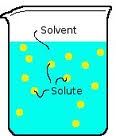
Chapter 4, Lesson 3 Vocabulary: Solute
|
Part of a solution that dissolves. Example sugar dissolved in water so sugar is the solute.
|
|
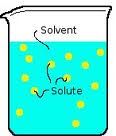
Chapter 4, Lesson 4 Vocabulary: Solvent
|
Part of the solution that does the dissolving (the work). Water is well know Solvent.
|
|
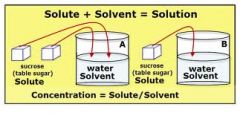
Chapter 4, Lesson 3 Vocabulary: Concentration
|
a measure of the amount of solute dissolved in a solute. In other words how much a particular substance is inside of another.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 3 Vocabulary: Solubility
|
The ability of the solute to dissolve into the solvent at a certain temperature.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 3 Vocabulary: Suspension
|
A suspension is a mixture in which particles are to large to stay in the mixed without being stirred or shaken. Think of a snow globe.
|
|

Chapter 4, Lesson 4 Vocabulary: Colloid
|
A mixture in which particles are mixed together and can't separate out. Jello is a colloid.
|

