![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What kind of cells line the stomach?
|
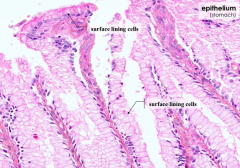
Surface lining cells = simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What kind of cells line the small intestine?
|
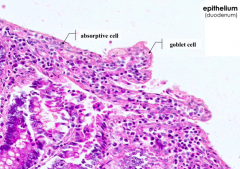
Absorptive cells (enterocytes) and goblet cells = simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What are the ultrastructural features of enterocytes in the small intestine? Functions?
|
- Microvilli - increase surface area
- Intercellular junctional complexes - prevent lumenal contents from accessing intercellular spaces - Mitochondria - high metabolic activity - Glycocalyx - protects plasma membrane from auto-digestion, binds secreted proteins, ions and water for localized proteolysis |
|
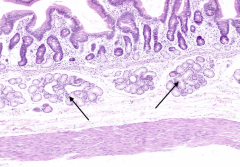
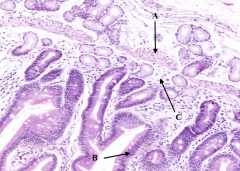
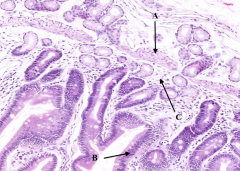
What are the arrows pointing out in the duodenum?
|
Submucosal glands of Brunner
|
|
|
What is the characteristic histological feature of the duodenum?
|
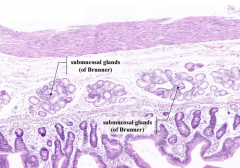
Presence of submucosal glands of Brunner
|
|
|
What is the function of the secretory product of Brunner's glands?
|
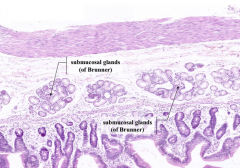
Alkaline mucous neutralizes acidic chyme from stomach
|
|
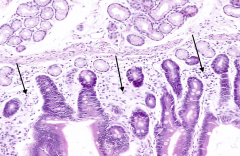
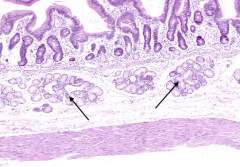
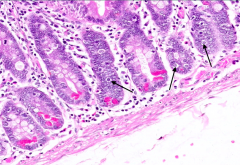
What are the arrows pointing out in this section of the duodenum?
|
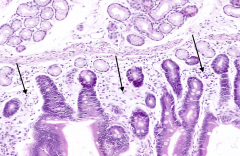
Basophilic cells in the submucosa and lamina propria = Lymphocytes
|
|
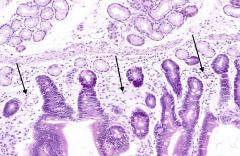
What term is used to describe the diffuse, unencapsulated lymphoid tissue in the mucosa of the GI tract?
|
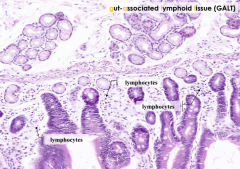
GALT: Gut-Associated Lymphatic Tissue
|
|
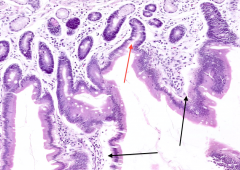
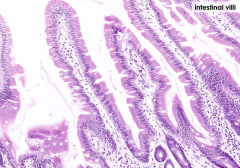
What projects into the lumen of the small intestine (black arrows)?
|
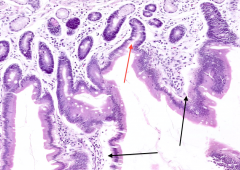
Intestinal Villi
|
|
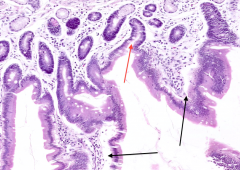
What are the spaces marked by the red arrow? What are they between (black arrows)
|
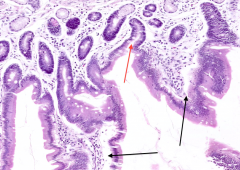
Red arrow = Crypts of Lieberkuhn
Found in between Villi (black arrows) |
|
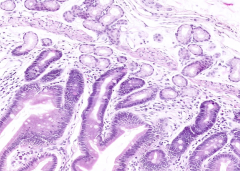
What are the three layers of the mucosa?
|
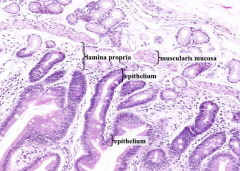
- Epithelium
- Lamina Propria - Muscularis Mucosa |
|
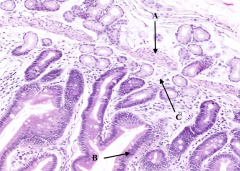
What is labeled with A?
|
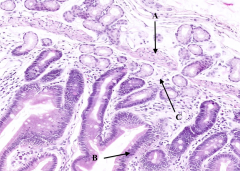
Muscularis Mucosa
|
|
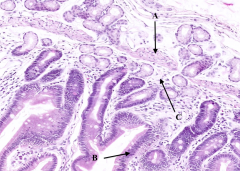
What is labeled with B?
|
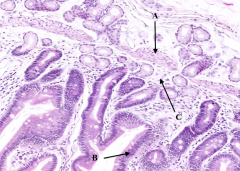
Epithelium (simple columnar)
|
|
What is labeled with C?
|
Lamina Propria
|
|
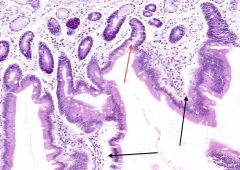
What tissue lies at the base of the Crypts of Lieberkuhn (red arrow)?
|
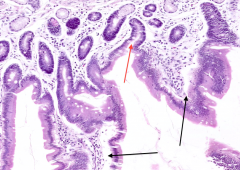
Muscularis Mucosa
|
|
|
What type of epithelium covers a villus?
|
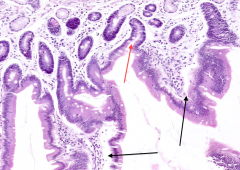
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
|
|
What is the principle cell type within the epithelium? What is its function?
|
Enterocyte - absorption of nutrients, production of digestive enzymes
|
|
|
What specialization of the apical plasma membrane is present on enterocytes? What is its function?
|
Brush border formed by microvilli increases the surface area for absorption
|
|
|
Does the submucosa extent into the core of a villus?
|
No
|
|
Are goblet cells present in the mucosal epithelium? Where?
|
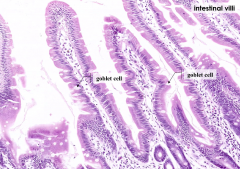
Yes
|
|
|
What is the function of Goblet cells?
|
Secrete mucin to lubricate and protect the epithelium
|
|
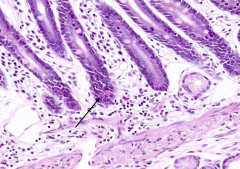
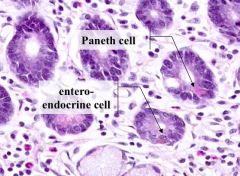
What is the cell containing a pink glob at the base of a Crypt of Lieberkuhn?
|
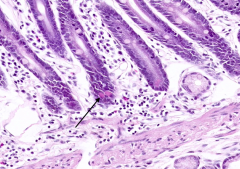
Paneth Cells
|
|
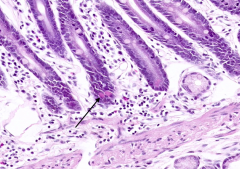
What is the function of Paneth Cells?
|
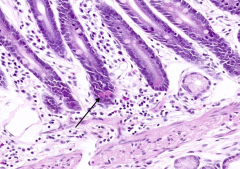
Secrete lysozyme and defensins to protect the organism against bacteria and viruses
|
|
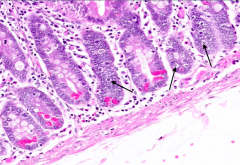
What is this cell type pointed out by the arrows?
|
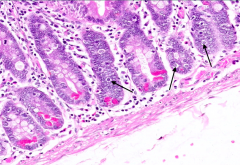
Enteroendocrine Cells
|
|
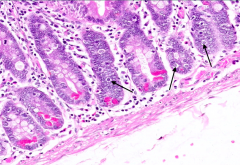
What do Enteroendocrine Cells contain?
|
- Contain secretory granules in basal cytoplasm
- Clear cytoplasm |
|
|
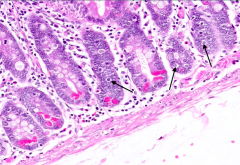
What is the difference in polarity of the secretory granules in an enteroendocrine cell and a Paneth cell? Reason for this difference?
|
- Enteroendocrine cells - secretory granules are basally located because they secrete into the bloodstream
- Paneth cells - secretory granules in are apically located because they secrete into the lumen of the gut |
|
|
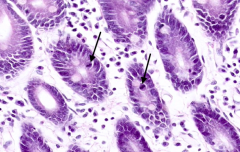
How could you positively identify enteroendocrine cells in a section of gut?
|
Immunostaining
|
|
What do the arrows point out?
|
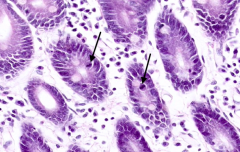
Stem cells (contain mitotic figures)
|
|
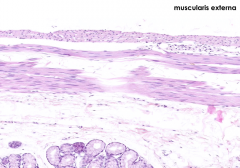
What are the components of the Muscularis Externa?
|
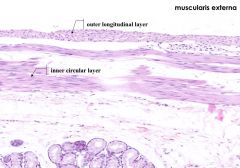
- Inner circular layer of smooth muscle
- Outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle |
|
|
What is the function of the muscularis externa in the small intestine?
|
Contracts to mix chyme with digestive enzymes and propels chyme (peristalsis)
|
|
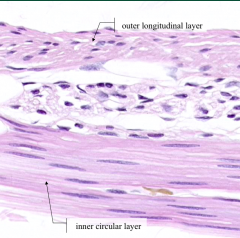
What is the cluster of large basophilic cells with large nuclei and prominent nucleoli?
|
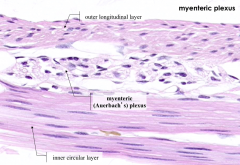
Myenteric (Auerbach's) Plexus in between the layers of the muscularis externa
|
|
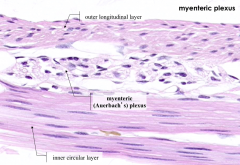
Which division of the autonomic nervous system innervates the myenteric plexus?
|
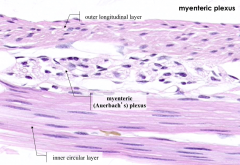
Parasympathetic division (CN X for foregut and midgut derivatives, S2-S4 for hindgut derivatives)
|
|
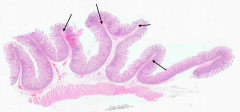
What are the large folds in the tissue (this happens to be jejunum)? What is it made of?
|
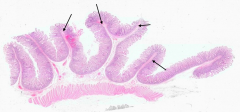
Plicae Circulares (valves of Kerckring)
- Folds have submucosa as their core - Villi project from the surface - Muscularis externa lies deep to the folds |
|
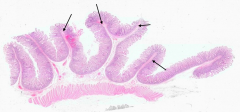
What happens to the Plicae Circulares during intestinal distention?
|
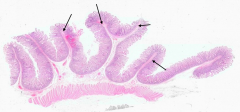
They do not obliterate with intestinal distention (unlike the rugae in the stomach)
|
|
|
What is the function of the Plicae Circulares?
|
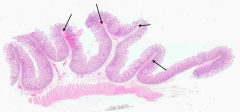
- Slow the passage of intestinal contents
- Increase the surface area for absorption |
|
|
How do you distinguish the myenteric from the submucosal plexuses?
|
Based on the surrounding tissues
|
|
|
What do the neurons of the myenteric and submucosal plexuses arise from?
|
Embryonic neural crest
|
|
|
What happens if there is failure of neural crest migration into the gut?
|
Congenital aganglionosis = Hirschprung's disease - congenital megacolon
|
|
|
What part of the GI tract is affected by Hirschprung's disease?
|
Usually the rectum and sigmoid colon
|
|
|
What are the symptoms in an infant with Hirschprung's disease?
|
- Failure to pass meconium
- Bilious vomiting - Irritability - Refusal to feed |
|
|
How do you diagnose Hirschprung's disease?
|
Biopsy of the affected bowel segment, it will show few or no ganglia and abnormal proliferation of nerve fibers in the mucosa
|
|
|
What can cause acquired Hirschprung's disease?
|
Bacterial infection possibly
|
|
|
Which histological, histochemical, or immunological stains might be used in the differential diagnosis of Hirschprung's disease?
|
H&E plus acetylcholinesterase
- Ganglion cells (or a lack of them) are visible in H&E - Acetylcholinesterase indicates the proliferation of nerve fibers in the mucosa Microtubule associated tau protein detected immunohistochemically - Tau normally appears in cell bodies and nerve fibers, staining is absent in aganglionic segments of colon |
|
|
Based ont he function of the myenteric and submucosal neurons, what would you expect to find on a lower abdomen x-ray of an affected patient following a barium enema?
|
- Affected region is reduced in diameter
- There is no peristalsis here, so it blocks inflow from more proximal portions, leading to distention (enlargement) of the unaffected colon |
|
|
What are the characteristics of the ileum?
|
- Presence of villi
- Absence of submucosal glands (of Brunner) - Abundance of GALT - Abundant lymphocytes in lamina propria, some in aggregates |
|
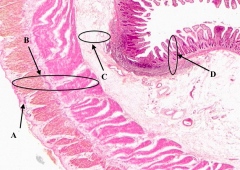
What is A?
|
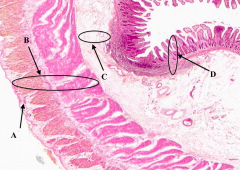
Serosa of the Ileum
|
|
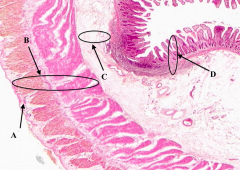
What is B?
|
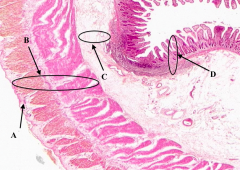
Muscularis Externa of the ileum
|
|
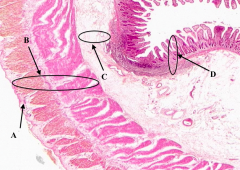
What is C?
|
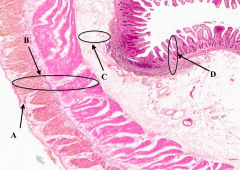
Submucosa of the ileum
|
|
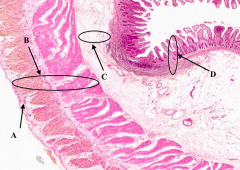
What is D?
|
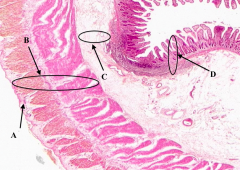
Mucosa of the Ileum
|
|
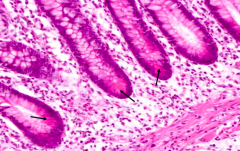
What is arrowed?
|
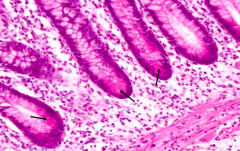
Paneth Cells
|
|
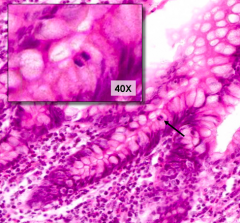
What is arrowed?
|
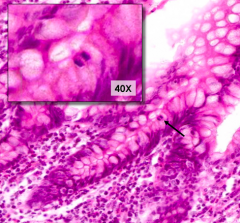
Mitotic Figures (Stem Cells)
|
|
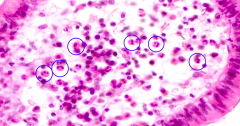
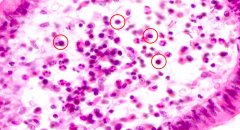
What cells are circled?
|
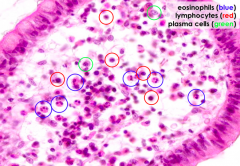
Eosinophils
|
|
What cells are circled?
|
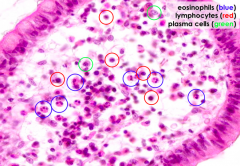
Lymphocytes
|
|
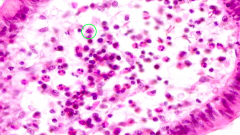
What cells are circled?
|
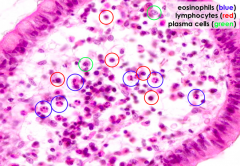
Plasma Cells
|
|
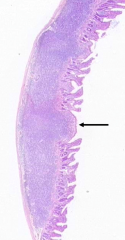
What is arrowed?
|
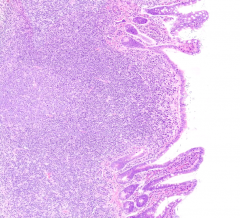
Peyer's Patch:
- Collection of lymphoid aggregates in the gut - Part of the organism's defense against pathogens which might penetrate the epithelium |
|
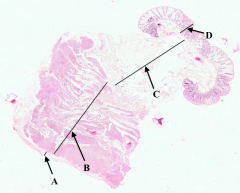
What is A?
|
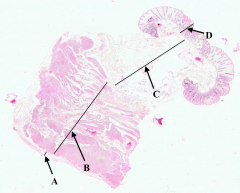
Serosa of colon
|
|
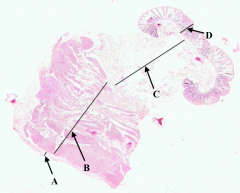
What is B?
|
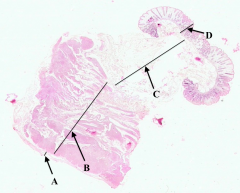
Muscularis Externa of colon
|
|
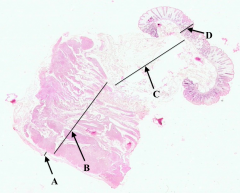
What is C?
|
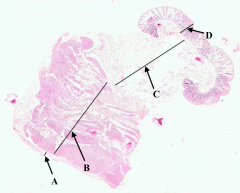
Submucosa of colon
|
|
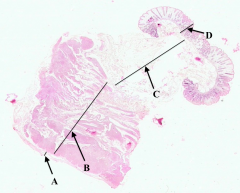
What is D?
|
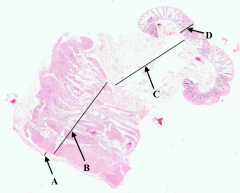
Mucosa of colon
|
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the lumen of the colon?
|
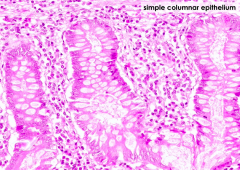
Simple columnar epithelium
|
|
|
Name two nutrients that are absorbed by enterocytes in the epithelium of the large intestine.
|
Water and electrolytes
|
|
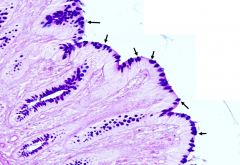
What do the bright blue blobs represent after this slide has been treated with the Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) reaction and Alcian blue stains?
|
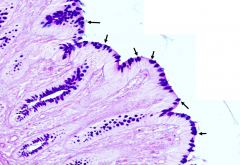
Goblet Cells
|
|
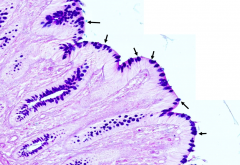
Why are Goblet cells abundant in this epithelium of the colon?
|
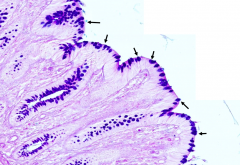
Goblet cells secrete mucous which facilitates the passage of feces through the large intestine
|
|
|
What is there a large amount of in the appendix? Where specifically?
|
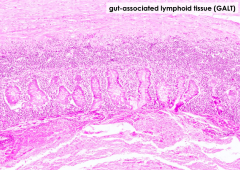
Lots of GALT in the lamina propria and submucosa
|
|
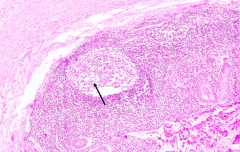
What does the arrow point out in this slide of the appendix?
|
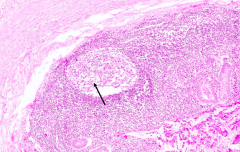
Lymph nodule
|
|
|
What kind of epithelium is found in the anus?
|
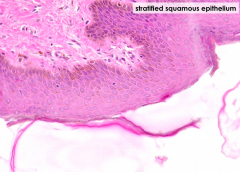
Stratifed squamous
|
|
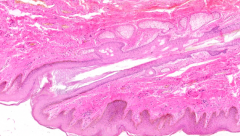
What is this structure in the anus?
|
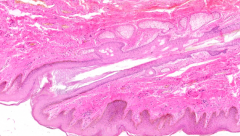
Hair follicle
|
|
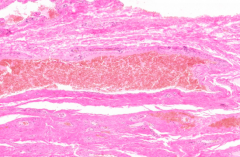
What is the bright red structure in the anus?
|
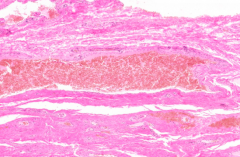
Rectal Venous Plexus
|
|
|
What surrounds the internal portion of the rectal venous plexus?
|
Loose connective tissue
|
|
|
Why are the veins of the internal rectal plexus affected more by portal obstruction? What happens to them?
|
- They are less supported by surrounding structures and less able to resist increased blood pressure
- They enlarge to cause varicose dilations = hemorrhoids |

