![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the characteristic signs / symptoms of hypothyroidism?
|
- Cold intolerance (↓ heat production)
- Weight gain, ↓ appetite - Hypoactivity, lethargy, fatigue, weakness - Constipation - ↓ Reflexes - Myxedema (facial / periorbital) - Dry, cool skin with coarse, brittle hair - Bradycardia, dyspnea on exertion |
|
|
What are the characteristic signs / symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
|
- Heat intolerance (↑ heat production)
- Weight loss, ↑ appetite - Hyperactivity - Diarrhea - ↑ Reflexes - Pretibial myxedema (Graves disease), periorbital edema - Warm, moist skin with fine hair - Chest pain, palpitations, arrhythmias, ↑ number and sensitivity of β-adrenergic receptors |
|
|
How do patients with hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism compare in terms of their bowel habits?
|
- Hypothyroidism: constipation
- Hyperthyroidism: diarrhea |
|
|
How do patients with hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism compare in terms of their reflexes?
|
- Hypothyroidism: decreased reflexes
- Hyperthyroidism: increased reflexes |
|
|
How do patients with hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism compare in terms of myxedema (swelling of the skin and underlying tissues giving a waxy consistency)?
|
- Hypothyroidism: facial and periorbital myxedema
- Hyperthyroidism: pretibial myxedema (Graves disease), periorbital edema |
|
|
How do patients with hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism compare in terms of their skin and hair?
|
- Hypothyroidism: dry, cool skin with coarse, brittle hair
- Hyperthyroidism: warm, moist skin with fine hair |
|
|
How do patients with hypothyroidism vs hyperthyroidism compare in terms of cardiac symptoms?
|
- Hypothyroidism: bradycardia and dyspnea on exertion
- Hyperthyroidism: chest pain, palpitations, arrhythmias, ↑ number and sensitivity of β-adrenergic receptors |
|
|
Why do patients with hyperthyroidism sometimes have chest pain, palpitations, and arrhythmias?
|
↑ number and sensitivity of β-adrenergic receptors
|
|
|
What are the lab findings associated with hypothyroidism?
|
- ↑ TSH (sensitive for 1° hypothyroidism)
- ↓ free T3 and T4 - Hypercholesterolemia (due to ↓ LDL receptor expression) |
|
|
What are the lab findings associated with hyperthyroidism?
|
- ↓ TSH (if 1°)
- ↑ free or total T3 and T4 - Hypocholesterolemia (due to ↑ LDL receptor expression) |
|
|
How do thyroid disorders affect cholesterol? Mechanism?
|
- Hypothyroidism: hypercholesterolemia due to ↓ LDL receptor expression
- Hyperthyroidism: hypocholesterolemia due to ↑ LDL receptor expression |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in iodine-sufficient regions?
|
Hashimoto Thyroiditis
|
|
|
What causes Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
Auto-immune disorder
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase and anti-thyroglobulin antibodies - Associated with HLA-DR5 |
|
|
What is there increased risk of in patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
|
|
|
What may be an early, contradictory finding seen in patients with Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
May be hyperthyroid early in course due to thyrotoxicosis during follicular rupture
|
|
|
What are the histologic findings of Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
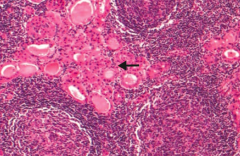
Hürthle cells, lymphoid aggregate with germinal centers
|
|
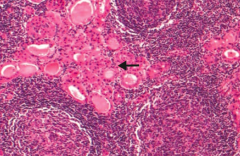
What does this histology indicate?
|
Hürthle cells, lymphoid aggregate with germinal centers → Hashimoto Thyroiditis
|
|
|
What are the expected thyroid findings on physical exam in a patient with Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
Moderately enlarged, non-tender
|
|
|
The presence of Hürthle cells should make you think of what?
|
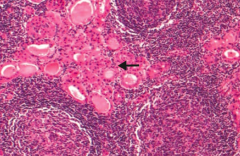
Hashimoto Thyroiditis
|
|
|
What can cause severe fetal hypothyroidism (congenital hypothyroidism)?
|
- Maternal hypothyroidism
- Thyroid agenesis - Thyroid dysgenesis (most common cause in US) - Iodine deficiency - Dyshormonogenic goiter |
|
|
What are the findings of a patient with congenital hypothyroidism?
|
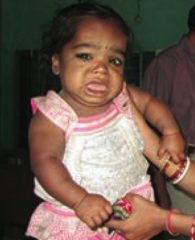
6 P's:
- Pot-bellied - Pale - Puffy-faced child - Protruding umbilicus - Protuberant tongue - Poor brain development |
|
|
What is cretinism?
|
Congenital hypothyroidism
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of congenital hypothyroidism in the US?
|
Thyroid Dysgenesis
|
|

What is wrong with the child on the left (before) and after treatment on the right?
|

Congenital hypothyroidism
|
|
|
What is the term for the self-limited hypothyroidism often following a flu-like illness?
|
Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)
|
|
|
What happens in Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)?
|
- May be hyperthyroid early in course
- Self-limited hypothyroidism often following a flu-like illness |
|
|
What is the appearance of the thyroid histologically in Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)?
|
Granulomatous inflammation
|
|
|
What cause of hypothyroidism is associated with a very tender / painful thyroid?
|
Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)
*de QuerVAIN is associated with PAIN* |
|
|
What are the findings in Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)?
|
- ↑ ESR
- Jaw pain - Early inflammation - Very tender thyroid - Granulomatous inflammation of thyroid |
|
|
What causes granulomatous inflammation of the thyroid?
|
Subacute Thyroiditis (de Quervain)
|
|
|
What disease causes the thyroid to be replaced with fibrous tissue? What does this cause?
|
Riedel Thyroiditis - causes hypothyroidism
|
|
|
What happens in Riedel Thyroiditis?
|
- Thyroid replaced by fibrous tissue (hypothyroid)
- Fibrosis may extend to local structures (eg, airway), mimicking anaplastic carcinoma |
|
|
What is Riedel Thyroiditis considered a manifestatoin of?
|
Manifestation of IgG4-related systemic disease
|
|
|
What are the findings of a patient's thyroid in Riedel Thyroiditis on physical exam?
|
- Fixed
- Hard (rock-like) - Painless goiter |
|
|
What are some other causes of hypothyroidism?
|
- Iodine deficiency
- Goitrogens - Wolff-Chaikoff effect - Painless thyroiditis |
|
|
What are the causes of hyperthyroidism?
|
- Toxic multinodular goiter
- Graves disease - Thyroid storm |
|
|
What pathology is associated with focal patches of hyper-functioning follicular cells that work independently of TSH due to a mutation in the TSH receptor?
|
Toxic Multinodular Goiter
|
|
|
What is wrong in Toxic Multinodular Goiter?
|
- Focal patches of hyper-functioning follicular cells
- Work independently of TSH due to mutation in TSH receptor - ↑ Release of T3 and T4 |
|
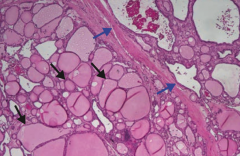
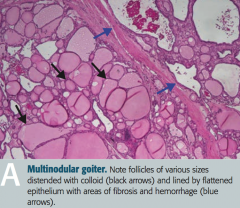
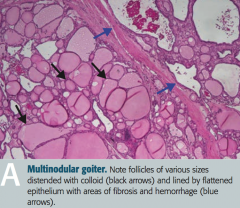
What does this histologic image of the thyroid show?
|
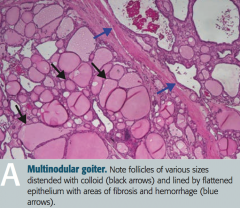
Toxic Multinodular Goiter
- Follicles of various sizes distended with colloid (black arrows) - Follicles are lined by flattened epithelium with areas of fibrosis and hemorrhage (blue arrows) - Nodules are rarely malignant |
|
|
What is the term for thyrotoxicosis when a patient with iodine deficiency suddenly is made iodine replete?
|
Jod-Basedow Phenomenon
|
|
|
What happens in the Jod-Basedow Phenomenon?
|
Thyrotoxicosis if a patient with iodine deficiency goiter is made iodine replete
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
|
Graves disease
|
|
|
What is the underlying pathophysiology responsible for Graves disease?
|
Auto-antibodies (IgG) stimulate TSH receptors on thyroid, retro-orbital fibroblasts, and dermal fibroblasts
|
|
|
What kind of antibodies are associated with Graves disease? Hashimoto Thyroiditis?
|
- Graves disease: IgG auto-Abs that stimulate TSH receptors
- Hashimoto Thyroiditis: anti-thyroid peroxidase and anti-thyroglobulin auto-Abs |
|
|
What are the implications of auto-antibodies (IgG) stimulating the TSH receptors on the thyroid?
|
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diffuse goiter |
|
|
What are the implications of auto-antibodies (IgG) stimulating the TSH receptors on retro-orbital fibroblasts?
|
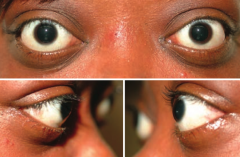
Exophthalmos: proptosis, extraocular muscle swelling
|
|
|
What are the implications of auto-antibodies (IgG) stimulating the TSH receptors on dermal fibroblasts?
|
Pretibial myxedema
|
|
|
When does Graves disease often present?
|
During stress (eg, childbirth)
|
|
|
What is the name for the stress-induced catecholamine surge seen as a serious complication of Graves disease and other hyperthyroid disorders?
|
Thyroid Storm
|
|
|
What causes a Thyroid Storm?
|
Stress-induced catecholamine surge seen as a serious complication of Graves disease and other hyperthyroid disorders
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of a Thyroid Storm?
|
- Agitation
- Delirium - Fever - Diarrhea - Coma - Tachyarrhythmia (cause of death) |
|
|
What lab value is possibly elevated in Thyroid Storm? Why?
|
↑ ALP due to ↑ bone turnover
|
|
|
How do you treat Thyroid Storm?
|
Treat with the 3 P's:
- β-blockers (eg, Propranolol) - Propylthiouracil - Corticosteroids (eg, Prednisolone) |
|
|
What are the indications for thyroidectomy?
|
Treatment option for thyroid cancers and hyperthyroidism
|
|
|
What are the potential complications of thyroid cancer?
|
- Hoarseness: due to recurrent laryngeal nerve damage
- Hypocalcemia: due to removal of parathyroid glands - Transection of inferior thyroid artery |
|
|
What are the types of thyroid cancers?
|
- Papillary carcinoma
- Follicular carcinoma - Medullary carcinoma - Undifferentiated / anaplastic carcinoma - Lymphoma |
|
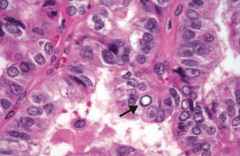
If you see this on a sample of the thyroid, what diagnosis do you need to think of?
|
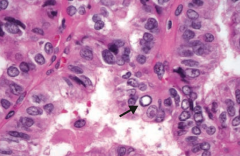
Papillary Carcinoma of the thyroid
- Empty appearing nuclei ("Orphan Annie" eyes) |
|
|
What is the most common type of thyroid cancer? Associations?
|
- Empty-appearing nuclei (Orphan Annie eyes), psamomma bodies, nuclear grooves
- Increased risk with RET and BRAF mutations and childhood irradiation - Excellent prognosis |
|
|
What are the histologic findings of Papillary Carcinoma of the thyroid?
|
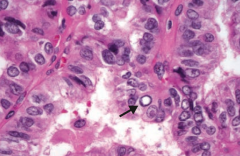
- Empty-appearning nuclei ("Orphan Annie" eyes)
- Psammoma bodies - Nuclear grooves |
|
|
What can increase your risk of getting Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid?
|
- RET mutations
- BRAF mutations - Childhood irradiation |
|
|
Which types of thyroid cancer are associated with a good prognosis?
|
- Papillary Carcinoma (excellent prognosis, most common type)
- Follicular Carcinoma (good prognosis) |
|
|
Which type of thyroid cancer has a very poor prognosis?
|
Undifferentiated / Anaplastic Carcinoma of thyroid
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a Follicular Carcinoma of the thyroid?
|
- Good prognosis
- Invades thyroid capsule (unlike follicular adenoma) - Uniform follicles |
|
|
What type of thyroid cancer arises from parafollicular "C cells"?
|
Medullary Carcinoma of the thyroid
|
|
|
What is the origin of Medullary Carcinoma of the thyroid? What does it produce?
|
- From parafollicular "C cells"
- Produces calcitonin |
|
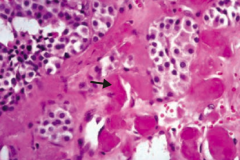
If you see this on a sample of the thyroid, what diagnosis do you need to think of?
|
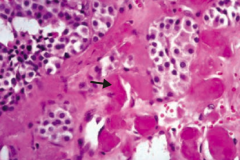
Medullary Carcinoma of the thyroid
- Solid sheets of cells with amyloid deposition (arrow) - Amyloid stroma |
|
|
What is Medullary Carcinoma of the thyroid associated with?
|
- MEN 2A and 2B
- RET mutations |
|
|
What type of thyroid cancer is more common in older patients?
|
Undifferentiated / Anaplastic Carcinoma of thyroid
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Undifferentiated / Anaplastic Carcinoma of thyroid?
|
- Affects older patients
- Invades local structures - Very poor prognosis |
|
|
Which type of thyroid cancer is associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis?
|
Lymphoma
|

