![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy |
The amount of work required to change the state of a physical system |
|
|
Name the three types of heat in transit |
Conduction - the transfer of heat through a substance through the vibration of particles
Convection - the transfer of heat from one region to another by the movement of particles
Radiation - doesnt require particles Reflected, transmitted or absorbed |
|
|
Order of the electromagnetic spectrum |
Radio, microwaves, infra-red radiation, visible light, ultra-violet rays, x-rays, gamma rays |
|
|
What are the 2 laws of thermodynamics |
First law - states that energy cannot be created or destroyed only transferred and transformed Second law - states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases |
|
|
Electromagnetic waves |
Transmit energy from one place to another through the air at around 300 000 000 metres per second. They are transverse waves |
|
|
Transverse waves |
Transverse waves are waves that travel at right angles to the direction of energy transfer. Transverse waves are waves on water but can also be made with a slinky |
|
|
Compression waves |
The particles in a compression wave move backwards and forwards. Can also be called longitudal waves. E.g. sound waves. |
|
|
8 types of energy and definitions |
Light energy - anything that gives off light Kinetic energy - anything that is moving Thermal energy - anything that gives off heat Sound energy - anything that makes noise Chemical energy - anything with stored energy that can be released by chemical action Elastic energy - anything that can be stretched or compressed Gravitational potential energy - anything that can fall Potential energy - stored energy; energy that will not work until released or changed |
|
|
How is energy measured |
Joules |
|
|
Parts of a plant cell |
Cell wall Cell membrane Vacoule Nucleus Ribosomes Chloroplast Golgi apparatus Mitochondria |
|
|
Is photosynthesis an exothermic or endothermic reaction and why |
Endothermic because it requires heat to under go the reaction |
|
|
Name the structure of the plant that converts light to energy |
In the thycanoid membrane located in the chloroplast |
|
|
What is a independent, dependent and controlled variable |
Independent - the one thing you change Dependent - the one you measure. The change that happens because of the independent Controlled - everything that stays the same |
|
|
What is potential energy |
Stored energy |
|
|
What should the discussion in a prac report include |
A summary of the experiment anything that went wrong/ mistakes made or could have been done better and answer any questions provided |
|
|
Draw a diagram of the inputs and outpust of the plant during photosynthesis |
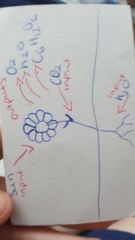
|
|
|
Name two differences between a plant cell and an animal cell |
Plant cell have a cell wall and chloroplast and animal cells dont |
|
|
Whay should the conclusion include |
A link to the aim and whether the hypothesis was correct. |
|
|
What is a hypothesis |
An educated guess of what you expect to happen during the experiment/ what your results will be |
|
|
Chemical equation for photosynthesis |
12H2O + 6CO2 > C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O |
|
|
Chemical equation for aerobic respiration |
C6H12O6 + 6O2 > 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy |
|
|
What is the carbon cycle |
The carbon cycle is the circulation of carbon between the sinks |
|
|
Draw the carbon cycle |

|
|
|
What are the green house gases |
Methane CH4 carbon dioxide CO2 water vapor H2O halogenated carbons CFC nitros oxide N2O carbon black |
|
|
What is peak oil |
A point in time when the production of oil has reached a maximum and after which the production will go down and the prices will go up |
|
|
Name the 7 tectonic plates |
Eurasian plate African plate Indo-australian plate Pacific plate North American plate South American plate Antarctic plate |
|
|
What is Pangaea |
The single land mass before the land split into different continents. 250 million years ago |
|
|
What is Gondwana and laurasia |
When Pangaea split into two. 200 million years ago |
|
|
What are constructive plate boundaries |
Constructive plate boundaries are divergent. The plates moving away from each other. Ocean crust goes apart creating more Ocean crust and there for constructive |
|
|
What are destructive plate boundaries |
Convergent. Destroys crusts. Normally one plate goes under the other |
|
|
What are Conservative plate boundaries |
Transform. The plates sliding past eachother. Doesnt create or destroy |
|
|
What are faults |
Cracks in the crust of the earth |
|
|
What are rift valleys |
A section of land that has dropped between 2 faults |
|
|
What makes tectonic plates move |
Convection currents make the magma move leading to the movement of tectonic plates |
|
|
What is carbon |
A chemical element that is a non-metal it occurs in almost everything living and dead |
|
|
What is the keeling curve |
The keeling curve is a graph that plots the ongoing changes in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the earth atmosphere |
|
|
Name three things that effect the rate of photosynthesis |
Light intensity Carbon dioxide concentration Temperature |
|
|
What is the greenhouse effect |
What being trapped by the gases in the atmosphere |
|
|
What is the enhanced green house effect |
The enhanced green house effect is the green house effect but with all the added gases that humans are pumping into the atmosphere |
|
|
What are the carbon sinks |
Lithosphere Hydrosphere Atmosphere Biosphere |

