![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Given a set of structures, identify the one that contains a phenothiazene ring.
|
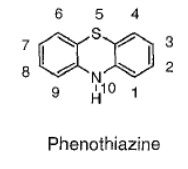
|
|
|
Given a phenothiazene molecule describe the structural requirements for dopaminergic antagonist activity (i.e., antipsychotic activity).
|
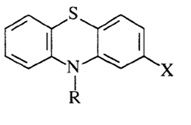
R = (CH2)3N(CH3)2 X = Cl
The three carbon spacer in the R group is important for antipsychotic activity (two carbon spacers lack antipsychotic activity but have increased antihistamine activity). |
|
|
Describe the different types of substitutions at the 10 position that are observed in phenothiazines and thioxanthenes and the pharmacological impact (both therapeutically and adversely) of these substitutions.
|
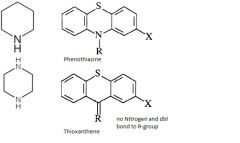
10 position = NITROGEN
Phenothiazines Aliphatic side-chain (like in chlorpromazine) is less potent, but still clinically efficacious. Piperidine-containing side-chain gives intermediate potency and moderate increase in extrapyramidal side-effects. (NOT FOUND IN THIOXANTHENES) others are the same Piperazine-containing side-chain gives higher potency but especially large increase in extrapyramidal side effects. Thioxanthenes |
|
|
In regards to phenothiazine derivatives, describe the impact on antipsychotic activity when the spacer length is changed and/or branched.
|
two carbon spacers lack antipsychotic activity but have increased antihistamine activity
Branched = variety of pharmacological effects |
|
|
Describe the structural and pharmacological differences between promethazine and chlorpromazine.
|
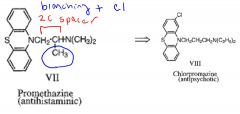
promethazine has only a 2-C spacer and methyl branch while chlorpromazine has the full 3-C spacer required for antipsychotic activity
|
|
|
Recognize a spiro compound.
|
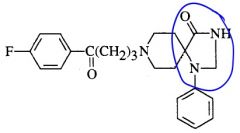
Two rings that share a carbon
|
|
|
Explain why Parkinson-like side effects are observed with many antipsychotics.
|
effects are a result of the proposed mechanism of action for these drugs (blockade of dopamine receptors).
Most prominent with the chronic administration of piperazine phenothiazines. |
|
|
Explain why compliance is an issue with some of the antipsychotics.
|
Elimination half-lives of approx. 24 hours means that daily dosing is required.
Daily dosing does not promote compliance in this patient population. |
|
|
Describe two efforts that are made to deal with the two major issues antipsychotic side effects.
|
Depot preparations results in long-acting injectable antipsychotics that are administered every 1 to 2 weeks.
Bypasses oral absorption variability Bypasses first-pass extraction by the liver Facilitates drug administration in psychiatric patients who are non-compliant. |
|
|
Describe the chemical changes that are necessary to make a depot prep.
|
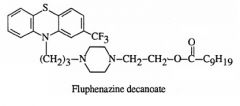
10C tail, The ester is dissolved in vegetable oil and administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly
Due to the lipophilicity, the ester is slowly released into the systemic circulation where it is hydrolyzed by plasma esterases to the active drug. |
|
|
Provide two chemical explanations for the extended half-life that is observed with a diphenylbutylpiperidine antipsychotic.
|
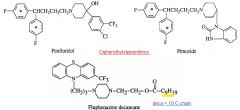
More lipophylic
Notice that they are structurally related to the butyrophenones, except that the ketone functionality is completely reduced. |
|
|
Describe a benefit of clozapine (Clozaril).
|
DOES NOT RESULT IN EPS
|
|
|
Describe an adverse effect associated with clozapine (Clozaril).
|
Agranulocytosis and seizure
|
|
|
Describe how loxapine (Loxitane) differs from clozapine (a compound to which it is structurally related).
|
ASSOCIATED WITH EPS
|
|
|
Describe how MPTP was discovered. Describe how MPTP is metabolized to a metabolite that leads to Parkinson-like disorders.
|
23 YR old college student develops PD, rapid onset
Assoc w/degen of substantia nigra MPP the suspected cause - metabolite |
|
|
Describe how the Parkinson-like effects of haloperidol might be related to the mechanisms observed in MPTP toxicity.
|
Dehydration of haloperidol leads to formation of HPTP, a close analog of MPTP. Apparently it is oxidized further to HPP+ as this metabolite is detected in human urine.
More studies are necessary to reveal if HPP+ is responsible for the development of extrapyramidal symptoms observed in haloperidol users. |

