![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
143 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Def: criterion measures
|
Measures of job performance, begins with job analysis
|
|
|
What tests have the highest validity for job selection?
|
Cognitive
Job knowledge |
|
|
What influences incremental validity of a personnel selection test? *
|
Base rate - % of successful current employees
Selection ratio - % of applicants to be hired Measure's validity coefficient |
|
|
Describe the steps in developing a training program
|
1. Needs analysis, including
organization analysis - is training nec task analysis - determine elements person analysis - who needs it 2. Program design 3. Program evaluation |
|
|
What is the advantage of Personnel Comparison Systems (PCS or ranking)
|
Reduction in rater bias
|
|
|
Def: halo effect
|
Tendency to extend judgement of all aspects of behavior on the basis of a single attribute or characteristic
|
|
|
Best way to reduce rater bias
|
Training in
recognition of multiple contribution objective evaluation techniques |
|
|
Def: biodata *
|
selection tool basedo nthe assumption that he the best predictor of future behavior is past behavior. (among the most valid)
Biographical data inventory including work |
|
|
Def: criterion contamination (When is it of concern?)
|
Performance on an objective test biases subjective evaluation (knowledge of predictor performance)
|
|
|
Def: adverse impact
|
Selection rates for minorities that are not distributed like their distribution in the population
Selection rate of the minority is less than 80% of the majority rate Exceptions can be made if the business shows the characteristic in question is a bona fide occupational qualification (BFOQ), (e.g., if you only intereview males for a male role in a play) as in job requirements when there are no alternative measures Legal issue |
|
|
Calculation of incremental validity
|
Positive hit rate - base rate
(proportion of positives identified e.g., those who are sick and identified as sick) Positive hit rate: % of successful hirees Base rate: % of successful current employees OR Taylor-Russell tables |
|
|
Factors considered in the Taylor-Russell tables
|
Validity coefficient
Base rate Selection ratio |
|
|
Def: selection ratio *
|
Job openings / Applicants
low selection ratio means lots of applicants |
|
|
Using Taylor-Russell tables, what maximizes incremental validity?
|
Large validity coefficient
Moderate base rate (.5) Low selection ratio |
|
|
Optimal interrelationship among multiple predictors
|
High correlation w criterion
Low correlation w one another |
|
|
Desc: Holland's theory of behavior / career choice *
|
Success is predicted by a congruence between personality and environmental variables
A highly differentiated person scores high on a single type and predicts best outcome for personality and occupational match but doesn't account for impact of discrimination |
|
|
What are Holland's personality types? *
|
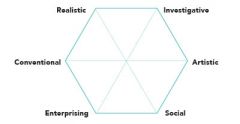
Realistic - mechanical
Investigative - analytic Artistic - expressive, original, introspective Social - people oriented Enterprising - manipulative Conventional - clerical
|
|
|
Def: BARS
|
Behaviorly Anchored Rating Scale
Assessment based on critical incidents |
|
|
Def 'realistic job preview' and describe its function
|
It provides an applicant w info about the job.
Goal is to reduce employee disillusionment and turnover. |
|
|
Describe Theory X leaders
|
Assume work is distasteful
Most workers lack direction Workers must be controlled or coerced Workers are motivated by greed Closer to scientific management |
|
|
Describe Theory Y leaders
|
Believe:
Work comes naturally Workers are self-directed, responsible and autonomous Closer to human relations approach |
|
|
Under what circumstances (according to Fiedler) is a leader most effective
LPC * |
Leaders describing their least preferred coworker (LPC) in negative terms:
are most effective in situation permitting either little or considerable influence; are task and achievement oriented Leaders describing their LPC in positive terms are most effective when moderate control is possible; are primarily relationship oriented Fiedler believes that leaders' style is fixed and the best you can do is to get a good match between style and the situation |
|
|
What is the fastest growing segment of the workforce
|
Women w children under one
|
|
|
Assumptions of Taylor's scientific management
|
Motivation affects performance
Workers motivated by money Average workers need constant supervision |
|
|
Which leadership style leads to the most productivity?
|
Autocratic, esp when the work is routine
|
|
|
What personality traits make for effective leadership?
|
It all depends
On: the supervisees the task the work environment |
|
|
Describe Japanese management style
|
Employment - longterm
Decision making - consensual Responsibility - collective Promotion - slow Career path - non-specialized Employee's organization knowledge - holistic |
|
|
Describe Hershey & Blanchard's
Situational Leadership Model * |
Optimal style depends on worker job maturity
Maturity is a function of ability and willingness to accept responsibility. Leadership styles vary with task and relationship orientation Styles include in ascending order telling - t high; r low-low in both ability & willingness selling - t high; r high- low ability & high willingness participating - t low; r high-high in ability & low in willingness. delegating - t low; r low-high in ability & high in willingness |
|
|
Role of job evaluation techniques
|
Determine job worth for salary determination
|
|
|
Identify needs in Maslow's hierarchy
|
Physiological
Safety Social Esteem Actualization Not supported by research in workplace, as far as 5 needs, order of needs, or number that can be activated at one time |
|
|
Describe Herzberg's 2-factor theory
|
Satisfaction and motivation Satisfaction and dissatisfaction are different constructsSatisfaction is a result of higher order needs (motivators intrinsic to the job, e.g.,responsibility, achievement, recognition) being met, challenge, responsibility; absence does not produce dissatisfaction Dissatisfaction results from the absence of lower order needs (hygiene factors), eg pay, job security; presence does not produce satisfaction Mixed results in the research |
|
|
Describe equity theory
|
Equity exists when contribution/reward ratios are perceived to be equal.
When inequity is perceived, equity is restored by: mondifying contributions attempting to alter rewards altering assessment of ratio |
|
|
Def: vestibule training
|
Physical replication of actual work conditions
Lets trainees learn w/o having to worry about safety or slowdowns |
|
|
Def: critical incidents *
|
Job behaviors characteristic of very good or very poor performance
|
|
|
Source of organizational inefficiency
|
Interpersonal dysfunction
(hence interventions target communications) |
|
|
Def: empirical-rational change strategy for organizations
|
Assumes people are rational and that given relevant information will act in their self-interest
|
|
|
Def: normative-reeducative change strategy for organizations
|
Assumes social norms underlie patterns of behavior in organizations
To facilitate change, focus on changing attitudes, values and relationships |
|
|
Desc: paired comparison technique rating system
|
Compares each person to every other person
Expensive and time consuming Results in maximal differentiation among employees |
|
|
What is the optimal level of anxiety of simple vs complex tasks?
|
Simple tasks best performed at high levels of anxiety; complex tasks at lower levels
|
|
|
What is the relationship between age and accidents in work settings
|
They are inversely correlated
|
|
|
Technique to avoid observer drift (decreasing accuracy of ratings over time)
|
Change or alternate raters
|
|
|
Characteristics of effective leaders (as opposed to managers)
|
Visionary
Creative Flexible Inspiring Courageous Independent |
|
|
Characteristics of self-directed work teams
|
Determine own goals
May hire own replacements Generalists with broad range of skills |
|
|
Purpose of trainability tests
|
To determine success in training (not job performance)
|
|
|
Cross cultural validity of job selection tests
|
While performance on the test may vary by group, tests are generally equally valid
|
|
|
Def: idiosyncratic credits
|
Akin to brownie points. The concessions to majority opinion on the part of a minority member in order to become a comopetent outsider, and thence be in a position to assume leadership or challenge majority opinion.
|
|
|
Protection for drug users under the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act)
|
Protects past addicts as long as they have completed or are enrolled in a drug rehab program and are not currently using
|
|
|
Factors considered in utility analysis
U=TxNxdxSD-NxC |
used to evaluate the effectiveness of training programs using a mathmatical equation to estimate the programs return on investment.
U = Utility measured in terms of dollar value T=number of years the program effects job performance N= number of people trained d= effect size of training program in standard deviation units SD= standard deviation of job performance for untrained employees in dollars |
|
|
Describe expectancy theory
|
Belief that effort (performance) will result in a positive (positve valence) specific outcome (instrumentality)
|
|
|
Def: theme interference
|
I/O analog to transference
worker displaces past or personal problems onto task / work situation |
|
|
House's path-goal theory
|
Optimal leader style varies with the situation but always involves helping workers achieve their goals
|
|
|
Super's theory of vocational development *
|
Life Span: Careerdevelopment occurs over the following five stages of the life span: growth(0-14), Exploration (14-25), Establishment (25-45), Maintenance (45-65),Disengagement (65+). In sequence of stages, each stage must be mastered beforemoving to next.
3) CareerMaturity: Person's ability to cope with developmental tasks of each life stage.4) Life Space:Various social roles person adopts at different points during life span (e.g.,parent, spouse, employee, etc.). *Life-CareerRainbow: Picture that depicts an individual's major life roles to five lifestages. Helps counselee recognize the impact of current and future roles andstages on career planning.*Archway: Depictspersonal and environmental factors that combine to determine career path (e.g.,interests, economy, peer group, etc.). |
|
|
Meaning of feedback in I/O or systems psychology *
|
disruption of the status quo designed to correct or change a pattern
|
|
|
strongest determinent of employee satisfaction with their leader
|
task orientation
consideration |
|
|
Compare transformational vs transactional leadership
|
Transformational:
empower employees raise their consciousness guide them thru organizational change Transactional: conform to rules and regulations maintain the status quo |
|
|
Factors affecting work - family conflict
|
Extent of involvement in work and family roles
Degree of impermeabily of boundaries between home and work |
|
|
Consequences of personal organizational fit to the person and organization
|
Good for the person
Too good a fit for the organization may result in loss of creativity, adaptability to change |
|
|
Difference between multiple hurdle and multiple cutoff predictors
|
In both cases all tests must be passed to succeed.
In multiple hurdle tests are administered in order, and failing one puts you out of the running (saves time and money) In multiple cutoff, tests may be administered in any order, but all need to be passed to succeed |
|
|
Risk factors for burnout
|
Being an insecure, unfulfilled compulsive workaholic
Being in a dead-end job with little hope of promotion inflexible work rules and procedures |
|
|
Desc: Life Career Rainbow
|
Nine major roles adopted throughout career development, eg student, parent, spouse, worker
|
|
|
Forms of job commitment
What increases commitment? Commitment effect on productivity? |
AffectiveCommitment: Worker's desire to stay with company due to concern for company'swelfare.
ContinuanceCommitment: Worker's desire to stay with company b/c he/she can't afford toleave. Highautonomy, interesting work, and job security increase commitment. Commitmenthas minimal effects on productivity. High Affectivecommitment related to high motivation and satisfaction, lower absenteeism andturnover, and greater willingness to make sacrifices for company. |
|
|
Slope bias/differential validity
|
Occurs when a test has different levels of predictability for different groups.
Determined by comparing the regression lines and y intercept. Different lines would result in different predictions |
|
|
Method of choice to reduce leniency bias
|
Forced choice questions
|
|
|
What are the Big Five personality traits?
Which is the best predictor of job performance? |
conscientiousness
extroversion agreeableness openness emotional stability/neuroticism -Conscientiousness |
|
|
What is the origin of the Big Five personality traits?
|
They are derived by a factor analysis of all personality terms found in the dictionary
Galton |
|
|
Job analysis |
conducted to clarify the requirements of the job |
|
|
job evaluation |
performed to determine the worth of jobs in order to set the salary |
|
|
Objective criterion measures Subjective Criterion measure |
Objective: direct quantitative measures such as units produced, sold, number of accidents, absenteeism Subjective: Supervisor ratings are most reliable, peers best predict training success and subsequent promotions, self rating is less susceptible to halo effect, but most lenient. |
|
|
Ultimate criterion actual criterion |
Ultimate: Ideal criterion like therapy effectiveness Actual: The way the performance is measure ie. client satisfaction |
|
|
Sub criterion measures/categories relative (comparative) technique absolute technique |
Relative technique: raters compare performance to two or more other employees Absolute: Provide rating without comparison |
|
|
Forced distribution |
assigning ratees to to a limited number of categories and base on a normal distriburtion on dimensions of the job performance |
|
|
Paired comparson |
rater compares each ratee in pairs on one or more dimensions |
|
|
Strictness/leniency Bias Central tendency bias Halo bias |
Rater tends to avoid the middle range of the rating scale Central tendency bias: raters rate consistently in the middle of the range halo |
|
|
frame of reference training (FOR) |
Best way to improve rating accuracy is provide training and focus on identifying specific behaviors (critical incidents). Do not train on biases |
|
|
Incremental validity
|
Increase in decision making accuracy for employer
|
|
|
Base Rate:
|
% employees doing okay without a predictor. from 0.0 to 1.0.
Moderate (.50) best Incremental VAlidity |
|
|
Adverse Impact
|
80% rule
|
|
|
Differential Validity
|
Valid for one group, not valid or less valid for another
|
|
|
Unfairness
|
Lower predictor cutoff, same performance
|
|
|
Incremental validity
|
Increase in decision making accuracy for employer
|
|
|
Base Rate:
|
% employees doing okay without a predictor. from 0.0 to 1.0.
Moderate (.50) best Incremental VAlidity |
|
|
Adverse Impact
|
80% rule
|
|
|
Differential Validity
|
Valid for one group, not valid or less valid for another
|
|
|
Unfairness
|
Lower predictor cutoff, but same validity, same performance
|
|
|
Multiple Regression
|
Compensatory way of combining predictors. (one predictor can offset others). Can use multiple cut-off then MR to hire as well.
|
|
|
Multiple cutoff
|
Non–compensatory: Have to get minimums to be considered.
|
|
|
Super: (associated terms)
|
Self Concept-changes overlifespan, but becomes more stable w/increased age; job satisfaction, stability,& success depend on match b/t job & indiv self-concept;
2) lifespan-5 stages: growth (0-14 yrs), exploration (14-25), establishment(25-45), maintenance (45-65), & disengagement (65+); each stage hasdifferent tasks & ability to accomplish tasks at each stage is called “careermaturity” (assessed by Career Development Inventory); 3) lifespace-various social roles (totalof 9) we adopt at different points during life span (e.g., child, student,citizen, worker); Life-Career Rainbow relates major life roles to 5 life stages &is useful for helping career counselors recognize impact of current/futureroles & stages on career planning. |
|
|
Holland (associated terms)
|
RAISEC: need to match personality to characteristics ofwork environment. More satisfaction,less turnover, more productivity when good person-envir fit. 6 basicpersonality/work envir types: realistic, artistic, investigative, , social, enterprising,& conventional. Person-envir matchis most accurate as predictor of outcomes if person is highly differentiated
|
|
|
Roe:
|
personality needs: Occupational choice is linked to personality and basic needs (influenced by Maslow,) Occupationshave 8 basic types & 8 levels. Basic oreintation is toward other people or not toward other people
Job changes have been found to most likely betransitions w/I one of these 8 types, not b/t. |
|
|
Tiedeman and Ohara
|
careeridentity development is an aspect of decision and ego identity development (describedin terms of Erikson’s psychosocial stages) & involves achieving a balanceb/t differentiation & integration. It is a decision-making processinvolving 7 stages that constitute 2 phases: anticipation/preoccupation(explore options) & implementation/adjustment (achieved vocational identity& enter workforce).I
|
|
|
Krumbolz:
|
Instrumental and associative learning, task approach skills-Behavior/social learning theory:
4 Factors: Genetic, Environmental, learning, task approach Career Belief Inventory social learning theory of career development; person’s career path has4 influencing factors: 1) genetics, 2) envir conditions & events (jobopportunities, technology), 3) learning experiences affecting genetics &envir (instrumental learning, associative learning), & 4) task approachskills are result of interaction b/t other 3 factors (work habits, performanceexpectations). 4 factors determine person’s self-observations & worldviewgeneralizations (beliefs) which influence educational & occupation choices &actions. Distinguishing feature: Emphasizes continual learning &self-development, not matching indiv characteristics to job. |
|
|
Brousseau & Driver
|
"Career Concept"
Decision Dynamic Career model: career decisions are based on one of four career concepts or vision toward ideal career path. Organizations should adopt a pluralistic career culture. Linear |
|
|
Dynamic career model explanations |
emphasis on career concept (indiv’s careerdecisions & motives).
4 career concepts vary in terms of 3 dimensions—freqof job change, direction of change, & type of change in job content: 1) linear career concept-progressive upward movement in terms of authority &responsibility; 2) expert career concept-lifelong commitment to occupational specialty & focus on developing knowledge & skills w/i specialty; 3) spiral career concept-periodic moves across occupational specialties or disciplines; 4) transitory career concept-ideal career as involving freq job changes,often to unrelated fields+ |
|
|
Job Characteristics Model (Hackman & Oldham)
|
Skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, performance feedback.
|
|
|
Expectancy Theory:
|
High Expectancy: effort=performance
High Instrumentality: performance = reward Positive Valence: Reward is desirable |
|
|
Bandura's Social Cognitive Theory
|
Goal Setting
Self–Observation– monitor progress Self–Evaluation–compare bx to goals Self–Reaction– affective/cognitive reaction to evaluation |
|
|
Contingency Theory: Fiedler
|
The LPC thing–
Low LPC = High task High LPC = high relationship Situational Favorableness: Amount of influence a leader has: ie, in more structured tasks, with positive relationships, amount of reward power Low LPC best in extremes– good or bad, High LPC best in moderate situations |
|
|
Path–Goal (House) Theory
|
Leaders help line up personal and professional goals
|
|
|
Situational: Hersey & Blanchard
Telling Selling Participating Delegatinvg |
High Task, Low relation
High task, high relation Low task, high relation Low task low relation This should be matched with "job maturity" willing/able to have responsibility |
|
|
Normative Decision Making (Vroom, Yetton, Jago)
AI Alone AII– seeks input, decides alone CI 1–1 consultation CII Group consultation Group |
Autocratic
Consultative Group DECISION TREE |
|
|
Group Tasks: (Steiner)
Additive Compensatory Disjunctive Conjunctive |
a: everything added together (computer program)
c: inputs averaged (job rating) d: select the input of the best member (best project represents the school) c: limited by worst (first team to climb the mountain) Group is Better than individual on additive or compensatory tasks, but the same for best member of disjunctive and worst member of conjunctive. |
|
|
Stages of group development (Tuckman & Jensen 5 stages)
|
Forming-acquainted and develop rules Storming-conflict as members resist leader Norming-members accept gorup and work together to achieve goals Performing- members accept each others strengths and weaknessess and focus on productivity Adjourning-group disbands because goals are met |
|
|
Lewin's Force Field theory of change
|
Organizations either promote (driving forces) or resist (restraining forces) change.
1. Unfreezing 2. Changing 3. Refreezing |
|
|
Nadlers THeory of change: (systems modle
|
Must change 4 things:
1. informal elements (communicaiton, leadership) 2. Formal elements (rules, processes) 3. Individual characteristics 4. Job characteristsics Change in one will cause change in all... |
|
|
Quality Circles vs. SMWT
|
Get informal group to work together on problems and make recommendations and present to managers-increases employee attitudes, but not job performance
SMWT: Do same but actually make decisions. Leadaership rotates |
|
|
Process consultation
|
Focus on behaviors and communication style over attitudes. Consultant helpsemployees perceive, understand, and alter processes that undermine interactions
|
|
|
Reliability |
The degree to which a measure of performance is unaffected by measurement error |
|
|
General mental ability test (GMA) Job knowledge tests |
consistently produce high validity coefficients across jobs and job settings Job knowledge test: Useful only to when applicants have had previous job training or experience |
|
|
Interest test |
See if their interests match interests of other employees. Easily faked and more reflective of predicting job choice, satisfaction, and persistence |
|
|
Training program development begins with a needs assessment-Needs assessment (analysis) |
1. Idneitfy organizational goals and if determine if it is training is need to achieve goals 2. Job analysis to determine what must be done to perform the job successfully 3. person analysis which employees need training and what skills/knowledge they need to acquire 4. demographic analysis to identify the training needs of different groups of workers (e.g., older versus younger workers) |
|
|
Principles of effective training feedback Overlearning active practice distributed practice appropriate learning focus transfer of training |
feedback- ongoing and frequent feedback about their training and most effective when it is provided as soon as possible after target behavior is performed Overlearning- promotes automaticity active practice- provide frequent opportunites becasue it is more effective than passively reading distributed practice- Most effective when it is spaced overtime rather than massed at one time appropriate learning focus- Whole learning involves representing and practicing the entire task at once and ism ore effective than part learning. transfer of training- results should result in positive transfer (improvements in actual on-the-job-performance. |
|
|
vestibule training |
physical replication or simulation of the work environment and is useful when on=-the-job training is to costly or dangerous |
|
|
Evaluation criteria to assess effective training four level (Kirkpatrick) |
reaction criteria- participants' reactions (satisfaction) Learning criteria-how much they learned from the training program behavioral criteria- assess participants' change in performance when they return to the job results criteria- were organizational goals met |
|
|
Contrast effect |
Tendency to giveratings based on comparisons to other ratees (e.g., if first three ratees arepoor workers and fourth is mediocre, rater may give mediocre workerexceptionally high rating). |
|
|
BusinessNecessity BonaFide Occupational Qualification (BFOQ) |
Employermust prove that use of a measure is job-related, and that it is required forsafe and efficient operation of the business. BFOQ: Whencharacteristic in question is essential determinant of the genuineness of a job(e.g., only male actors for male role), or when it maintains communitystandards of propriety (e.g., male restroom attended for male restroom).p |
|
|
Title VII 1964 civil rights act ADA act of 1991 |
Cannot discriminate in hiring ADA: Companies with 25+employees can not use procedures that discriminate against people with physicalor mental disabilities. When disabled person is able to perform essentialqualities of the job, the employee must provide reasonable accommodations,unless it results in hardship to the employer. -All pre-employmentprocedures must be directly related to job requirement and can not require medicalexams (drug testing not considered medical exam). |
|
|
Informal work group norms |
Productionabove or below norm resulted in social pressure to conform to by coworkers. |
|
|
Time in motion study |
Identifiedhow workers can complete tasks in less time and with increased efficiency. |
|
|
Piece-rate system |
which workers whoexceed standard of performance are paid more.Money is most important motivator |
|
|
Theory X and Theory Y (Mcgregor) |
X: managers believe employees dislike work and avoid it when possible and must be controlled and directed. Y: Managers view work as being as natural as play, and assume that employees arecapable of self-control and self-direction. Theory Y is likely to increasemotivation of employees and effectiveness of the organization. |
|
|
Strong-Campbell Interest Test KuderOccupational Interest Survey success |
Both very susceptible to faking. Research showsinterest tests are more valid for predicting job choice, satisfaction, &persistence than interest or success |
|
|
Most valid predictor of job success across organizations |
General Mental (Cognitive) Ability Tests- r = .53 to .75 |
|
|
Theory Z |
Theory Z (Ouchi): Distinction betweentraditional American (A) and Japanese (J) philosophies. American Japanese Employment duration Short-term Long-term Decision-Making Individual ConsensualResponsibility Individual CollectiveEvaluation/Promotion Rapid Slow Career Path Specialized Non-SpecializedKnowledge of Organization Segmented Holistic |
|
|
Total Quality Management (TQM) |
Emphasis on product quality. Involves"flattening" of managerial hierarchy, increased teamwork, and reducedratio of managers to non-managers. Also characterized by skill variety, taskvariety, autonomy, task significance, and feedback. |
|
|
(Motivation) Performance = |
Ability + Motivation + Environment |
|
|
(Motivation) ERG theory (Alderfer) |
ERG Theory:Reduced Maslow's needs to three: Existence, relatedness, and growth. Proposed thatpeople can be motivated by more than one need at a time, and that needs do notalways progress from lower to higher-order. Moreempirical support than Maslow |
|
|
Need for Achievement (McClelland) (motivation) |
need for achievement, power and affiliation Used TAT to identify needs underlying job motivation Need forachievement (nACH) studied the most: Employees with high nACH usually chosetasks of moderate difficulty and risk, prefer frequent and concrete feedback,tend to be preoccupied with a task until it is finished, and prefer to assumepersonal responsibility than to delegate work. |
|
|
Herzberg- job enrichment, enlargement Most important for motivation |
Job Enlargement:Increase number and variety of tasks. Reduces boredom Job Enrichment:Greater responsibility, freedom, autonomy, and control. Works best with highnACH employees. Feedback |
|
|
social loafing |
When a person exerts less effort acting in a team than when working alone. Can be corrected by recognizing contribution and reward. Occurs when the group is large and the task is additive |
|
|
social facilitation |
Presence of others increases task performance (usually on simple or familiar tasks) |
|
|
Associations of homogeneity in group and heterogeneity in group |
Homogeneity in group- greater cohesiveness and better performance on simple tasks Heterogeneity- greater creativity and better decision-making |
|
|
Decision Making Models (SIMON) Rational Economic Model Bounded rationality model |
Rational Economic Model: Decision makers maximize benefits by searching and considering all alternatives before selecting optimal ones Bounded rationality model: That "satisfice" and select the first decision that meets the minimum criteria of acceptability (due to limited capabilities, resources, and time) |
|
|
Compressed work week is associated with Flextime |
improved employee attitude flex: Choice of when to begin and end work, adn does not affect productivity |
|
|
Worker at high risk for stress related illness |
Assembly-line Worker who is machine paced |
|
|
Dawes and Lofquist- theory of job adjustment. Satisfaction depends on... |
The degree to which characteristics of the job correspond to the workers needs and values |
|
|
Voluntary arbitration binding conventional |
V: Agree to enter into arbitration, but not to agree Binding: Agree to therms of the arbitrator before the process begins Conventional arbitration: The arbitrator can choose any solution |
|
|
Dimensions of National Culture (Hofstede)
|
Power Distance:Extent to which people accept an unequal distribution of power.UncertaintyAvoidance: Willingness or ability of people to tolerate ambiguity anduncertainty. Individualism:Extent to which individuals are the basis of the social system. Masculinity: Valueplaced on assertiveness, independence, and competitiveness. Long-TermOrientation: Extent to which people focus on the future. |
|
|
Levels of Organizational Culture (Schein) |
Observable Artifacts: 1st level: Dress code, stories,rituals, etc. EspousedValues and Beliefs: 2nd level:Organization's norms, goals, and ideologies. Basic UnderlyingAssumptions (2rd and deepest level): Unconscious perceptions, beliefs, thoughts, and emotions. Theseare conceptualized as cognitive defense mechanisms that provide stability andmeaning and reduce uncertainty. Unfortunately, they also contribute toresistance to change.servic5y| |
|
|
Person-organization fit what is it associated with? How is it achieved? Mentors-hip has positive effect on PO fit |
Extent to which values held by specific individuals match those of the organizations. Achieved-socialization process and selection good fit associated with satisfaction, motivation, and organizational commitment, low level of stress, and voluntary turnover. |
|
|
Yerkes-Dodson Law |
Highest levels of learning and performance are associated with moderate arousal, especially on moderate level task difficulty (inverted U-Shape) |
|
|
Demand-control (job strain) model (Karasck) |
Job demand (workload, time pressure, responsibility) and job control (decision of latitude of autonomy and discretion for using different skills) primarily contribute to job stress High job demand and low control is associated with emotional exhaustion, depression, heath problems |
|
|
Hours of greatest fatigue Forward shift rotation |
4th and 8th Forward roation: moving day to evening or evening to night has less effect on circadian rhythm swing shift: the night shift hasmost effect, most problems, but are freedom of choice reduces it. |
|
|
person-machine fit (human factor/general systems theory) Goals of this are to... |
Performance is the result of an interaction between people and machines and any failure is due to a mismatch. Goals: ensure workers fit the job through effective selection and training and the job fits the capabilities and limitations of the worker through tasks, equipment, and environment. |

