![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 Types of Arrhythmias
|
Irregular Rhythms
Escape Premature Beats Tachy-arrythmias |
|
|
3 Types of Irregular Rhythms
|
Wandering Pacemaker
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Fibrilation |
|
|
Wandering Pacemaker
|
Paced by SA Node and other atrial automaticity foci
Irregularly Irregular Different shaped P waves Normal Rate |
|
|
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
|
Same as wandering pacemaker but tachy-arrhythmia because atrial foci have entrance block (not overdrive suppressed).
COPD, digitalis toxicity |
|
|
Atrial Fibrilation
|
Rapid firing multiple atrial automaticity foci
No impulse depolarizes atria completely (no P waves). Irregularly Irregular May be fast or slow ventricular rate |
|
|
Escape Rhythms / Beats
|
SA node stops pacing for a beat or all together and another foci starts pacing
Atrial Escape Rhythm / Beat Junctional Escape Rhythm / Beat Ventricular Escape Rhythm / Beat |
|
|
Atrial Escape Rhythm
|
Rate: 60-80
P waves not identical to SA P waves May see an arrest of SA pacing followed by escape rhythm |
|
|
Junctional Escape Rhythm
|
Rate: 40-60 (may become accelerated)
Failure of SA node and atrial foci OR complete AV conduction block No P waves but may get retrograde depolarization leading to inverted P waves before, after or within QRS complex. |
|
|
Ventricular Escape Rhythm
|
Rate: 20-40 (may become accelerated)
Complete AV conduction block or downward displacement of pacemaker Leads to Stokes-Adams Syndrome Ventricular escape beat may occur with burst of parasympathetic activity as blocks all other foci |
|
|
Premature Beats
|
Premature Atrial Beat
Premature Junctional Beat Premature Ventricular Beat |
|
|
Cause of Atrial and Junctional Premature Beats
|
Adrenaline
Increased sympathetic stimulation Caffeine, amphetamines, cocaine, Beta 1 receptor agonists Digitalis, ethanol Hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Premature Atrial Beat
|
Early P prime wave that resets SA node so next cycle is at regular interval.
Abberant condution: early depolarization down one bundle branch causing widened QRS for that cycle. Non-Conducted PAB: AV node still repolarizing so no QRS but resets SA node for next cycle. Looks like a block because missing QRS. |
|
|
Atrial Bigeminy/Trigeminy
|
PAB coupled to the end of a normal cycle leading to two successive QRS depolarizations with a stretch in between.
Trigeminy: PAB after every second QRS. |
|
|
Premature Junctional Beat
|
Premature irritable focus from AV junction.
Aberrant Ventricular Conduction: widened QRS if one BBB depolarizes before the other Retrograde Atrial Depolarization: inverted P wave before, during or after. This will reset SA node pacing. |
|
|
(AV) Junctional Bigeminy / Trigeminy
|
Premature junctional beat coupled with normal cycle or after every second normal cycle. May see retrograde P waves.
|
|
|
Causes of Irritable Ventricular Focus
|
Hypoxia: airway obstruction, air with poor O2, minimal blood oxygenation (PE, pneumothorax), reduced CO, poor coronary blood supply
Hyokalemia Pathology: mitral valve prolapse, myocarditis |
|
|
Premature Ventricular Contraction
|
Produces a Premature Ventricular Complex (PVC)
QRS: wide, large amplitude, inverse Pause afterwards caused by repolarization of ventricles, not resetting of SA node >6/min = pathological >2 in a row = V tach, if >30seconds = sustained V tach |
|
|
Ventricular Bigeminy / Trigeminy
|
Quickly exceeds 6 PVCs/min so hypoxia likely
|
|
|
Ventricular Parasystole
|
Ventricular automaticity focus with entrance block.
Paces at its own rate regardless of SA node pacing. |
|
|
R on T
|
PVC falls on T wave which can cause dangerous rhythm
|
|
|
Tachyarrhythia Rate
|
150-250: Paroxysmal Tachycardia
250-350: Flutter 350-450: Fibrillation |
|
|
Paroxysmal Tachycardia
|
Types: Atrial, Junctional, Ventricular
Irritable focus suddenly paces rapidly 150-250 |
|
|
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia with AV block
|
150-250
Spiked P prime waves 2:1 P:QRS Digitalis Toxicity (excites atrial foci but causes depression of AV node) |
|
|
Paroxysmal Junctional Tachycardia
|
150-250
May see retrograde P prime waves May have aberrant ventricular conduction wtih widened QRS AVNRT - AV nodal re-entry |
|
|
Ventricular Tachycardia
|
150-250
SA still paces atria but hidden by huge QRS Looks like consecutive PVCs Usually from hypoxia |
|
|
SVT with aberancy vs. V tach
|
V tach: coronary artery disease, QRS > .14s, AV dissociation, extreme R axis deviation
|
|
|
Torsades de Pointes
|
From long QT segment
1. hypokalemia 2. Long QT syndrome |
|
|
Atrial Flutter
|
250-350
Saw tooth pattern 2:1 or 3:1 P:QRS Vagal maneuvers slow AV node so possible to see difference between P and QRS |
|
|
Ventricular Flutter
|
250-350 - smooth sine waves
Usually decompensates into v fib which requires defib No good CO |
|
|
Fibrillation
|
Multiple irritable foci.
Parasystolic: no overdrive suppression Atrial: irregular ventricular rhythm; QRS rate depends on AV refractoriness Ventricular: type of cardiac arrest; defibrillation required |
|
|
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
|
Bundle of Kent accessory pathway conducts before normal delay through AV node producing pre-excitation and delta waves. Shortened PR interval.
May get paroxysmal tachycardia in 3 ways 1. rapid conduction: supraventricular tachycardia conducted 1:1 causing high ventricular rate 2. may contain automaticity foci that initiate tachycardia 3. Re-entry: ventricular depolarization may restimulate atria retrograde causing re-entry loop. |
|
|
Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome
|
AV node bypassed by extension of Anterior Internodal Tract (James tract).
Conducts tachy atrial rate 1:1 to ventricles P adjacent to QRS (no PR interval) |
|
|
Sinus Block
|
SA node does not pace for one cycle. May start next cycle or may be an escape beat in between.
|
|
|
Sick Sinus Syndrome
|
SA node dysfunction with unresponsive atrial and junctional automaticity foci so no escape beats.
Sinus bradycardia Bradycardia-Tachycardia Syndrome: Sinus brady with intermittent SVT |
|
|
1st Degree AV Block
|
Prolonged PR interval > .2s (1 large square) - measured from beginning of P wave to start of QRS.
Seen in every cycle the same amount. |
|
|
Second Degree AV Block
|
Wenkebach (Type I): progressive PR interval lenghtening until 1 P wave is not transmitted. Consistent P:QRS ratio (3:2, 4:3, 5:4). Increased parasympathetic activity (not harmful). Originates in AV node so vagal maneuvers increase P:QRS ratio.
Mobitz (type II): several P waves that don't conduct followed by normal cycle with consistent P:QRS ratio (3:1, 4:1). Pathological. May see widened QRS (originates in His Bundle). |
|
|
Third Degree Heart Block
|
Independent atrial and ventricular rates (AV dissociation)
Block high in AV node - junctional escape rhythm (40-60). Block lower - Ventricular escape rhythm (20-40). May lead to Stokes Adams Syndrome (not enough CO). |
|
|
Bundle Branch Block
|
1. wide QRS >.12s (3 small boxess)
2. Check V1/V2 (RBBB), V4/V5 (LBB) for R/R prime |
|
|
Axis (normal and abnormal causes)
|
0 to 90
1. Body habitus: R = obese, L = slim 2. Hypertrophy: toward 3. Infarction: away |
|
|
Lateral Leads
Inferior Leads |
1. I, AVL
2. II, III, AVF |
|
|
Axis
|
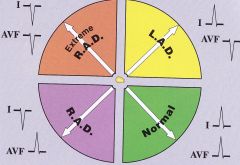
|
|
|
Left Axis Deviation in Degrees
|
|
|
|
Left Axis Deviation in Degrees
|
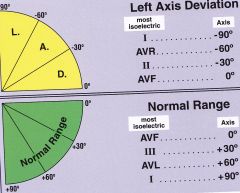
|
|
|
Right Axis Deviation in Degrees
|
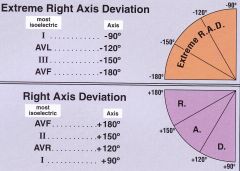
|
|
|
+ / - QRS in chest leads
|
1. negative
2. negative - through AV node and over anterior and posterior LV wall 3. isoelectric 4. slightly positive 5/6. positive Heart rotates in horizontal plane toward hypertrophy and away from infarct. |

