![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Piaget's theory |
Development as a self regulating exploration of environment (knowledge system evolves) Schema is altered to fit new environment Applied to newly encountered environments |
|
|
Four stages |
Sensorimotor stage (0-24 months)- learning through action Preoperational stage (2-7years)- learning through perception Concrete operation stage(7-11years)- mental operations based on stable knowledge Formal operations stage (11+)- abstract hypothetical, deductive READ IN BERK CHAPTER 6 PLZPLZ |
|
|
What is a stage |
Qualitative difference in thinking, invariant order of emergence, concurrence across stages in different domains Universal |
|
|
Sensorimoter stage |
0-24 months Thinking and reasoning based on interaction with world Progressive grown and knowledge refinement Accommodation and assimilation |
|
|
Object concept in sensorimotor stage |
Stage 1 - reflexes Stage 2 - primary circular reactions, motr habits centered around infants body, no anticipation of events, object in inextricably linked to act of manipulating it so no search Stage 3 -secondary circular reactions, aimed at repeating interesting effects, no search for hidden object because inflexible repetitious Stage 4 - co-ordinate secondary circular reactions, improved event anticipation, goal directed, hidden object retrieved but residual errors Stage 5 - tertiary cr's, exploration of objects by novel intimation flexible novel, cannot solve invisible displacements Stage 6 - object permanence through mental representation, internal visualisation, solved invisible displacement |
|
|
A not B error |
Stage 4 error Hide object at Location A Allow search infant finds object at A Hide object at Location B Infant goes to Location A regardless Due to incomplete understanding of permanence of the object Action- object relationship bound to location and 'reaching makes it reappear' |
|
|
Kellman and Spelke (1983) |
Four month olds Habituation - dishabituation Patterns of dishabituation suggest infants perceive boundaries of objects that's partially hidden through analysing movement. Refutes Piaget's theory that object perception is simplistic |
|
|
Nativist |
Most skills are hard wired into brain, born with it |
|
|
Hood and Willatts 1986 |
Shows 5 month old's ability to reach for objects when lights were turned on was reliable and they remembered positions (left or right) Refutes theory of object permenance |
|
|
Baillargeon 1985 |
When object is blocked, object search still goes on refutes object permenance out of site is not out of mind |
|
|
Baillargeon critiques |
Results not always reproduced Effect may be perceptual not conceptual |
|
|
Piaget's critique |
Underestimates initial knowledge Emphasis on motor ability Underestimates representational power Tight criterion for knowledge |
|
|
Pre-operational period |
Pre-logical About 2 to 7 years Where infant started as solipsist, Pre-schooler is egocentrist Thinking and reasoning and by manipulation of symbols Incompatible beliefs held at times 5+3=8 does not indicate 8=3+5 |
|
|
Pre-operational child |
Holds more than one mutually incompatible belief Grown and refinement of knowledge by equilibration -progression is not by teaching, formation of a new strategy to get rid of unpleasant feeling of incompatible beliefs Leads to stable systems of knowledge |
|
|
Preop vs concrete operations |
Operations are reversible mental transformations Operations not subject to interference from perception Preops cannot have these reversible transformations, dominated by immediate perception |
|
|
Egocentrism and perspective-taking |
Pre operational children pick picture of what themselves can see |
|
|
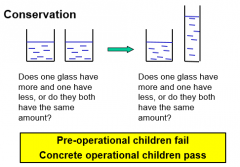
Conservation failure in the preop stage |
A failure to distinguish relevant from irrelevant transformations Children lack knowledge of invariance Conservation failures occur in number liquid mass |
|
|
Challenges to Piagetian account |
Memory Misunderstanding Language difficulty since tasks don't make sense and subtle changes affect performance Degree of difficulty Recall may have been slower |
|
|
Bryant and Trabasso 1971 |
Five rods, training study Four year old learned if a>B and B>C then C>D and D>E Information can be trained in children in pre-op |
|
|
Misunderstanding criticisms |
Piaget underestimated role of language - Donaldson 1978 Rose and Blank argues that asking same Q twice causes doubt Incorrect response may be primed by interaction of perceptual context and linguistic input |

