![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter
|
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
|
|
|
Energy
|
When matter is altered, energy results.
|
|
|
Atom
|
Fundamental unit of matter.
|
|
|
T/F - All matter is composed of atoms, or tiny invisible particles.
|
True
|
|
|
Atom consist of 2 parts:
|
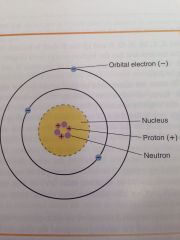
1) a central nucleus
2) orbiting electrons |
|
|
Nucleus
|
Dense core of the atom, is composed of particles known at protons and neutrons (also known as nucleons)
|
|
|
Protons
|
Carry positive electrical charges.
|
|
|
Neutrons
|
Carry no electrical charge.
|
|
|
Mass number/Atomic weight
|
Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
The number of protons inside the nucleus equals the number of electrons outside the nucleus and determines the 'atomic number' of an atom.
|
|
|
Elements
|
Substances made up of only one type of atom.
|
|
|
Electrons
|
Tiny, negatively charged particles that have very little mass; an electron weighs approximately 1/1800 as much as a proton or neutron.
|
|
|
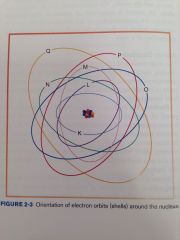
Orbits/Shells
|
Electrons travel around the nucleus in well-defined paths.
|
|
|
An atom contains maximum of 7 shells, each located at a specific distance from the nucleus and representing different energy levels. The shells are designed with the letters K, L, M, N, O, P, and Q; the K she'll is located closest to the nucleus and has the highest energy level.
|
|
|
Binding energy, or binding force, of an electron.
|
Electrons are maintained in their orbits by the 'electrostatic force', or attraction, between the positive nucleus and the negative electrons.
|
|
|
K Shell
|
Strongest binding energy is found closest the nucleus.
Electrons located in the outer shells have weak binding energy. |
|
|
Electron volts (eV)
Kilo electron volts (keV) |
Are what binding energies of orbital electrons are measured in.
(One kilo electron volt = 1000 electron volts) |
|
|
Maximum number of electrons each shell can hold:
|

|
|
|
Molecules
|
Two or more atoms joined by a chemical bond, or smallest among of a substance that possesses it characteristics properties.
Formed in one of two ways: 1) by the transfer of electrons 2) by sharing of electrons between the outermost shells of atoms. Example of simple molecule is water (H2O); the symbol H2 represents two atoms of hydrogen, and the symbol O represents one atom of oxygen. |
|
|
Neutral atom
|
Contains an equal number of protons (+ charges) and electrons (- charges). Atoms can exist in a neutral state or in an electrically unbalanced state. Normally, most atoms are neutral.
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom that gains or loses an electron and becomes electrically unbalanced.
|
|
|
Ionization
|
The production of ions, or process of converting an atom into ions. Deals only with electrons and requires sufficient energy to overcome the electrostatic force that binds the electrons to the nucleus.
|
|
|
Ion pair
|
When an electron is removed from an atom in the ionization process.
|
|
|
Radiation
|
The emission and propagation of energy through space or a substance in the form of waves or particles.
|
|
|
Radioactivity
|
The process by which certain unstable atoms or elements undergo spontaneous disintegration, or decay, in an effort to attain a more balanced nuclear state.
|
|
|
Ionizing radiation
|
Radiation that is capable of producing ions by removing or adding an electron to an atom.
Classified into 2 groups: 1) particulate radiation 2) electromagnetic radiation |
|
|
Particulate Radiation
|
Tiny particles of matter that possess mass and travel in straight lines and high speeds. Transmit kinetic energy by means of their extremely fast-moving, small masses.
|
|
|
4 Types of Particulate Radiation
|
1 - Electron can be classified as beta particles or cathode rays.
2 - Alpha particles are emitted from the nuclei of heavy metals and exist as two protons and neutrons, without electrons. 3 - Protons are accelerated particles, specifically hydrogen nuclei, with a mass of 1 and a charge of +1. 4 - Neutrons are accelerated particles with a mass of 1 and no electrical charge. |
|
|
Beta Particles
|
Fast-moving electrons emitted from the nucleus of radioactive atoms.
|
|
|
Cathode Rays
|
Stream of high-speed electrons that's originate in and x-Ray tube.
|
|
|
Electromagnetic Radiation
|
The propagation of wavelike energy (w/o mass) through space or matter.
|
|
|
Electromagnetic Spectrum
|
Electromagnetic radiation are arranged according to their energies.
|
|
|
Photons/quanta
|
Bundles of energy with no mass or weight that travel as waves at the speed of light and move through space in a straight line, 'carrying the energy' of electromagnetic radiation.
|
|
|
Velocity
|
Speed of the wave.
All electromagnetic radiations travel as waves or a continuous sequence of crest at the speed of light (3x108 meters per second [186,600 miles per second]) in a vacuum. |
|
|
Frequency
|
Refers to the number of wavelengths that pass a given point in a certain amount of time.
High frequency = short wavelengths Low frequency = long wavelengths |

