![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What percentage of restorations utilize amalgams?
|
75%
|
|
|
Amalgam has served as a restorative material in dentistry for how many years?
|
Over 165 years
|
|
|
T/F Hypersensitivity to amalgam is common
|
False rare
|
|
|
Amalgam _______ at a similar rate as tooth structure
|
wears
|
|
|
Amalgam is the least ______ of the long term materials
|
expensive
|
|
|
What is the composition of amalgam?
|
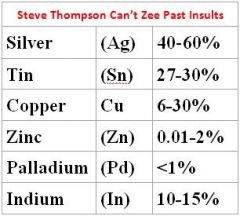
Silver (Ag) 40‐60%; Tin 27‐30%; Copper (Cu) 6‐30%; Zinc (Zn) 0.01‐2%; Palladium (Pd) less than 1%; Indium (In) 10‐15% in the Hg (Steve Thompson Can’t Zee Past Insults)
|
|
|
An admix of amalgam is a mixture of what?
|
Mixture of lathe cut and spherical particles. (Irregular was first used – lathe cut type)
|
|
|
When an alloy containing 27% tin is slowly cooled below a temperature of ___, an intermediate compound Ag3Sn known as the _____ phase is produced ***
|
480° and gamma
|
|
|
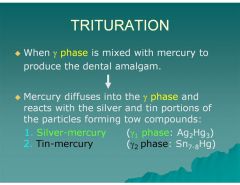
Mercury diffuses into the γ phase and reacts with the silver and tin portions of the particles forming two compounds?
|
1. Silver‐mercury (γ1 phase: Ag2Hg3)
2. Tin‐mercury (γ2 phase: Sn7‐8Hg) |
|
|
During the reaction Mercury dissolves into the amalgam. What amount dissolves into Copper, Silver, and Tin?
|
1 mg Hg in copper, 10 mg of Hg in Silver, 170 mg of Hg in Tin
|
|
|
What phase causes the γ2 phase to be eliminated?
|
ε phase
|
|
|
Which phase is the weakest and most susceptible to corrosion?
|
γ2 phase
|
|
|
What is the compressive strength of amalgam?
|
Good: (200 MPa in 1 hour)
|
|
|
Is the tensile strength of amalgam good?
|
No; (50 MPa)
|
|
|
The elastic modulus is considered?
|
Good ( 11‐62 MPa)
|
|
|
What is creep as it relates to amalgams?
|
Permanent deformation under static loads (0.05 – 6.3%)
|
|
|
Dimensional changes are greatest during the first _____.
|
20 minutes (contraction)
after that expansion then stable at 6‐8 hours, capable of normal function after 24‐48 hours. |
|
|
When zinc containing alloy gets contaminated with water it will cause?
|
Excessive expansion
|
|
|
Corrosion: Progressive ___________of a metal by chemical or electrochemical reaction.
|
Destruction (Porosity > marginal integrity < Loss of strength and release of metallic products)
|
|
|
Phosphate buffer solutions _________ the corrosion process (saliva).
|
inhibit
|
|
|
Zinc cause too much ________. Therefore, new products have aimed to remove zinc.
|
expansion
|
|
|
Admixed allows for _______ time compared to spherical.
|
more
|
|
|
True or False: Even 2‐3 sec difference can produce an over or under mixed amalgam.
|
True
|
|
|
A dull and crumbly amalgam would indicate what type of error?
|
Undermixed
|
|
|
A soupy and tends to stick to walls of the capsule would indicate?
|
Overmixed
|
|
|
What instrument is used to place the amalgam restoration?
|
Amalgam carrier
|
|
|
Ivoclar‐Vivadent used in the dental clinic eliminates which phase?
|
γ2 phase
|
|
|
Lateral condensation is important for __________ particles of amalgam
|
spherical
|
|
|
Use a flat‐faced small __________ to condense the amalgam over the pulpal and gingival floor of the preparation.
|
condenser
|
|
|
Each increment of amalgam should fill ____ to ____ the cavity prep.
|
1/2 to 1/3
|
|
|
Overpack prep by ______ .
|
1mm
|
|
|
Condensation of the mix should be completed in ______ to ______ minutes.
|
2.5 to 3.5
|
|
|
True or False: Deep occlusal grooves should be carved into the restoration?
|
False
|
|
|
An amalgam restoration overcarved more than _____ should be replaced.(referred to as ditching)
|
0.2 mm
|
|
|
To smooth the carved surface you may use a _____ _________ _________.
|
Dry cotton pellet
|
|
|
Try to avoid occlusal contacts on the _________.
|
Inclines
|
|
|
Finishing and Polishing of the restoration will make it less prone to ___________ and ‐___________.
|
Tarnishing and corrosion
|
|
|
What is the recommended sequence for performing an amalgam restoration?
|
1. Field Isolation
2. Establish outline 3. Remove Caries 4. Smooth cavosurface angle 5. Place base if deep or close to pulp. 6. Insert amalgam as explained. |
|
|
_________ __________ wears at a rate similar to tooth structure?
|
Dental Amalgam
|
|
|
What type of Amalgam do we use at CWRU?
|
Valiant PhD by Ivoclar Vivadent
High Copper Alloy (to eliminate the gamma2 phase) 1. Higher Strength 2. Less Corrosion 3. Better longevity at the margins |
|
|
What does Undermixed amalgam look like?
|

Dull and crumbly
|
|
|
What does properly mixed amalgam look like?
|

Shiny and separates in a single mass
|
|
|
What does overmixed amalgam look like?
|

Soupy and tends to stick to the walls of the capsule
|
|
|
What is creep, when referring to amalgams?
|
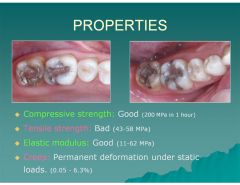
Permanent deformation under static loads (0.05-6.3%). Creep is especially prevalent in high mercury amalgams
|
|
|
What is the compressive strength like in amalgams?
|
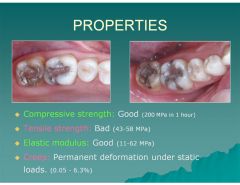
Good (200 MPa in 1 hour)
|
|
|
What is the tensile strength of amalgam like?
|
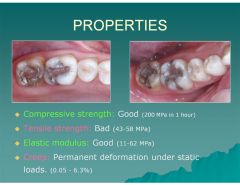
Bad (43-58 MPa)
|
|
|
What is the elastic modulus like in amalgams?
|
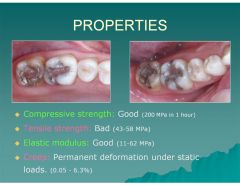
Good (11-62 MPa)
|
|
|
Why do you tell patients not to eat anything for 1 hour after having an amalgam placed?
|
The amalgam reaction is not complete
|
|
|
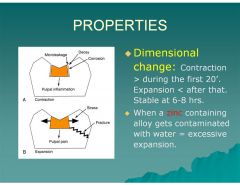
What happens when a Zinc containing alloy gets contaminated with water?
|
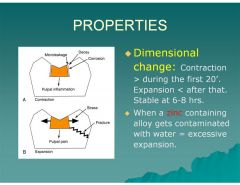
Excessive expansion
|
|
|
What is the dimensional change of amalgam during the first 20 minutes?
|
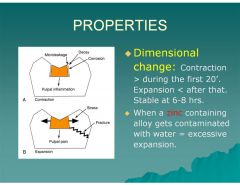
Contraction
|
|
|
What is the dimensional change of amalgam after 20 minutes then stabilizes at 6-8 hours
|
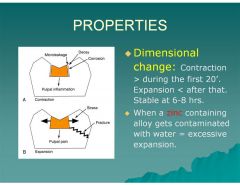
Expansion
|
|
|
What is the Υ phase?
|
When an alloy containing Tin is cooled below 480 deg C an intermetallic compound is formed (Ag3Sn)
|
|
|
What happens when the Υ phase is mixed with mercury?
|
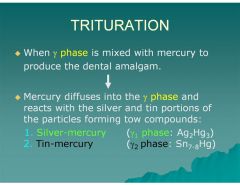
Υ1 phase (Ag2Hg3) Silver-mercury
Υ2 phase (Sn7-8Hg) Tin-mercury |
|
|
What is the amalgamation reaction?
|

See Above
|
|
|
What causes the Υ2 phase to be eliminated within a few hours after its formation?
|

ε phase
|
|
|
What phase is the weakest and most susceptible to corrosion?
|

gamma 2 phase
|
|
|
How do amalgam particles present?
|

Irregular or Lathe-cut
Spherical Admixed |

