![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is gypsum used for?
|
Used in dentistry to:
make models for studying casts for restorations & dies obtained from master cast |
|
|
What are the qualities of gypsum?
|
1. accuracy
2. dimensional stability 3. ability to produce fine details 4. strength/resistance to abrasion 5. ease of adaptation 6. color 7. safety |
|
|
T/F Gypsum is compatible with many different types of material
|
True
|
|
|
What materials is gypsum compatible with?
|
agar, alginate, condensation silicones, addition silicones, polysulfides, polyethers, model plasters, die stones
|
|
|
What is the definition of gypsum?
|
Dihydrate from calcium sulfate, found in compact mass in nature, white or milky yellow, source of plaster of paris
|
|
|
What is the importance of gypsum?
|
Used for fabricating study models, cast, or dies
They are replicas of the hard and soft tissues Used for diagnosis and treatment of oral disease. Material should flow into details of the impression. Controlled expansion/contraction during setting |
|
|
When is each type of material used?
a. Type I b. Type II c. Type III d. Type IV e. Type V |
a. Type I- (mounting plaster) used for impressions, not used very much any more
b. Type II- for diagnosis models, also for mounting. (stronger than type I) c. Type III- (microstone) used for making models like what we have been in MD d. Type IV- Has the highest strength for casts (fixed, removable, ortho appliance) Snap stone or Silky rock is the label on the package e. Type V- has the highest strength for casts (fixed, removable, ortho appliance) |
|
|
What are the four different types of gypsum used at case?
|
Die stone
Microstone-Model stone Snap stone-specialty stone Mounting plaster |
|
|
Silky rock compressive strength (Die Stone)
a. Hardness ___ after 1 hr b. Hardness ___ after 48 hrs c. expansion ___% |
41%
90% .09% |
|
|
Microstone compressive strength (model stone)
a. Hardness ___ after 1 hr b. Hardness ___ after 48 hrs c. expansion ___% |
31%
59% .12% |
|
|
Snap Stone compressive strength (specialty stone)
a. Hardness ___ after 1 hr b. Hardness ___ after 48 hrs c. expansion ___% |
41%
97% .15% |
|
|
Mounting plaster compressive strength (plasters)
a. Hardness ___ after 1 hr b. Hardness ___ after 48 hrs c. expansion ___% |
4%
12% .09% |
|
|
What is the chemical reaction when hemihydrate becomes dihydrate (gypsum)
|
CaSO4•½H2O + 1½H2O -> CaSO4•2H2O + Heat
|
|
|
What are the physical forms of gypsum?
|
Crystal
|
|
|
What are the accelerators?
|
Accelerators are chemicals that increase the rate of setting: examples of accelerators include: potassium sulfate & terra alba
|
|
|
What are retarders?
|
Retarders are chemicals that decrease the rate of setting (example borax)
|
|
|
Excess water in gypsum causes:
|
1. increase setting time
2. reduce strength 3. reduces expansion 4. reduces hardness 5. stone can be so weak that it easily breaks |
|
|
What happens to the setting time of the gypsum temperature in the room if it is raised up to 37.5 deg C?
|
The setting time decreases
|
|
|
What happens to the gypsum if the water temperature is increased?
|
The setting time increases. Heat is a byproduct of dehydrate so warm water increases setting time
|
|
|
What are hardening solutions used for?
|
hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the ability of a substance to attract water molecules from the surrounding environment through either absorption or adsorption |
|
|
What are the 5 important properties of gypsum?
|
Important qualities of gypsum
a. setting time b. reproduction of detail c. strength d. hardness and abrasion resistance e. dimensional accuracy |
|
|
Investments are stone-like material that can resist the _________ __________ experienced during casting
|
High temperatures
|
|
|
What is the composition of the investment?
|
Binders (gypsum) hold investment together and refractory material (form of silica)resists the heat of burnout and casting
|
|
|
What are the investment types? (there are two types used at case)
|
1. Gypsum bonded (novocast)- resist temperatures less than 1200 deg C, ideal for gold type II, III, IV
2. Phosphate- bonded investments (fast-fire 15); used for higher-melting alloys, they are stronger ideal for PFM & RPD framework |
|
|
Casted metals shrink __% to __% when they cool from the solid state at a high temperature to room temperature
|
1%
2.5% |
|
|
T/F investments are designed to expand to compensate for casting shrinkage
|
True
|
|
|
Expansion is provided by _____ & ______ expansion.
|
Hygroscopic, thermal
|
|
|
What are the components of waxes?
|
1. natural waxes from: minerals, plants or animals
2. synthetic waxes from gum, fats, fatty acids, oils, various resins |
|
|
What are the classification of dental waxes?
|
1. Pattern: inlay, casting, baseplate
2. Processing: boxing, utility, sticky 3. Impression: corrective, bite |
|
|
What is the lost wax technique?
|
Lost wax technique is the process utilized to create the cast for the final restoration. The wax-up is placed in casting stone, then heated to a point where the wax is burned out.
|
|
|
T/F Waxes have a higher thermal coefficient of thermal expansion of any dental material
|
True - when waxes are heated they expand
|
|
|
Is it the higher or lower the coefficient of thermal expansion, the greater the expansion?
|
Higher
|
|
|
What is residual stress as it relates to wax?
|
Stress remaining in a wax as a result of manipulation during heating, cooling, bending, carving or other manipulation
|
|
|
Base plate wax is used in the construction of ________
|
Dentures
|
|
|
Boxing wax is used to create a __________ around the impression.
|
form
|
|
|
What is sticky wax made from?
|
honey
|
|
|
Describe the chemical reaction of gypsum
|
CaSO4•½H2O + 1½H2O -> CaSO4•2H2O + Heat
|
|
|
What is the hardness of dental materials reported in?
|
knoop hardness
|
|
|
The affinity of a liquid for a solid is used as a measure of?
|
wettability
|
|
|
When waxes are heated, they expand significantly. This expansion can be qualified as:
|
Parts per million of expansion per C degree and coefficient of thermal expansion
|
|
|
Increasing the inorganic filler particles would:
|
1. improve the physical chemical and mechanical properties of the matrix
2. decrease the polymerization shrinkage 3. Reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion |
|
|
T/F The primer has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
|
True
|
|
|
_____ _____ wears at a rate similar to what tooth structure?
|
Dental Amalgam
|
|
|
There is no current evidence of hazard of the dental amalgam or relation to any disease. Hypersensitivity to mercury is extremely rare.
a. first statement is true, the second is false b. second statement is true, the first is false c. neither statement is true d. both statements are true |
Both statements are true
|
|
|
What's the definition of composite?
|
A compound of two or more different materials with properties that are superior or intermediate to those of the individual constituents
|
|
|
The following are functions of inorganic filler particles EXCEPT:
a. improve the physical and mechanical properties of the matrix b. reduction of water sorption & coefficient of thermal expansion c. improves the optical qualities of the matrix d. polymerization shrinkage is reduced due to less resin |
C. improve the optical qualities of the matrix
|
|
|
T/F A sealant is a type of composite resin?
|
True
|
|
|
Inorganic filler particles are made up of ____ or ______ shaped particles.
|
spherical or irregular
|
|
|
Filler particles include the following EXCEPT:
a. quartz b. silver c. copper d. zinc e. strontium f. barium g. gold h. zirconia i. Lithium aluminum silicate |
B. silver
C. copper G. gold |
|
|
What size are macro filler particles?
a. 0.04-0.2 micrometers b. 1-20 nanometers c. 0.4-3 micrometers d. 20-30 micrometers |
D. 20-30 micrometers
|
|
|
Micro-filled composite is for what type of cavity class?
a. class I b. class II c. class IV d. none of the above |
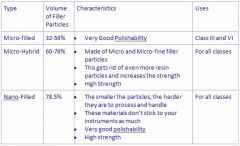
C. class IV
Class IV Caries affecting proximal including incisal edges of anterior teeth. |
|
|
Micro-hybrid composites is made of what two types of filler particles?
a. macro and micro b. micro and micro-fine c. nano and micro d. none of the above |

B. micro & microfine
|
|
|
Nano-filed composites are used for what type of cavity classes?
a. Class I b. Class III c. All classes d. Class II |
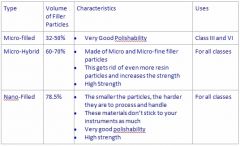
C. all classes
|
|
|
Silanes are a type of what?
a. coupling agent b. composite resin c. optical modifier d. all of the above |
A. coupling agent
|
|
|
Define coupling agents
|
Bi-functional molecule that provides bonding of the inorganic filler particle to the resin matrix
|
|
|
Inorganic oxides to match different shades are known as _____
|

Optical modifiers
|
|
|
A n[monomer] + n[monomer] -> polymer is a _______ reaction
|
polymerization reaction
|
|
|
Name three types of catalysts for polymerization reactions
|
light, heat, chemicals
|
|
|
What are the three steps in a polymerization reaction?
|
Initiation
Propagation Termination |
|
|
Composite resins _____ during polymerization.
a. expand b. shrink c. remain the same |
B. shrink
|
|
|
Define the c-factor
|
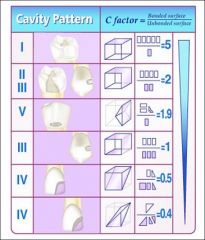
Shrinkage direction determined by cavity shape and bonded surfaces
|
|
|
C-factor = bonded surface divided by what?
|
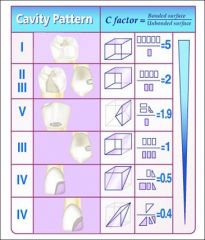
Unbonded surfaces
c factor = bonded surfaces/ unbonded surfaces |
|
|
Name three things that cause mechanical stress
|
Postoperative shrinkage, microleakage, secondary caries
|
|
|
The following are ways to reduce polymerization shrinkage except?
a. more and more fillers b. warm weather c. use soft start curing lights d. layer composite in 2 mm increments with low c- factor |
B. warm weather
|
|
|
Give three examples of composite layering techniques
|
Vertical
Horizontal Oblique Cusp build-up Centripetal Three-site technique |
|
|
Bonding agents provide what function?
|
Provide resin composites w/attachment to tooth structure/ceramic/metal
|
|
|
Define adherend
|
Substrate that it is bonded to (enamel/dentin)
|
|
|
Define adhesive
|
Material providing adhesion to adherend (bonding agent)
|
|
|
Name three types of bonding mechanisms
|
1. micromechanical
2. chemical 3. Van-der-Waals bonds |
|
|
The following are factors affecting adhesion to tooth structures EXCEPT:
a. oral environment b. surface contamination c. stress d. wettability e. mechanical properties of the composite f. physio-chemical properties of adhesive |
C-stress
|
|
|
What is the composition of enamel by weight?
|
95% inorganic
4% water 1% organic |
|
|
Name the properties of dental composite
|
1. Resists solubility and dehydration
2. Abrasion resistant 3. Low thermal conductivity 4. Low coefficient of thermal expansion 5. Excellent marginal adaptation 6. Repairability |
|
|
The following are percent composition of phosphoric acid in etchants EXCEPT:
a. 3% b. 10% c. 35% d. 37% |
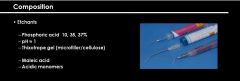
A. 3%
|
|
|
Primers are ___ monomers
a. hydrophobic b. hydrophilic c. acid d. all of the above |

Hydrophilic
|
|
|
Adhesives are ______ dimethylacrylate oligomers
|

Hydrophobic
|
|
|
What are the two functions of acid etch?
|

Dissolving of HA crystals leading to mechanical undercuts
Cleaning and removing smear layer Smear layer is a thin layer with small crystalline characteristics. It appears on the surface of teeth that have undergone dental instrumentation procedures, including root planing and cutting done with a dental bur. Not easily rinsed away, it must be removed by acid etching. |
|
|
What are the objectives of bonding agents?
|
Minimizing tooth prep, reduces microleakage, reinforces tooth structure, sealing
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of dentin bonding agents?
|
Bond to dentin with an equal or greater strength than that of composite to enamel, rapidly attain max bond strength, biocompatible, prevent microleakage, stable, easy to use
|
|
|
What are the indications of dentin bonding agents?
|
Direct composites
cementation of indirect composites and veneers cementation of ceramics |
|
|
What are the two classifications of etches?
|
Etch-and-rinse (total etch), non-rinse (self-etch)
|
|
|
What is the purpose of wet bonding?
|
Keeps the dentin moist to prevent collagen networking from collapsing
|
|
|
What is the hybrid layer?
|

Resin microtags that are within intertubular dentin and surrounding collagen fibers
|
|
|
What are the ten uses of polymers in dentistry?
|
a. CD or RPD base to support artificial teeth
b. orthodontic appliance c. soft liners d. prosthetic teeth e. provisionals f. composites and sealants g. impression trays h. impression materials i. Maxillofacial material j. Occlusal appliance |
|
|
What is an oligomer?
|
A short polymer composed of two, three, or four mer units
|
|
|
What is a copolymer?
|
When two or more different types of monomers are joined
|
|
|
What is polymerization?
|
The conversion of low-molecular-weight compounds called monomers to high-molecular weight compounds called polymers
|
|
|
In a polymerization reaction what is the initiator?
|
An organic peroxide (benzoyl peroxide)decomposed into active free radicals either by heating or by the addition of an organic accelerator
|
|
|
Products that use heat for decomposition of the initiator are called what?
|
Heat-curing acrylic
|
|
|
Products that use amines for decomposition of the initiator are called what?
|
chemically or self-curing acrylic
|
|
|
The addition of oils such dibutyl phthalate do what to the polymer?
|
they plasticize it
|
|
|
What are three distinguishing characterstics of a monomer?
|
a. volatile liquid (BP 100 deg C)
b. Sweetish odor that is TOXIC if inhaled for a prolonged period c. They are converted to a solid with essentially no vapor pressure during the polymerization process |
|
|
What are five things that someone should know about the polymerization reaction?
|
a. Heat is liberated
b. Heat processing should be under control c. excessive heat causes vaporation of monomer (POROSITY) d. excessive heat can cause tissue damage (can damage pulp) e. volumetric contraction |
|
|
What are some denture based polymer properties?
|
a. low thermal conductivity
1) metals have high thermal conductivity 2) patients w/complete acrylic dentures don't have good sensation of temperature i)can't tell if something is too hot or too cold ii) acrylic acts as a barrier against temperature b. heat distortion @ 95 deg C c. Linear dimensional shrinkage 0.3%-2.0% d. water sorption is fairly high (0.6 mg/cm2) can go to 2% e. the sorption of water causes the base to expand slightly, resulting in better fit f. good color stability g. no taste h. no odor i. good biocompatibility j. no allergic reaction if it is properly processed |
|
|
What is the main component of a powder acrylic denture base material?
|
Poly (methyl methacrylate) polymer
|
|
|
What is the main component of a liquid acrylic denture base material?
|
Methyl methacrylate monomer
|
|
|
What are the six benefits or characteristics of heat-cured acrylic bases
|
a. most popular
b. lower cost of processing c. adequate strength d. fairly flexible e. high resistance fatigue fracture f. LESS UNREACTED METHYL METHACRYLATE MONOMER |
|
|
What is the tensile strength of heat-processed acrylic base denture material
|
55 MPa
|
|
|
What is the heat distortion temperature of heat-processed acrylic base denture material?
|
95 deg C
|
|
|
What is the water sorption of heat processed acrylic base denture materials?
|
0.6 mg/cm2
|
|
|
Is there a taste or odor to heat-processed acrylic base denture materials?
|
No taste or odor
|
|
|
What are the five uses of light cured dimethylacrylates?
|
a. repair of acrylic dentures
b. orthodontic appliances c. reline dentures d. impression trays e. fabrication of dentures |
|
|
What are fully compounded light-cured dimethacrylates?
|
When the liquid and powder come already mixed
|
|
|
Why are light cured dimethylacrylates provided in tight packages?
|
To avoid premature polymerization
|
|
|
If you are using custom trays made of light cured dimethacrylates, why do you have to wait a minimum of 24 hrs before taking your final impression
|
The custom trays will continue to shrink for up to 24 hrs after you complete them and cause your impression to be distorted
|
|
|
What is the powder to liquid ratio in dough molding?
|
3:1 (powder:liquid)
|
|
|
During manipulation and processing, what are two types of molding that you can do?
|
Dough molding and injection molding
|
|
|
Which of the molding techniques is more accurate?
|
Injection molding
|
|
|
When dough-molding, how does the material change once you add water?
|
It goes from sandy to a sticky dough-like consistency
|
|
|
When processing the denture, how long do you cook it in the pressure pot?
|
8-10 hrs
|
|
|
What are the four uses for soft liners?
|
a. severe undercuts of the ridge
b. patients with continue sore ridges c. tissue tx after oral surgery d. obturators for defects of the palate |
|
|
Are soft liners soft & rubbery?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Do soft liners get hard
|
No
|
|
|
T/F soft liners are used to realign the denture and make it more stable?
|
True
|
|
|
What are the two classifications of soft liners?
|
acrylic & silicone
|
|
|
Which soft liner can be used for long term?
|
acrylic
|
|
|
Which soft liner can be used for short term?
|
silicone
|
|
|
What is the composition of long-term soft liners?
|
a. polyethyl methacrylates
b. acrylic copolymers plus plasticizers c. silicone rubber |
|
|
What are used in prosthetic teeth to produce different shades?
|
pigments
|
|
|
T/F prosthetic teeth are NOT made in layers of various colors
|
FALSE, They are made in layers of various colors
|
|
|
Are the properties of prosthetic teeth the same as the denture base?
|
YES
|
|
|
What kind of bond occurs between the denture and prosthetic tooth?
|
A chemical bond
|
|
|
What is the tensile bond strength of prosthetic teeth?
|
41 MPa
|
|
|
T/F Prosthetic teeth are hard to grind and polish
|
FALSE, they are easy to grind & polish
|
|
|
What are four indications of prosthetic teeth?
|
a. low stress bearing areas
b. poor ridges c. opposing natural teeth d. limited inter-arch distance |
|
|
What is a provisional?
|
temporary protection for the prepared tooth, used while work is being completed
|
|
|
What are the four purposes for placing a provisional?
|
a. maintenance of abutment relationship
b. function c. aesthetics d. Periodontal health |
|
|
How long is the interim partial denture put into the pressure pot?
|
20-30 minutes
|
|
|
What are the current materials available for making provisionals?
|
Poly (methyl methacrylate)
Poly (alkyl methacrylate) micro-filled composite (automixing system) Light-cured resins |
|
|
What is the difference between Poly (methyl methacrylate) & Poly (alkyl methacrylate)?
|
The chemical reaction
a. methyl produces a lot of heat, you may burn the surrounding pulp and tissue b. alkyl doesn't produce as much heat but takes more time to polymerize |
|
|
Which is stronger Poly (methyl methacrylate) or Poly (alkyl methacrylate)?
|
Poly (methyl methacrylate)
|
|
|
What are the four types of composite polymer systems?
|
a. Belle glass HP
b. Fibercore sculpture c. Cristobal d. Sinfony |
|
|
What are maxillofacial materials used for?
|
a. Loss of tissues of the face as a result of accident or disease
b. replacement of eye, ear, nose, etc |
|
|
What materials are used for maxillofacial surgeries?
|
Plasticized acrylics and vinyls
|
|
|
What is an example of an occlusal appliance?
|
night guard
|
|
|
When are night guards recommended?
|
For patients with TMJ problems or for patients who grind their teeth (bruxism)
|
|
|
Increasing the inorganic filler particles would:
a) Improve the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of the matrix b) Decrease the polymerization shrinkage c) Reduce the coefficient of thermal expansion d) All of the above |
All of the above
|
|
|
T/F
The primer has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties |
True
|
|
|
What does dental amalgam wear fairly comparably with?
|
Dental amalgam wears at a rate similar to tooth structure
|
|
|
T/F
There is no current evidence of hazard of the dental amalgam or relation to any disease. Hypersensitivity to mercury is extremely rare. |
Both statements are True
|

