![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What gives ceramic bonding alloys the chemical and mechanical retention?
|
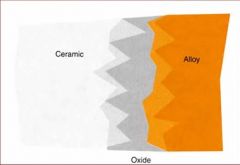
An oxide layer
|
|
|
What is the amount of expansion or contraction called?
|
Coefficient of thermal expansion
|
|
|
What is the melting range of ceramic bonding alloys?
|
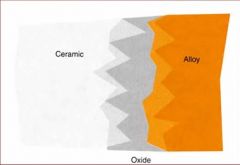
850-1350 deg C
|
|
|
In ceramic bonding alloys, what elements are added to high-noble & noble alloys to form the oxide layer?
|
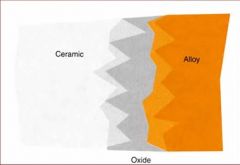
Gallium, indium, or tin
|
|
|
What are solders used for?
|
a. join an orthodontic wire to a band
b. join a clasp wire to a RPD c. join two units of a FPD d. Add proximal contact e. Repair an occlusal defect in a casting |
|
|
What is the melting point of solder?
|
425 deg C
|
|
|
A material that cleans the alloy to be soldered and dissolves any surface oxide on the metal is called what?
|
Flux
|
|
|
What is the advantage of a laser solder
|
Very precise and solders in seconds
|
|
|
What is the relationship between the melting point of the solder and that of the metal you are soldering to?
|
MP (melting pt) of solder has to be lower than the MP of the metal you are soldering
|
|
|
What are some common uses for wrought alloys?
|
a. orthodontic wires
b. endodontic files c. RPD clasps |
|
|
What are wrought alloys?
|
Alloys that are shaped into another form by mechanical force
|
|
|
What is significant about the grain structure of wrought alloys?
|
Wrought alloys have a grain structure often described as fibrous
|
|
|
When might you be suspicious of a metal allergy?
|
Inflammation around the margin- if the crown is placed correctly, etc suspect that it might be an allergy
|
|
|
What is the most common allergy to metal?
|
Nickel
|
|
|
What is the biocompatibility of alloys related to?
|
Corrosion
|
|
|
Why is corrosion bad?
|
Corrosion releases more of its elements into the mouth increasing the risk for unwanted reactions
|
|
|
What symptoms might a patient experience from corrosion of an alloy?
|
a. unpleasant tastes
b. irritation c. allergy |
|
|
What do base-metal alloys primarily contain?
|
Nickel, cobalt, or titanium
|
|
|
What alloy is considered the most difficult to manipulate in the laboratory?
|
Base-metal alloys
|
|
|
What are the best features of base-metal alloys?
|
a. Extremely high yield strength & hardness
b. Very low cost |
|
|
What are the negative features of base metal alloys?
|
High corrosion and questionable biocompatibility in the mouth
|
|
|
What are the main uses for base-metal alloys?
|
Crowns, FPD, RPD, implants, & wrought forms
|
|
|
What % of noble metal content do noble alloys contain?
|
At least 25% of noble metal content
|
|
|
What are the primary bases that compose noble alloys?
|

a. gold-based
b. palladium-based c. silver-based |
|
|
What alloy has a higher yield strength and hardness, high-noble alloys or noble alloys?
|
Noble alloys
|
|
|
What are the biggest draw-backs to noble alloys?
|
They are expensive
|
|
|
What is the corrosion like in noble alloys?
|
Low
|
|
|
What are the main uses for noble alloys?
|
FPD and crowns
|
|
|
What % of gold, palladium, or platinum must an alloy be to be considered a high-noble alloy?
|
60%
|
|
|
What alloy is easy to manipulate in the lab?
|
High-noble alloys
|
|
|
What is corrosion like for high-noble alloys?
|
Very low corrosion
|
|
|
What are the grains between crystals referred to as?
|
Grain boundaries
|
|
|
What are grain refiners?
|
Small size of the grains give better properties to the alloy
|
|
|
What are the grains between crystal called?
|
Grain boundaries
|
|
|
What is the benefit of nickel added to an alloy?
|
Improves mechanical properties of base metal alloys
|
|
|
What are some base metals?
|
a. Nickel
b. Silver c. Zinc d. Copper e. Titanium |
|
|
What is the benefit of copper added to an alloy?
|
It increases strength and hardness
|
|
|
What is the benefit of zinc added to an alloy?
|
a. Acts as a scavenger (deoxidizing agent)
b. Improves the castability and fluidity of the alloy |
|
|
What is the benefit of silver added to an alloy?
|
Improves mechanical properties of gold alloys
|
|
|
What properties are base metals required in alloys for?
|
a. strength
b. flexibility c. wear |
|
|
What is a negative feature of base metals?
|
Corrosion
|
|
|
What does a higher melting temperature indicate?
|
Harder to cast
|
|
|
What system is used to describe gold-based dental solders?
|
Fineness
|
|
|
How is fineness obtained?
|
F = %gold x 10
|
|
|
What is the melting temperature of platinum?
|

1755 deg C
|
|
|
What is the melting temperature of palladium?
|

1555 deg C
|
|
|
Which noble metal has a higher melting temperature, platinum or palladium?
|

Platinum (1755 deg C)
|
|
|
How are carats calculated?
|
K = 24 x %gold/100
|
|
|
How may gold content be expressed in terms of?
|
a. percentages
b. carat c. fineness d. color |
|
|
What is the melting temp of gold?
|

1063 deg C
|
|
|
What are the noble metals?
|
Au Pt & Pd
|
|
|
What are the good properties of gold?
|
Soft, malleable, ductile metal w/high nobility that resists tarnish & corrosion
|
|
|
What is an alloy?
|
Mixture of different metals
|
|
|
What is a casting?
|
The melting process of the metal forming the alloy
|
|
|
How are solders heated?
|
a. blow torch
b. traditional oven c. laser |
|
|
_______ & ________ are combined to create an alloy
|
Metals & nonmetals
|
|
|
What is the yield strength of a soft alloy, restorations subjected to low stress: some inlays?
|
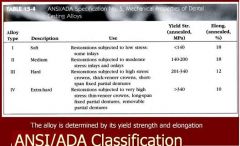
type I alloy <140
|
|
|
What is the yield strength of a medium alloy, restorations subjected to moderate stress: inlays & onlays
|

Type II alloy 140-200
|
|
|
What is the yield strength of a hard alloy, restorations subjected to high stress: crowns, thick veneer crowns, long-span FPD, RPD
|

Type III alloy 201-340
|
|
|
What is the yield strength of a extra hard alloy, restorations subjected to very high stress: thin veneer crowns, long span FPD, RPD
|

Type IV alloy >340
|
|
|
What are some problems associated with Ceramic Bonding alloys?
|
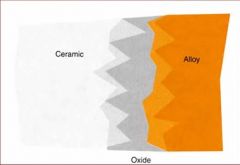
The color of the oxide
Greening Debonding of the ceramic |
|
|
What is greening in ceramic bonding alloys?
|
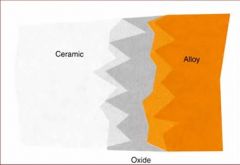
Vaporization of metal alloys that will discolor the ceramic matrix, making it look greenish, due to high amounts of silver and copper.
|

