![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
205 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Classes of molecular drug modes of transport |
Bulk flow Diffusional |
2 |
|
|
Diffusional transfer: location Mechanisms |
Across boundaries lipid, channels, carrier |
3 |
|
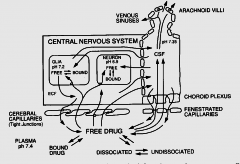
|
Blood Brain Barrier |
|
|
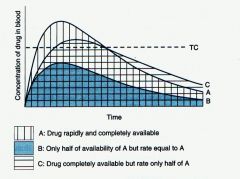
|
Bioavailability |
|
|
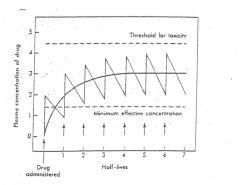
|
Chronic dosing |
|
|
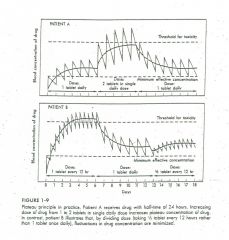
|
Chronic dose scheduling |
|
|

|
Clearance |
|
|
|
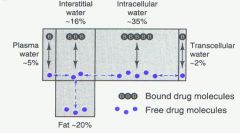
Distribution |
|
|
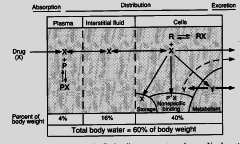
|
Distribution |
|
|
|
Mechanisms of Biotransportation |
Passive Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis |
4 |
|
|
Factors that influence passive diffusion |
Solubility Permeability pH Partition Mechanism Fick's Law |
4 |
|
|
Partition coefficient |
[D]eq lipid/[D]eq H2O |
ratio |
|
|
Permeability |
quality of a substance that is correlated with partition coefficient and molecular size |
correlated (2) |
|
|
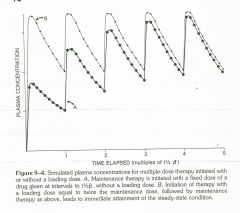
Loading dose |
|
|
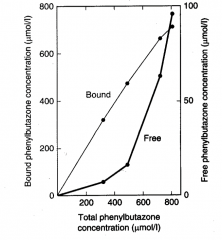
|
Plasma Protein Binding Saturation |
|
|
|
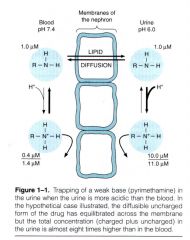
Ion Trapping |
|
|
|
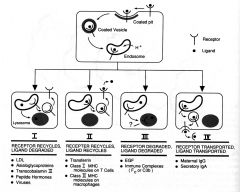
Receptor-mediated endocytosis |
|
|
|
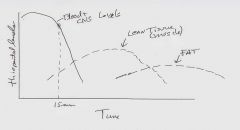
Redistribution |
|
|
|
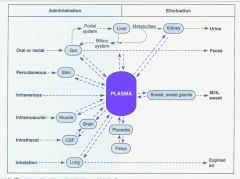
Routes of administration |
|
|
|
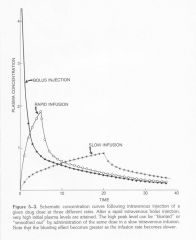
Speed of injection for acute dose of IV |
|
|
|
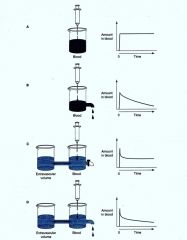
Volume of Distribution |
|
|
|
Fick's Law of Diffusion |
Flux=molecules/time =([D]i-[D]0)(Area)(PermCoeff)/Thickness |
|
|
|
pH Partition Mechanism: Bases Diffusion increased |
pH>pKa |
|
|
|
pH Partition Mechanism: pH>pKa |
Diffusion of Bases increase Acids decrease |
|
|
|
pKa |
pH at which half the compound is in a charged state |
|
|
|
Concentrations of weak acids and bases at equilibrium across boundaries |
Neutral species are equal Ionic species depend on balance of charge |
|
|
|
Henderson-Hasselbach |
pH=pKa+log([base]/[acid]) |
|
|
|
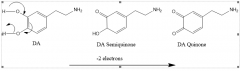
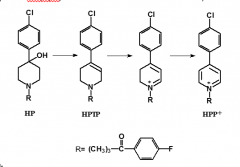
Endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxicants |
|
|
|
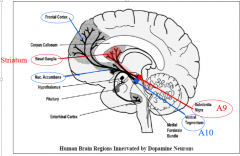
extrapyrimidal dopaminergic nigrostriatal system |
|
|
|
haloperidol |
|
|
|
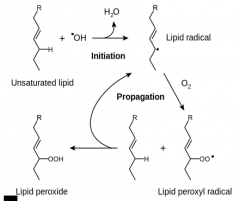
Lipid peroxidation |
|
|
|
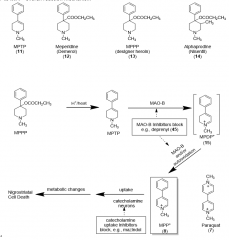
Pyridines MPP+ neurodegen Paraquat |
|
|
|
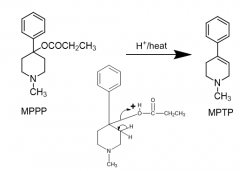
MPTP formation mechanism |
|
|
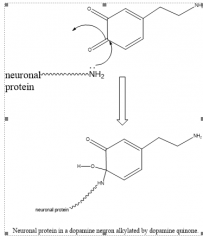
|
Neuronal Protein alkylated by dopaminergic quinone |
|
|
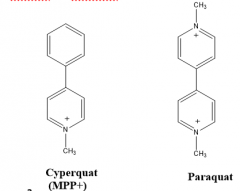
|
Paraquat |
|
|
|
Dopaminergic Neurotoxicants fall under which class of compounds? |
quinone |
|
|
|
L-DOPA |
L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine Carboxylated precursor to dopamine |
precursor |
|
|
Dopaminergic neurotoxicants cause neuronal death by |
inhibition of complex IV of Mitochondrial ETC |
ATP producer |
|
|
Complex IV relation to neuronal death Location |
inhibited by dopaminergic neurotoxicants Mitochondrial ETC |
inhibited by |
|
|
Dopamine and norepinephrine are |
Catecholamines
|
|
|
|
Oxidation of what by what forms H2O2? |
catecholamine NTs MAO |
NT |
|
|
MAO produces what from oxidizing catecholamine amines by what? |
H2O2 Transferring electrons to O2 |
|
|
|
Haber Weiss equation |
H2O2+superperoxide= neurocytotoxic hydroxy radical |
|
|
|
H2O2+superperoxide= neurocytotoxic hydroxy radical |
Haber Weiss equation |
|
|
|
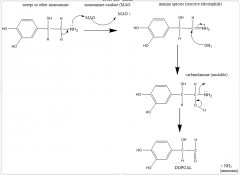
Oxidation of the dopamine amine group produces |
ammonia NH3 DOPGAL |
|
|
|
Byproduct of faulty MPPP-reverse ester synthesis |
MPTP |
|
|
|
MPPP full name Street name |
N-methyl-4-propionoxy-4-phenylpiperidine designer heroin |
|
|
|
MPTP full name |
Methyl-phenyl-tetrahydro-pyridine |
|
|
|
reverse ester of MPPP |
Meperidine Demerol |
Street name Trade name |
|
|
Herbicide trade name of MPP+ |
Cyperquat |
|
|
|
haloperidol is what that does what? |
antipsych drug PD-like, side effects |
|
|
|
Genetic mutation found in familial cases of PD
Effect |
alpha-synuclein
synucleinpathy |
|
|
|
Synucleinpathy |
aggregation of protein in dopaminergic neurons causing pathological inclusions/plaques |
|
|
|
Endogenous Neurotoxicants are formed by what producing what? |
auto-oxidation of dopamine quinones and hydroxy radicals |
reaction of 2 |
|
|
Quinones are a compound class that can be used to describe what formed from what? |
Endogenous neurotoxicants
autooxidation of dopamine |
|
|
|
Dopaminergic quinone neurotoxicants react with what via what? |
Amine group of neuronal proteins oxygenated carbon |
|
|
|
What enzyme forms MPDP+ from which molecule? |
MAO-B MPTP |
|
|
|
MAO-B oxidizes which exogenous molecule to form what? |
MPTP MPDP+ |
|
|
|
Exogenous neurotoxicants vs Endogenous Neurotoxins |
Pyridines
Quinones |
Compound classes |
|
|
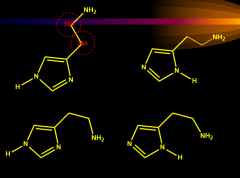
This autocoid is a NT |
histamine
|
2 |
|
|
H1 receptors are located where on the neuron? |
presynaptic membrane |
|
|
|
what H1 G-protein subunit stimulates PLC pathway? |
alpha q |
|
|
|
What H1 G-protein subunit stimulates AC? |
alpha s |
|
|
|
PLC pathway stimulates what causing what? |
PKC by Ca2+ release
smooth muscle contraction
|
|
|
|
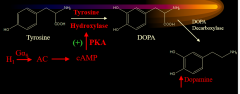
The activation of the H1 Galpha_s stimulates what (1) which produces what (2) that stimulates what (3) that produces what (4) from what (5)? |
AC cAMP PKA DOPA tyrosine |
|
|
|
The endpoint of H1 Galpha_s activation is.... |
dopamine formation |
|
|
|
The endpoint of H1 Galpha_q activation is.... |
smooth muscle contraction |
|
|
|
Which H1 Gprotein subunit has the endpoint of dopamine formation? |
Galpha_s |
|
|
|
Which H1 Gprotein subunit has the endpoint of smooth muscle contraction? |
Galpha_q |
|
|
|
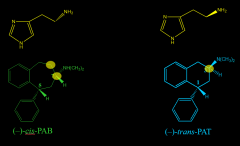
trans-PAT is a conformationally H1 selective drug that selects for the activation of which Gprotein subunit? |
Galpha_s |
|
|
|
cis-PAB is a conformationally H1 selective drug that selects for the activation of which Gprotein subunit? |
Galpha_q |
|
|
|
What molecule is used in comparative binding studies of trans-PAT? |
Mepyramine |
|
|
|
What are the major classes of G-protein dimer formation models? |
Contact Domain-swapped |
2 |
|
|
What are the types of contact dimerization models for G-proteins? |
Lateral packing/microaggregation disulfide bond formation coiled coil interactions |
3 |
|
|
Mechanism for the domain-swapped G-protein dimer models |
Trans-complementation |
|
|
|
COMT |
Catechol-O-Methyltransferase |
|
|
|
Dopamine+MAO |
Oxidizes amine group double bond to amine Water attacks tri-subbed C O double bond and formation of ammonia + DOPGAL |
4 last step=2 products |
|
|
Mechanism of MAO inhibition made possible by |
third-order substitution of nitrogen on dopaminergic molecule |
resonance |
|
|
A dopaminergic molecule with a tertiary nitrogen provides the capability of what? E.g. drug |
inhibiting of MAO Deprenyl |
|
|
|
dopaminergic drug substrate with tertiary N |
deprenyl |
|
|
|
deprenyl |
dopaminergic drug substrate with tertiary N |
|
|
|
Alzheimer's is a product of what neurochemical condition? |
ACh deficiency |
|
|
|
ACh deficiency is the neurochemical cause of what? |
Alzheimer's |
|
|
|
Neuropathology of Alzheimer's |
degeneration of cerebral cholinergic neurons |
|
|
|
What areas of the brain does Alzheimer's effect? |
Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital lobes |
4 |
|
|
The initial precursor of Ach |
serine |
|
|
|
Serine is the initial precursor to which NT? |
Ach |
|
|
|
Serine modification to choline involves what chemical modifications? |
Decarboxylation tertiary-methylation of amine N |
2 |
|
|
What components form Ach? What enzyme allows for this conjugation? |
Choline Acetyl-CoA choline acetyltransferase |
|
|
|
What triggers ACh release from presynaptic neuron? |
Depolarization allowing for Ca2+ influx |
|
|
|
How are ACh molecules condensed while in storage? |
N attracted to phosphate Os on ATP |
|
|
|
The interaction of AChase phenyl groups with quaternary N of ACh |
pi-pi stacking |
|
|
|
pi-pi stacking can be used to describe what enzyme-ligand interaction |
AChase phenyl groups with quaternary N of ACh |
|
|
|
What chemical modification inhibits the protease activity of the AChase serine residue? |
Carbomylation |
|
|
|
Carbomylation of AChase serine residue mechanistically inhibits hydrolysis by what means? |
Resonance of N electrons |
|
|
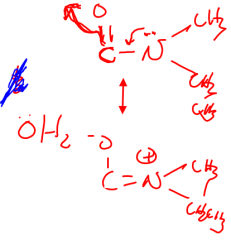
|
Achase Serine carbomylation |
|
|
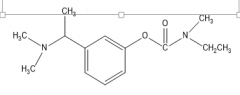
|
Rivastigmine |
|
|
|
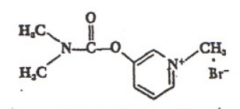
Pyridostigmine |
|
|
|
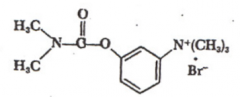
Neostigmine |
|
|
|
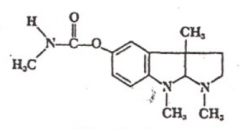
Physostigmine |
|
|
|
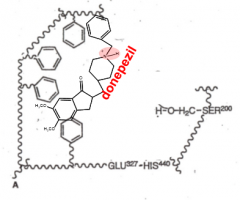
Donepezil-AChase competitive inhibition |
|
|
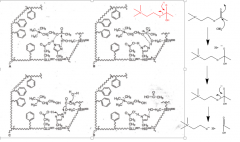
|
ACh-AChase |
|
|
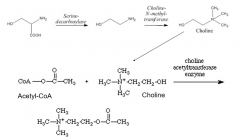
|
ACh formation |
|
|
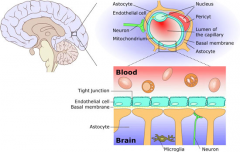
|
BBB |
|
|
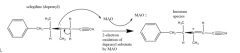
|
MAO inhibition by Deprenyl |
|
|
(MAO+2e-) +O2+(2H+)>H2O2 |
MAO mechanism |
|
|
|
cis-PAB vs trans-PAT and histamine |
|
|
|
Dopamine formation |
|
|
|
histamine |
|
|
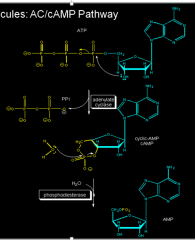
|
AC-cAMP formation |
|
|
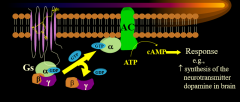
|
H1 AC cAMP pathway |
|
|
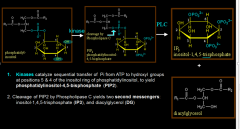
|
PLC-IP3-DAG |
|
|
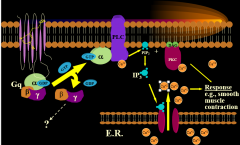
|
H1 PLC pathway |
|
|
|
Bioavailability equation |
C_oral abosrption/C_IV |
|
|
|
Bioavailability integration of curve for |
Concentration vs Time graph |
|
|
|
Integration of a Drug Concentration vs time drug curve gives what value? |
bioavailability |
|
|
|
Dosage formulations of sustained release tablets |
coated multiple layer with slow release core |
2 |
|
|
Dosage formulations of sustained release capsules |
Microencapsulation mixed release granules coated release beads |
3 |
|
|
Volume of distribution equation |
Vdist=dose/C_0 equilibrium concentration |
|
|
|
Initial equilibrium concentration of drug is determined by |
extrapolation of curve on drug plasma concentration vs time graph |
|
|
|
Extrapolation of the curve for a plasma concentration vs time graph yields |
initial equilibrium concentration of drug |
|
|
|
equation of Vdist% for deuterated water |
![or [V_(dist_D2O)/V_body] x 100%](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/31/92/34/14319234_m.png)
or [V_(dist_D2O)/V_body] x 100% |
|
|
|
What happens to the compartmentalization of drug when there is no elimination? |
it becomes biphasic |
|
|
|
First order elimination Integrated equation |
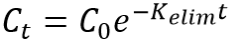
|
|
|
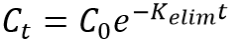
|
Integrated equation first order elimination |
|
|
|
bioequivalence |
how the bioavalabilitiesof two preparations of a drug compare |
|
|
|
how the bioavailabilities of two preparations of a drug compare |
bioequivalence
|
|
|
|
Cp equals |
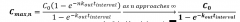
|
|
|
|
Toxicology is a product of |
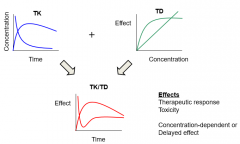
|
|
|
|
Top reasons for drug attrition 1991 |
Pharmacokinetics Lack of efficacy |
2 |
|
|
Top reasons for drug attrition besides Lack of efficacy 2001 |
Animal Toxicity Adverse Effects on man |
2 |
|
|
Toxicity |
degree of damage that a substance can cause a living system |
|
|
|
Inherent properties of Toxicity |
Immediate vs Delayed (time of onset) (ir)Reversible (duration of effect) Local vs Systemic (Location) Graded vs Quantal |
4
|
|
|
Factors that determine degree of toxicity |
dose route of exposure age gender genetics lifestyle health medication |
8 |
|
|
Factors of toxicity: Route of exposure |
rate of exposure extent of exposure |
2 |
|
|
Factors of toxicity: Age |
Variation in absorption variation in organ function |
2 |
|
|
Factors of toxicity: Genetics |
variation in acetyltransferase activity variation in expression or mutation in enzymes that effect absorption/distribution |
|
|
|
Factors of Toxicity: Lifestyle |
Diet Nutritional Status Smoking Alcohol Consumption |
4 |
|
|
How does food affect toxicity? |
food decreases absorption certain foods effect enzyme activity |
2 |
|
|
How does smoking affect toxicity? |
increases susceptibility to inhaled poisons Enhances metabolic activation |
2 |
|
|
How does drinking affect toxicity? |
increases susceptibility to hepatotoxicity alters nutritional status |
2 |
|
|
Poisons |
any agent producing toxicity |
|
|
|
Major types of toxicants |
Solvents/vapors Pollutants Pesticides Drug (side effects) Metals |
5 |
|
|
Pesticides are largely these classes of compounds |
organo- phosphorous chlorine |
2 |
|
|
Phenytoin side effect |
teratogenicity |
|
|
|
Essential metals |
iron manganese zinc copper |
4 |
|
|
How does Arsenic interfere with normal physiology? |
binds to enzyme thiol groups |
|
|
|
This nonessential metal binds to enzyme thiol groups |
Arsenic |
|
|
|
what variation of Iron produces molecular oxygen radicals? |
Ferrous Fe(II) |
adjective
oxidation state abbreviation |
|
|
Ferrous Iron |
Fe(II) |
|
|
|
Fe(II) |
Ferrous Iron |
|
|
|
Fe(III) |
Ferric Iron |
|
|
|
Ferric Iron |
Fe(III) |
|
|
|
Fenton Rxn |
Ferrous iron produces either produces superperoxides from O2 or hydroxyl radicals from H2O2 or Cu does the same from H2O2 |
3 |
|
|
When Ferrous iron either produces superperoxides from O2 or hydroxyl radicals from H2O2 or Cu(I) produces hydroxyl radicals from H2O2 |
Fenton Rxn |
|
|
|
Antioxidase System |
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) Catalase (CAD) Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) |
3 |
|
|
SOD: name and role |
superoxide dismutase converts superoxide to H2O2 |
|
|
|
SOD1 location and metal |
cytosolic Cu and Zn |
2 |
|
|
SOD2 location and metal |
Mitochondrion Mn |
|
|
|
SOD3 location and metal |
Extracellular Cu and Zn |
2 |
|
|
Catalase Tissues Metal Inhibitors |
liver; kidney; erythrocytes Fe for heme Heavy metals and cyanide |
2 inhibitors |
|
|
Catalase: role |
convert 2 H2O2s to O2 and 2x H2O |
2 |
|
|
GPx: name and role |
Glutathione Peroxidase Reduction of lipid hydroperoxide |
|
|
|
GSH: name and role |
Glutathione Regenerates GPx by forming GSSG |
|
|
|
GR: name Regenerates two molecules of GSH with protons from which molecule? |
Glutathione Reductase NADPH |
|
|
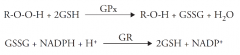
|
GPx and GR mechanisms |
|
|
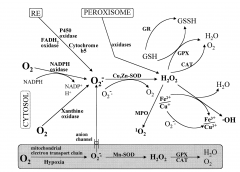
|
Antioxidant system |
|
|
|
Excess zinc causes |
anemia |
|
|
|
Zinc deficiency causes |
neuronal damage |
|
|
|
Excess iron causes |
hepatotoxicity |
|
|
|
Manganese deficiency causes |
bone deformation |
|
|
|
Excess manganese causes |
neurotoxicity |
|
|
|
Copper deficiency causes |
neurodegeneration |
|
|
|
Excess copper causes |
hepatotoxicity |
|
|
|
Arsenic causes |
neurotoxicity |
|
|
|
Cadmium causes |
Nephrotoxicity |
|
|
|
Lead causes |
Anemia |
|
|
|
Mercury causes |
neurotoxicity |
|
|
|
nickel causes |
cancer |
|
|
|
Excess of these metals cause hepatotoxicity |
Iron Copper |
2 |
|
|
Excess of these metals cause Neurotoxicity |
Mercury Arsenic Manganese |
3 |
|
|
Excess of these metals cause anemia |
Lead Zinc |
2 |
|
|
Deficiency of these metals negatively influences the nervous system |
Copper Zinc |
2 |
|
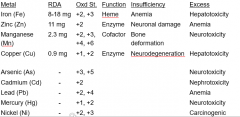
|
Metals |
|
|
|
Subfields of toxicology |
Mechanistic Regulatory/Occupational Forensic Clinical Environmental Developmental Reproductive |
7 |
|
|
Hazard |
the ability to cause damage |
|
|
|
the ability to cause damage |
hazard |
|
|
|
Chance of toxicity from exposure to a hazardous substance |
Risk |
|
|
|
Risk |
chance of toxicity from exposure to a hazardous substance |
|
|
|
Curve for toxicokinetics |
Concentration vs time |
|
|
|
Curve for toxicodynamics |
Effect vs concentration |
|
|
|
concentration of toxin vs time |
toxicokinetics |
|
|
|
effect vs concentration of toxin |
toxicodynamics |
|
|
|
effect of toxin vs time |
toxicology |
|
|
|
toxicology curve |
effect vs time |
|
|
|
Factors that influence dose-effect |
|
|
|
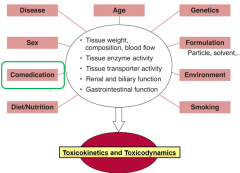
Factors that influence dose-effect of toxins/toxicants |
Route of administration Disposal/elimination Comedication Disease Age Genetics Formulation Environment Lifestyle |
9 |
|
|
What do the factors of dose-effect response of toxins determine per physiology? |
Tissue weight Tissue composition blood flow Enzyme activity Transporter activity Renal/biliary function GI function |
7 |
|
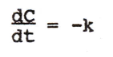
|
differential equation of zero-order elimination |
|
|
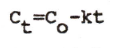
|
Integrated equation of zero-order elimination |
|
|
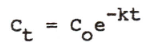
|
Integrated equation of first-order elimination |
|
|
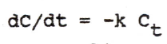
|
differential equation of first-order elimination |
|
|
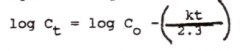
|
Straight-line equation of first-order kinetics |
|
|
|
How to determine elimination half life. Formula |
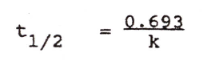
solve Straight-line first order equation for t when Ct=50 and C0=100 |
|
|
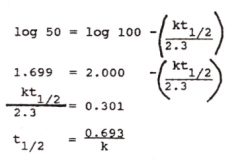
|
half-life of elimination |
|

