![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Scientific Method
|
Process of using systematic and rigorous procedures to evaluate theories by testing empirical hypotheses derived from them
|
Significant because it is central to the study of comparative politics but it is also difficult. Studying humans and their choices is much more complicated than studying something with a set of laws.
|
|
|
Theory
|
A set of logically consistent statements that generate abstract explanations of a general category of outcomes: a model of the causal processes that produce our world
|
Test hypotheses derived from theories, cannot directly test theories because they refer to abstract objects.
Basis of comparative politics experiments. |
|
|
Observational vs. Experimental Data
|
Observational Data is data that is directly observed from humans/nature acting on its own.
Experimental Data is data collected from intervening in the world to observe an outcome of an experiment. |
Experiments give capacity to control for confounding variables.
|
|
|
Confounding Variable
|
A variable that is systematically related to the independent and dependent variable
A difference between the treatment and control groups that affects the response variable. |
Often very difficult to determine what the confounding variable is, but if we do not control for the confounder, the measurement of association will be biased. When the confounder is controlled for, the original association may grow stronger or weaker.
|
|
|
Correlation vs. Causation
|
Correlation: The departure of two variables from independence- association/relationships
Correlation does not equal causation. |
x may cause y or y may cause x.
x and y may be joint effects of a common cause. A third variable z could cause association to appear between two variables. |
|
|
Endogeneity
|
X causes y but is not independent of it. x <----> y
|
|
|
|
Omitted Variable Bias
|
If the confounder is not controlled for, the measurement of the association will be biased and the direction/magnitude of the bias will no be predictable.
-Spurious correlation: When the original association disappears when the confounder is controlled for. |
|
|
|
Most Similar Research Design
|
a common approach of the comparative method that selects cases that are alike in a number of ways but differ on a key question under examination
|
|
|
|
Theory of Political Culture
|
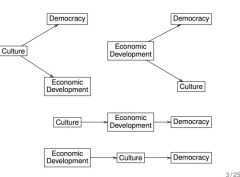
Multiple Theoretical Conceptions of Political Culture:
-Civic Culture -Modern vs. traditional culture -Religion |
|
|
|
Civic Culture
|
Does democracy require a civic culture? Or does democracy--> civic culture.
-Political efficacy -interpersonal trust -civic engagement -associational life |
|
|
|
Modern vs. Traditional Cultures.
|
-Traditional values versus secular-rational values
-Survival values versus self-expressive values |
Endogenous Culture:
Economic development--> secular-rational and self-expressive cultures. Shift from agratian to industrial society produces shift from traditional to secular-rational values. Industrial society to post industrial society produces shift from suvival to self expressive values. |
|
|
Fish, Islam and Authoritarianism
|
Does islam lead to authoritarianism?
Fish states that democracy is prevented from forming due to the oppression of women. |
The advancement of women has not been shown to create democracy, however.
Women did not have rights in US, still a democracy. |
|
|
Institutions
|
The formal and informal "rules of the game"
-university is an institution because it imposes a large set of rules |
Deliberate human artifacts-tools designed to achieve some goal
|
|
|
Institutional Theories
|
Origins-why do political systems have different institutions
Institutional consequences: what are the consequences of changing the rules of the game |
Endogeneity:
Political institutions--> political outcomes Causes of institutions affect both |
|
|
How to Build a Democratic Iraq
|
-Institutional Engineering
-Construct a federal system, but not along ethnic lines. -weak president mixed with prime minister -multimember districts |
-will these institutions works/should they be imposed by external actors.
|
|
|
Rationality
|
-Political culture: Actors are rational if they possess a complete and transitive preference ordering over a set of outcomes.
- If an actor prefers a to b and b to c, then she must prefer a to c. |
Rational actors seek to alter instituos to create new distributive outcomes--institutions are endogenous.
|
|
|
The State
|
Organizations that enjoy a preponderance of control over power resources and therefore claim and exercise priority over households, extended kinship groups, religious organizations, business enterprises, and all other forms of social organization within substantial territories.
|
State capacity is different from this definition: ability of the state to achieve its objectives.
Despotic power vs. infrastructural power |
|
|
Infrastructural and Despotic Power
|
Infrastructural power: capacity of the state to implement its decisions and elicit compliance from the population.
Despotic Power: power to make decisions without consultation with non-state actors |
low infra + desp = feudal
high infra + low desp. = bureaucratic high desp. + low infra = imperial High desp. + high infra = authoritarian |
|
|
Principal Agent Problem
|
-Dilemma of infrastructural power
-Ruler delegates authority to subordinates that might have goals that differ--exploit relationship--loss of delegated authority--lower levels of infrastructural power |
faithfulness/loyalness of agents
|
|
|
Public Goods
|
Goods that can be consumed by everyone, even if those that did not contribute to the cost of their supply.
non excludability and non rivalry |
-Free Rider Problem: Rational members of the group have little inceive to contribute to the costs of supplying a public good because all members of the gorup can enjoy its benefits.
Function of state is to provide public goods and use coercion to defeat free rider problem |
|
|
The Military Revolution
|
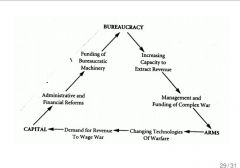
1450-1650
Taxation--infrastructural power--state building Handheld guns organize large number of people cost of war--bureaucracy |
|
|
|
Predation and Bargaining as Strategies of State Building
|
Predation: confiscation through violence. as you invest more, you can take more..diminishing returns
Bargaining: greater aspect to capital, give more in return--public goods |
bargains with merchants and nobilities.
States mix predation and bargaining |
|
|
Development
|
Development as growth in income, structural change, and elevated capacity
|
|
|
|
Market vs. State-Led Development
|
Market: -If economy is based primarily on markets, you get rapid economic growth
-decentralized decision making, everyone makes up their own mind--invisible hand. States: Active and interventionist state can make economies better than the would be on their own. Developmental state based on high infra power/motivations to develop can produce outcomes superior to those created by markets. |
Misconceptualized debate: no markets without political prerequisites.
|
|
|
Developmental vs. Predatory State
|
Developmental state based on high infrastructural power and urgent motivations to develop can produce outcomes uperior to those created by markets.
Other states do not wish to develop their economies and prefer to act predatorily. |
|
|
|
Inclusive vs. extractive economic institutions.
|
Inclusive: broad opportunities for ordinary people to make investments that maximize returns to their talent and skill
Extractive institutions are designed to extract incomes and wealth from one subset of society to benefit a smaller subset of society |
Inclusive is more congruent to modern state, extractive aligns with premodern systems.
|
|
|
Capitalism
|
A system of profit making enterprises with heavy investment in fixed capital and a rational organization of free labor which is orientated to the market purchases of the private consumer.
|
Originated from infrastructurally powerful states whose rulers have determined that optimal resource extraction strategy favors bargaining over predation.
-Private property -Decentralized economic organizations |
|
|
Regime
|
Set of rules and procedures that determine who gains access to government offices and how power holders can treat non-powerholders.
|
Dictatorship and democracy are types
|
|
|
Procedural Definitions of Democracy
|
-Institutions and rules of the regime, quality of rule
Observable indicators of democracy: -election of chief executive -election of legislature -more than one party competes in elections -alternation of power between parties |
|
|
|
Condorcet's Paradox and Condorcet Winner
|
-Problem of majority rule- a group composed of entirely rational individuals (with complete and transitive preference orderings) does not necessarily have collectively rational preferences. No clear winner. Individual rationality does not ensure group rationality.
|
Majority rule is not necessarily incompatible with intransitive group preferences.
Majority rule cannot ensure a Condorcet winner-the option that defeats every other option |
|
|
Preference Orderings and Utility Functions
|
Utility function is nothing more than a numberical representation of a preference ordering that follows the rule that if u(a)>u(b) then a>b. if you prefer a over b then your utility function must assign a higher number to a than b.
|
|
|
|
Single Peaked Preference Ordering
|
If utility declines in either direction as we move from the ideal point than there is a single peaked utility function representing a single peaked preference ordering.
|
Intuiton is that most idividuals prefer outcomes that are closer to their ideal point than outcomes that are farther away.
Sometimes this intuition is wrong-people either prefer hot coffee or iced coffee-not lukewarm coffee. Centrist and leftist members have single peaked po. rightest does not. -prefers an option that is farther away from ideal point to the option that is closer to it. If rightest does have singlepeaked uf, all three voters have spuf. |
|
|
The Median Voter Theorem
|
Centrist voter is a member of all three winning coalitions.
Voters must have single peaked preferences, vote sincerely, and the number of votes must be odd. Median voter is a condorcet winner |
Parties have incentive to get as close as possible to the position of the median voter. Deviation from that posititon will incur electoral loss.
|
|
|
Sincere vs. strategic voting
|
sincere vote is a vote for one's most preferred option. strategic vote is one for a less-preferred option out of the calculation that this will produce a more preferred outcome.
|
We don't always know if voters will vote sincerely. Affects median voter theorem.
|
|
|
Arrow's Impossibility Theorem
|
To guarantee group transitivity and hence stable outcomes, one principle of fairness must be sacrificed.
-non-dictatorship -universal admissibility -independence Unamity and Independence as non-controversial assumptions. --> impossibility theorem. Must sacrifice non-dictatorship/universal admissibility |
|
|
|
Presidential vs. Parliamentary Systems
|
Presidential system: population at large votes for chief executive and legislature is a separate branch of gov..
Parliamentary: voters select members of parliaments which then select a head of gov/chief executive--prime minister. |
Presidential systems are more prone to breakdown than parliamentary systems.
-consensus systems are less prone to breakdown in ethnically heterogeneous societies. -presidential systems are more likely to be selected in poorer, larger countries colonized by a power other than britain. |
|
|
Varieties of Electoral Systems
|
Majoritarian: territorially-based districts/constitutencies -single member districts and multi-member districts.
Proportional Rep.: Allocation of seats is proportional to number of votes parties receive. Open list/closed list |
-hybrid systems combine features of both
-there are opportunities for strategic actors to manipulate electoral rules to achieve political objectives. |
|
|
consociational democracy
|
Use formal mechanisms to coordinate power sharing among diverse groups, including minority groups.
|
Grand coalition gov. that guarantee participation by parties representing all ethnic groups
|
|
|
Political Parties and Party Systems
|
an organization comprising a group of officials or office seekers and a group of citizens dedicated to keeping officials in office and helping office seekers gain office by voting for party members or working on political campaigns to elect party members.
|
party systems
-nonpartisan democracy -single party system -one party dominant system -two party system -multi party system |
|
|
Reinforcing and Cross Cutting Social Cleavages
|

Politicial competition and clusterings of preference orderings oftern emerge among cleavages and divide voters. individuals have attributes that place them on different locations along cleavages
|
reinforced attributes-correlated with one another
cross cutting attributes- uncorrelated with one another |
|
|
Types of Dictatorships
|
-monarchy: rely on kin networks to obtain/retain power
-military: rule is often by committee of highest-ranking officers. have interest in protecting military as corporate body. civilian: do not have immediate access to support coalition/institutionalized basis of rule--> dominant-party dictatorships or personalistic dictatorship |
-dom. party: single party dominates access to politcal office and control over policy
-personalistic: individual retains control over policy decisions/selection of regime personnel. |
|
|
Cult of Personality
|
Heads of civilian dictatorships will try to create a personality cult-present highly exaggerated sense of personal virtues to obtain loyalty.
|
Play an important functional role in maintaining power
|
|
|
Preference Falsification
|
-Citizens falsify preferences for fear of repression.
|
dictator does not know his true level of support and the sources of opposition to him
|
|
|
Transition Matrix of Regimes
|

|
|
|
|
endogeneous and exogenous modernization theory
|
endo: wealth is directly causing democracy
Exo: rising income causes probability of death of democracy to decrease. Doesnt cause regime to become democratic, but causes it to stay democratic. |
Boix and stoke- endogenous effect is present, but not constant
|
|
|
sample selection bias
|
non random sample for a study/statistical observation
|
boix and stokes began in the 19th century, not 1950.
|
|
|
rentier state
|
resource-rich economies in which substantial export revenues accrue directly to state.
|
|
|
|
youll
|
be fine
|
|

