![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are all substances made of? |
Atoms |
|
|
What are atoms split into? |
Neutrons Electrons Protons |
|
|
What is the electric charge of an atom? |
No electric charge |
|
|
Why do atoms have no electric charge? |
They have the same amount of protons and electrons |
|
|
What is the charge of neutrons? |
Neutral charge (0) |
|
|
What is the charge of electrons? |
Negative charge (-1) |
|
|
What is the charge of protons? |
Positive charge (+1) |
|
|
What is the mass of a neutron? |
1 amu |
|
|
What is the mass of an electron? |
1/1840 amu |
|
|
What is the mass of a proton? |
1 amu |
|
|
What is the radius of an atom? |
0.1 nm |
|
|
What is an element? |
A substance that is made up of one kind of atom only, it is the smallest part if an element that can exist |
|
|
What is the nucleus made up of? |
Protons and neutrons Nearly all the mass of an atom is in the nucleus |
|
|
What is atomic number? |
The amount of protons/electrons in the atom |
|
|
What is mass number? |
The amount of protons and neutrons in the atom |
|
|
Around how many elements are in the periodic table? |
100 |
|
|
How are compounds formed? |
Compounds are formed from elements by chemical reactions |
|
|
What do compounds contain? |
Two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions |
|
|
How can mixtures be separated? |
Filtration, crystallisation, simple distillation, fractional distillation and chromatography |
|
|
Atoms that have different mass numbers but the same atomic numbers are called? |
Isotopes |
|
|
What is relative atomic mass? |
Is the average value that takes account of the abundance of the isotopes of the element. |
|
|
How many electrons fill each shell? |
Simple : 2,8,8,1 Advanced: 2,8,18,32 |
|
|
What on the periodic table can tell you the amount of valance electrons in an element? |
The group number |
|
|
What does the period number tell you about atoms? |
How many electron shells there are |
|
|
What are molecules? |
A group of atoms that are bonded together |
|
|
The further away the electrons are from the nucleus... |
The more energy they have |
|
|
How to separate compounds? |
Through chemical reactions |
|
|
What is a mixture? |
Consists of two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together. Chemical properties remain unchanged |
|
|
Fractional Distillation |
Separates misable (completely mixed together) liquids. Separates liquids from a mixture of 2+ liquids Have different bp's so one liquid evaporates before the other |
|
|
Chromatography |
Separates dissolved substances, that are coloured |
|
|
Evaporation |
Separates a dissolved substance from a salt solution |
|
|
Simple Distillation |
Separates solute and solvent |
|
|
Crystallisation |
Separates a solute from a solvent, liquid substance changes to a solid form as liquid has evaporated beyond solubility limit |
|
|
Filtration |
Separates an insoluble solid from a liquid |
|
|
What is a mixtures composition? |
Variable, can vary property amounts. But each substance retains its own properties. Easily separated by physical processes |
|
|
Who came up with the plum pudding model? |
J.J Thompson |
|
|
Plum pudding model |

|
|
|
What did J J Thompson discover |
Electrons, tiny negatively charged particles in 1897 |
|
|
What did John Dalton discover? |
Beginning of the 19th century Atoms were thought to be the smallest possible particles Compounds are formed when two + types of atoms join togethee |
|
|
Nuclear Model |

|
|
|
Who discovered the nuclear model? |
Ernest Rutherford (w/ Hans Greiger and George Marsden) in 1911
Fired alpha particles at a thin piece of gold. They thought particles would pass but a tiny fraction bounced back. Scattering meant tiny positive nucleus |
|
|
What did Niels Bohr do? |
Adapted the nuclear model in 1913. Electrons moved on stable orbits at specific distances. Further experiments led to protons being discovered. |
|
|
James Chadwick |
In 1932 Discovered a new particle inside the nucleus. Same mass as proton and no charge : neutron. |
|
|
How to calculate relative atomic mass? |
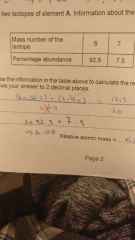
|
|
|
Rf Value |

|
|
|
How are different dyes separated by paper chromatography? |

|

