![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
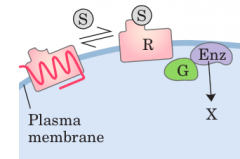
G Protein-coupled Receptor |
|
|
|
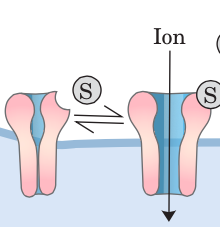
Gated ion channel |
|
|
|
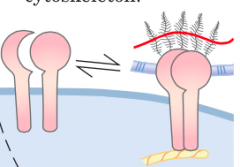
Adhesion receptor (integrin) |
|
|
|
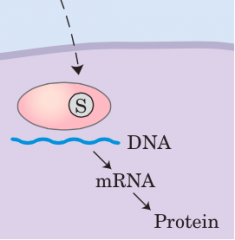
Nuclear receptor |
|
|
|
Receptor Tyrosine kinase |
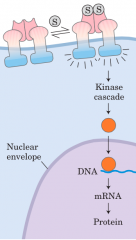
|
|
|
Receptor Guanylyl cyclase |
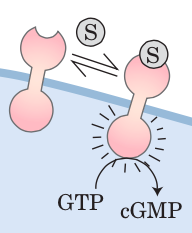
|
|
|
Specificity |
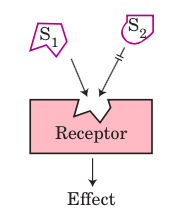
Signal molecule fits binding site on its complementary receptor; other signals do not fit. |
|
|
Amplification |
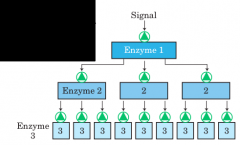
|
|
|
Desensitization/Adaption |
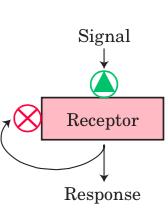
|
|
|
Integration |
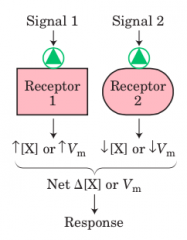
|
|
|
stimulatory G protein, or GS (the turning on an off mechanism) ~ diagram |
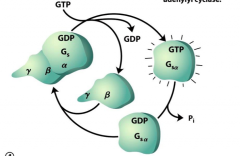
displaced GDP allows for activation of adenyl cyclase; GTPase turns off Gs-GTP by hydrolyzation |
|
|
Adenylyl cyclase - functions |
integral protein of the plasma membrane, with its active site on the cytoplasmic face
The association of active Gs" with adenylyl cyclase stimulates the cyclase to catalyze cAMP synthesis from ATP
The interaction between Gs" and adenylyl cyclase is possible only when the “switch” regions of Gs" are exposed by a GTP-induced conformational change. |
|
|
cAMP-dependent protein kinase or PKA - functions |
catalyzes the phosphorylation of other proteins, including glycogen phosphorylase b kinase
This enzyme is active when phosphorylated and can begin the process of mobilizing glycogen stores in muscle and liver in anticipation of the need for energy |
|
|
Epinephrine Cascade - diagram |
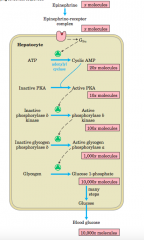
|
|
|
Desensitization of the b-adrenergic receptor in the continued presence of epinephrine |
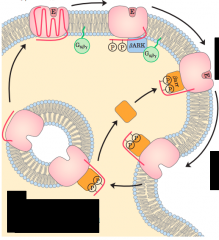
|
|
|
Hormone-activated phospholipase C and IP3 |
Two intracellular second messengers are produced in the hormone-sensitive phosphatidylinositol system: inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol. Both contribute to the activation of protein kinase C.
By raising cytosolic [Ca2+], IP3 also activates other Ca2+-dependent enzymes; thus Ca2+ also acts as a second messenger. |
|
|
Calmodulin |
When intracellular [Ca2+] increases in response to a stimulus, calmodulin binds Ca2", undergoes a change in conformation, and activates the CaM kinase. The kinase then phosphorylates target enzymes, regulating their activities |
|
|
Regulation of gene expression by insulin through a MAP kinase cascade - diagram |
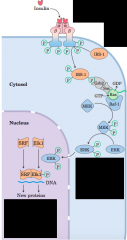
|
|
|
Activation of glycogen synthase by insulin - diagram |
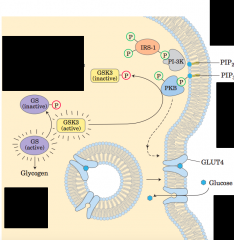
|
|
|
Adrenergic |
working on adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine) |
|

|
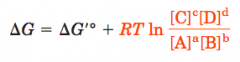
|
|
|
ATP is the chemical link of... |
catabolism and anabolism. It is the energy currency of the living cell. The exergonic conversion of ATP to ADP and Pi , or to AMP and PPi , is coupled to many endergonic reactions and processes. |
|
|
dehydrogenases |
many enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions |
|
|
Oxidation |
the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion (becoming more positive) |
|
|
Reduction |
gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion (becoming more negative) |
|
|
Nernst Equation |
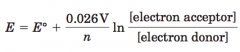
|
|
|
Major pathways of glucose utilization |
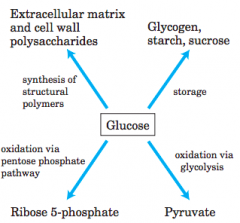
|
|
|
glycolysis |
converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate |
|
|
Phosphorylation of Glucose- diagram
~Energy required? ~Location of phosphorylation? ~Structure of Glucose? |
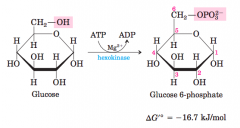
Step 1 |
|
|
Hexokinase (enzyme) |
enzyme used for phosphorylation of glucose into glucose 6-phosphate
requires Mg for its activation |
|
|
Isoomerization of glucose 6-phosphate, an aldose, to fructose 6-phosphate, a ketose - diagram |
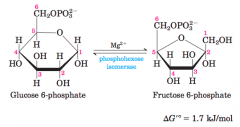
Step 2 |
|
|
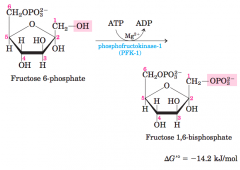
Phosphorylation of Fructose 6-Phosphate to Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate |
Step 3 |
|
|
bisphosphates |
Compounds that contain two phosphate or phosphoryl groups attached at different positions in the molecule |
|
|
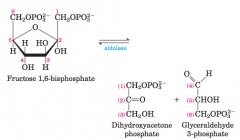
Cleavage of Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate |
Step 4
cuts them into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
and
dihydroacetone phosphate |
|
|
Phosphofructokinase -1 (enzyme) |
Fructose 6-phosphate --> fructose 1,6 bi-phosphate
requires Mg2+ --- adds a phosphate group to 1 carbon |
|
|
Overall equation for glycolysis |
one molecule of glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvate (carbons)
Two molecules of ADP and two of Pi are converted to two molecules of ATP (phosphates)
Four electrons (as two hydride ions) transferred to two of NAD+(electrons). |
|
|
glyceraldehydes dehydrogenase (enzyme) |
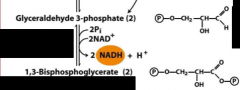
reduces glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into 1,3-biphosphoglycerate |
|
|
phosphoglycerate mutase |
"mutates" moves phosphate group on C-2 to C-3 |
|
|
Reversibility in Glycolysis |
Every step is reversible EXCEPT steps that involve conversion of ATP or ADP |
|
|
Gluconeogenesis |
reverse pathway of glycolysis |
|
|
Glucose regulation |
On a slightly longer time scale, glycolysis is regulated by the hormones glucagon, epinephrine, and insulin, and by changes in the expression of the genes for several glycolytic enzymes |
|
|
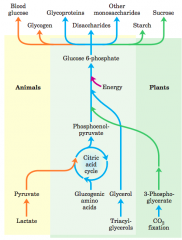
Carbohydrate synthesis from simple precursors |
|
|
|
Kinases |
ATP to ADP |

