![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fermentation
|
A partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen.
|
|
|
|
Cellular Respiration
|
Consumes oxygen as a reactant along with organic fuel
|
|
|
|
Coenzyme
|
An organic molecule serving as a cofactor
|
|
|
|
Function of an electron transport chain. (Cell respiration)
|
Shuttles electrons down a series of redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP
|
Electron Bus
|
|
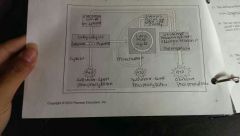
What is this showing?
|
Cellular Respiration
|
|
|
|
3 Phases of Aerobic (O2) Respiration
|
1.Glycolysis
2.Citric Acid Cycle 3.Oxidative Phosphorylation |
1. Breaking down sugar
2.Lemon circle 3.Loss of electrons due to phosphorus |
|
|
Where does Glycolysis occur?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
|
Two major phases of Glycolysis
|
1.Energy investment phase
2. Energy payoff phase |
Think banking
|
|
|
The starting product of glycolysis is this six-carbon sugar
|
C6H12O6
|
C__H__O__
|
|
|
The ending product of glycolysis is two organic carbon compounds termed ________
|
Pyruvate
|
|
|

This is the second form of phosphorylation known as _____________
|
Substrate level
|
___________ level
|
|
|
The Citric Acid Cycle converts _________ to _______
|
Pyruvate
Acetyl CoA |
The end product of glycolysis
Coenzyme A |
|
|
To enter the Citric Acid Cycle pyruvate must enter the _________ by ________ transport
|
Mitochondria
Active |
Powerhouse
Requires energy |
|
|
First step in Citric Acid Cycle
|
Pyruvate's carboxyl group is removed and given off as CO2
|
COO to CO2
|
|
|
Second step in Citric Acid Cycle
|
Enzyme transfers extracted electrons to NAD+, storing them as NADH
|
adds electrons
|
|
|
Third Step in Citric Acid Cycle
|
CoA is attached to acetate (by an unstable bond) forming acetyl CoA
|
Coenzyme attaches to something to form the final product
|
|
|
How many times does the citric acid cycle occur for each molecule of glucose?
|
Twice
|
|
|
|
During oxidative phosphorylation, ______________ couples electron transport to ATP synthesis
|
chemiosmosis
|
|
|
|
What are the two components involved in oxidative phosphorylation?
|
Electron transport chain
ATP synthesis |
Electron Bus
creating energy |
|
|
Why is oxygen the ultimate electron acceptor?
|
It is so electronegative
|
|
|
|
What are the two electron carrier molecules that feed electrons into the electron transport system?
|
FADH2
NADH |
|
|
|
How does ATP synthase use the flow of hydrogen ions to produce ATP?
|
ATP synthase acts as a rotor which allows for the production of ATP from ADP +Pi by activating catalytic sites in the knob
|
|

