![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy flow and chemical recycling in ecosystem:
|
|
|
|
Fermentation:
|
a partial degradation of sugars that occur without the use of oxygen
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration:
|
oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel
|
|
|
aer =
|
air
|
|
|
bios =
|
life
|
|
|
anerobic respiration:
|
processing harvests chemicals without using any oxygen.
|
|
|
an =
|
without
|
|
|
cellular respiration:
|
include both aerobic and anerobic processes, but is often used to refer to the aerobic process.
|
|
|
overall process of aerobic respiration:
|

|
|
|
cellular respiration in the degradation of the sugar glucose:
|
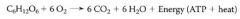
- breakdown of glucose is exergonic having a free energy change of -686kcal (-2,870kJ) per mole of glucose decomposed.
- recall that a -delta G indicates that the products of the chemical reaction can happen spontaneously. |
|
|
what is the fuel that cells most often use?
|
glucose
|
|
|
Redox reactions:
|
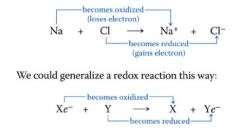
electron transfer reactions
|
|
|
Oxidation:
|
- the loss of electrons from one substance
- reducing agent |
|
|
reduction:
|
- addition of electrons to another substance
- oxidizing agent |
|
|
The redox reaction of respiration:
|
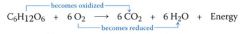
- the oxidation of glucose transfers electrons to the lower energy state, liberating energy that becomes available for ATP synthesis.
|
|
|
NAD+
|
(nicotinamide adenine dinucelotide)
- an electron acceptor - functions as an oxidizing agent during respiration |
|
|
How does NAD+ trap electrons from glucose and other organic molecules?
|

enzymes called dehydrogenases remove a pari of hydrogen atoms (2 electrons & 2 protons) from the substrante therefore oxidizing it. The enzyme delivers the 2 electrons along with 1 proton to the coenzyme NAD+. The other proton is released as hydrogen ion (H+) into the surrounding solution.
|
|
|
NAD+ as an electron shuttle:
|
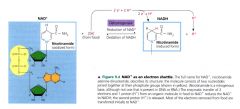
|
|
|
What does each NADH molecule formed during respiration represent?
|
stored energy that can be tapped to make ATP when the electrons complete their "fall" down an energy gradient from NADH to odygen.
|
|
|
Electron Transport Chain:
|
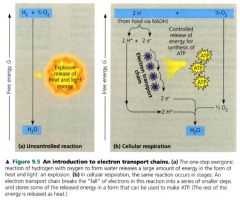
- consists of a number of molecules, mostly proteins, built into the inner membrane of mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and the plasma membrane of aerobically respiring prokaryotes.
- oxygen pulls electrons down the chain into an energy-yielding tumble analogous to gravity pulling objects downhill. |
|
|
during cellular respiration, most electrons travel the following "downhill" route:
|
glucose --> NADH --> electron transport chain --> oxygen.
|
|
|
Respiration is a cumulative function of what three metabolic stages?
|

|
|
|
An overview of cellular respiration:
|
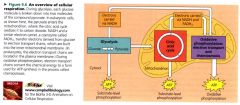
|
|
|
Glycolysis:
|
occurs in the cytosol, begins the degradation process by breaking glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate.
"sugar splitting" - occurs whether or not oxygen is present. (however, if oxygen is present, the chemical energy stored in pyruvate and NADH can be extracted by the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. |
|
|
Citric Acid Cycle:
|
takes place within the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells or simply the cytosol of prokaryotes,
completes the breakdown of glucose by oxidizing a derivative of pyruvate to carbon dioxide. |
|
|
Oxidative Phosphorylation:
|
- ATP synthesis from energy released at each step of the chain, it is powered by the redox reactions of the electron transport chain.
- occurs in teh inner membrane of the mitochondrion - accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by respiration. |
|
|
Substrate-level Phosphorylation:
|
- the production of smaller amounts of ATP in teh reactions of glycolysis & the citric acid cycle.
- occurs when an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP, rather than adding an inorganic phosphate to ADP. |
|
|
"substrate molecules" refer to what?
|
to an organic molecule generated as an intermediate during the catabolism of glucose.
|
|
|
compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration
|
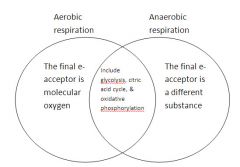
|
|
|
The energy input and output of glycoolysis:
|
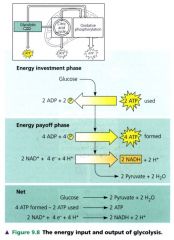
|
|
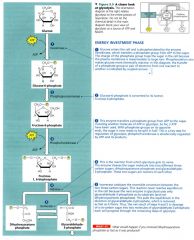
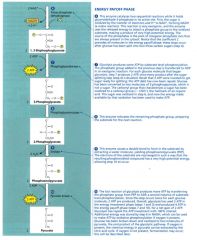
A closer look at glycolysis:
|
|

