![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Functions of bone
(5) |
•Supports & protects soft tissues •attachment for muscles •stores calcium &phosphate •red bone marrow produces blood cells •yellow bone marrow stores fat |
Two things it does. Two things it stores. One thing it produces. |
|
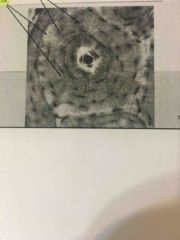
Label. Towards the top of the figure is ? Towards the bottom? |
•tissues consists of widely separated Cells surrounded by non-living matrix |
|
|
|
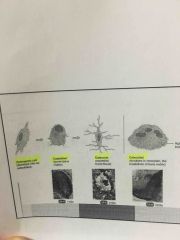
4 types of bone cells:
•______undifferentiated. Can divide, replace themselves, become osteoblasts (think generator)
•______For matrix and collagen fibers but can't divide.
•______mature cells that in a longer secrete matrix. (Retired)
•______huge cells.breakdown bone tissue. Function and bought a reapply option (release calcium from bone). (Think calcium) |
Osteoprogenitor
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
Osteoclast
|
All start with O. Two sound similar. Two different. |
|
Osteocytes communicate through tiny canals filled with extracellular fluid, which are called? |

Canaliculi |
|
|
|
Makes up the shaft of long bones and the external layers of all bones. |
Compact or dense bone |
Resist stresses produced by weight and movement |
|
|
Histology of compact bone
______________ - Functional unit of bone tissue consists of concentric rings of classified matrix surrounding a blood vessel.
____________ Are found in lacunae-Spaces in the matrix. |
Osteon
osteocytes |
|
|
|
Histology of spongy bone
Spongy cancellus bone consists of _______ (struts) surrounding spaces filled with a red marrow (where blood cells are made)
forms the structure of which three bones?
That's when you're going is light and strong and it's purpose is to _______________. |
Trabeculae
Short, flat and irrlegular bones, gives epiphysis of long bones.
Supports and protects the red bone marrow
|
|
|
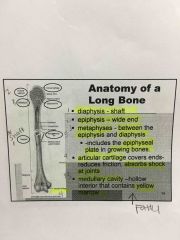
Know it.
Where is the metaphysics located?
What does it include?
What does the articular cartilage do?
What does the Medullary cavity contain?
|
Between the epiphysis and diaphysis.
epiphyseal plate in growing bones
Absorbs shock at pints and reduces friction
Yellow bone marrow (fatty) |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Know how to Label it |
|
|
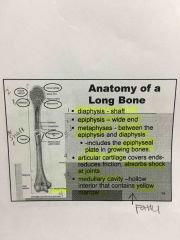
Know it.
Where is the metaphysics located?
What does it include?
What does the articular cartilage do?
What does the Medullary cavity contain?
|
Between the epiphysis and diaphysis.
epiphyseal plate in growing bones
Absorbs shock at pints and reduces friction
Yellow bone marrow (fatty) |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Know how to Label it |
|
|
|
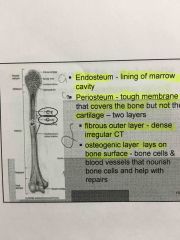
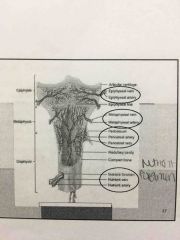
Blood and nerve supply to bone
____________ arteries that supply periosteum that covers bones
Nutrient arteries go into bone through nutrient ___________-supply diaphysis of long bones and red marrow.
Metaphyseal & epiphyseal arteries supply ________ & ________ of epiphyses.
|
periosteal
Foremen
Red bone marrow & bone tissue |
|
|
|
Look over it |
|
|
|
Bone formation ( in embryo)
____________ -soft tissue that is the template model for bone formation.
Bone formation is termed as?
|
Mesenchyme
Osteogenesis or ossification |
|
|
|
Two types of ossification occur |
Intramembranous ossification
Endochondrial ossification |
One step process
two-step process |
|
|
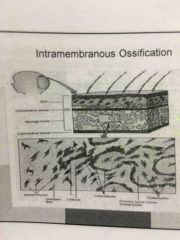
The one step process that forms flat bones like the skull. |
Intramembranous ossification |
|
|
|
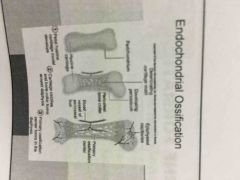
The two-step process where mesenchyme first becomes hyaline Cartilage that is then replaced by bone |
Endochondrial ossification |
|
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Cartilage cells are produced by _______ on epiphyseal side of plate
Cartilage cells are replaced by _________
Between ages __ to ___ epiphyseal plates close and growth stops. |
Mitosis
Bone
18-25extr |
Extra knowledge
Cartilage cells stop dividing and Boner replaces the Cartilage leaving an epiphyseal line |
|

Know it |
Know it |
|
|

Front (Term) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|

Front (Term) |
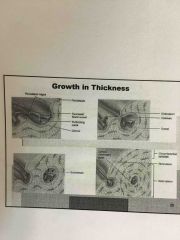
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Nutritional Factors affecting bone growth
•calcium and phosphorus for _______ •vitamin C for________ •Vitamin k and B12 for_______ |
Bone growth
collagen formation
protein synthesis |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Nutritional Factors affecting bone growth
•calcium and phosphorus for _______ •vitamin C for________ •Vitamin k and B12 for_______ |
Bone growth
collagen formation
protein synthesis |
|
|
|
(Hormones) factors affecting bone growth
Insulin like growth factor promotes cell division a epiphyseal plate
Name 3
Sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone)"kick in" at puberty and do two things |
hGH (growth), thyroid (T3 & T4) and insulin
Stimulate growth And modify the skeleton (create male& female forms) |
|
|
|
Hormonal of abnormalities can affect bone growth
____________ of hGH - produces gigantism
____________ of hGH - produces short stature
Both men or women that Lack ________ receptors on cells grow taller than normal |
Oversecretion
under secretion
Estrogen |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
Fracture repair
Step 1 damaged blood vessels produce ________in 6-8 hours damaged bone cells die.
Step 2 formation of _________ callus
Step 3 formation of __________ callus (3-4 months)
Step 4 _______ ____________ |
Clot
Fibrocartilagenous
Bony
Bone remodeling
|
|
|
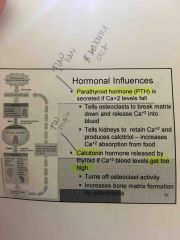
Front (Term) |
Look over |
|
|
|
Exercise & bone tissue
Within limits bone gets stronger through exercise by increasing deposition of _______ ______ and production of ________ |
Mineral salts
Collagen fibers |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Look over |
|
|
|
Exercise & bone tissue
Within limits bone gets stronger through exercise by increasing deposition of _______ ______ and production of ________ |
Mineral salts
Collagen fibers |
|
|
|
Removal of mechanical stress leads to __________ of the bone through demineralization and collagen reduction |
Weakening |
|
|
|
Osteoporosis is ?
Those at risk? (3) |
Decreased bone mass results in zporous bones
White white, thin menopausal, smoking, drinking, female with family history
Athletes who are not menstruating due to decrease body fat and decreased estrogen levels
People allergic to milk or with eating disorders whose intake of calcium Is too low |
|
|
|
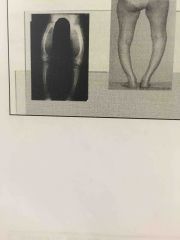
Ossification disorders
What are rickets? Why does this happen ?
What is Osteomalacia? |
Calcium salts are not deposited properly. Bones of growing children are small. But likes school rib cage and public deformities result.
New Adult bone produced during remodeling feels to ossify. Hip fractures are common |
|

