![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the three portions of the brain?
|
1.cerebum
2.cerebellum 3.brainstem |
|
|
|
The cerebellum consists of two hemispheres separated by...
|
1.fissue
2.gyri (bumps) 3.sulci (grooves) |
|
|
|
The cerebellum is where?
|
Is posterior to the cerebrum
|
|
|
|
The brainstem consist of...
|
1.pons
2.midbrain 3.medulla oblongata |
|
|
|
What is the menings?
|
It is a protective covering which enclose the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
What is the menings?
|
It is a protective covering which enclose the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
|
What are the layers of the menings from superficial to deep?
|
1.dura mater
2.periosteal layer 3.meningeal layer 4.sub arachnoid (space) large blood vessels 5.arachnoid mater 6.cerebrospinal fluid 7.pia mater |
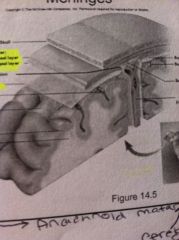
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) provides what?
|
1.buoyancy
2.protection 3.chemical stability |
|
|
|
CSF is formed how?
|
By filtration of fluid from the blood in the choroid plexuses in each ventricles.
|
|
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) provides what?
|
1.buoyancy
2.protection 3.chemical stability |
|
|
|
CSF is formed how?
|
By filtration of fluid from the blood in the choroid plexuses in each ventricles.
|
|
|
|
After the CSF is formed then what?
|
1. It circulates from the lateral ventricles
2. into the third ventricles 3. into the fourth ventricle 4. Central canal of the spinal cord 4. Goes through openings leading to the cisterns magna 5. Into subarachnoid space 6. Arachnoid villi 7. Into venous blood |
|
|
|
What is the medulla oblongata's function
|
Vital centers-cardiac, Vasomotor and respiratory; nonvital reflexes-vomiting, coughing, and sneezing
|
|
|
|
What is the medulla oblongata's function
|
Vital centers-cardiac, Vasomotor and respiratory; nonvital reflexes-vomiting, coughing, and sneezing
|
|
|
|
The medulla has fibers that do what?
|
Decussate (crossover) for counter lateral effects
|
|
|
|
What is the pon's function?
|
Regulating respiration, sleep, posture and some cranial nerve fibers
|
|
|
|
The midbrain's function is...
|
Auditory and visual effect (track moving objects) and some muscular control
|
|
|
|
The midbrain's function is...
|
Auditory and visual effect (track moving objects) and some muscular control
|
|
|
|
The parkinson disease is due to what?
|
Degeneration of the substantia nigra nuclei in the midbrain
|
|
|
|
What is the thalamus function?
|
Major relay station for sensory impulses on their way to the cerebral cortex ("gateway") and associating sensory impulses w/ pleasantness and unpleasantness.
|
|
|
|
What is the thalamus function?
|
Major relay station for sensory impulses on their way to the cerebral cortex ("gateway") and associating sensory impulses w/ pleasantness and unpleasantness.
|
|
|
|
In the thalamus, the impulses what?
|
Similar function are filtered, condensed, processed and relayed as a group to the cerebral cortex
|
|
|
|
What is the thalamus function?
|
Major relay station for sensory impulses on their way to the cerebral cortex ("gateway") and associating sensory impulses w/ pleasantness and unpleasantness.
|
|
|
|
In the thalamus, the impulses what?
|
Similar function are filtered, condensed, processed and relayed as a group to the cerebral cortex
|
|
|
|
The hypothalamus has what functions?
|
Neural and hormonal
|
|
|
|
The neural functions include...
|
Regulating and coordinating autonomic activities (appetite & body temperature)
|
|
|
|
The hormonal functions include...
|
Synthesizing hormones (secreted by posterior pituitoary)
|
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is...
|
Record of the electrical activity of the brain
|
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is...
|
Record of the electrical activity of the brain
|
|
|
|
The cerebellum interacts with the cerebrum because?
|
To plan and provide precise timing and appropriate patterns of skeletal muscle contraction and help control posture.
|
|
|
|
Electroencephalogram (EEG) is...
|
Record of the electrical activity of the brain
|
|
|
|
The cerebellum interacts with the cerebrum because?
|
To plan and provide precise timing and appropriate patterns of skeletal muscle contraction and help control posture.
|
|
|
|
The cerebellar processing include...
|
1.Receiving impulses for initiating muscle movement
2.receiving impulses on the body position 3.state (best movement) |
|
|
|
What is the cerebral cortex?
|
Outer surface of the cerebellum; composed of gray matter
|
|
|
|
What is the cerebral cortex?
|
Outer surface of the cerebellum; composed of gray matter
|
|
|
|
What is found deep inside the cerebral cortex?
|
White matter that connects with different areas of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
What is the cerebral cortex?
|
Outer surface of the cerebellum; composed of gray matter
|
|
|
|
What is found deep inside the cerebral cortex?
|
White matter that connects with different areas of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord
|
|
|
|
The cerebrum provides...
|
1.sensory functions
2.motor functions 3.higher functions: thoughts, emotions, & consciousness |
|
|
|
What does the cerebral hemisphere receive?
|
Sensory impulses from and dispatches motor impulses to the opposite side of the body
|
|
|
|
What does the cerebral hemisphere receive?
|
Sensory impulses from and dispatches motor impulses to the opposite side of the body
|
|
|
|
The primary motor cortex is located where and controls what?
|
Located: precentral gyrus
Controls: controls movement of the skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
What does the cerebral hemisphere receive?
|
Sensory impulses from and dispatches motor impulses to the opposite side of the body
|
|
|
|
The primary motor cortex is located where and controls what?
|
Located: precentral gyrus
Controls: controls movement of the skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
What is included in their or association area?
|
Memory bank for skilled motor activities ; sending information to the primary motor cortex
|
|
|
|
The primary somatosensory cortex resides in...
|
The postcentral gurus and receives sensory input from the body
|
|
|
|
The primary somatosensory cortex resides in...
|
The postcentral gurus and receives sensory input from the body
|
|
|
|
What does really somatosensory association ares process?
|
Sensory information and gives meaning to the information
|
|

