![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
109 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ANATOMY |
study of structure |
|
|
SUBDIVISIONS OF ANATOMY |
Gross, Microscopic, and Developmental Anatomy |
|
|
WHAT IS GROSS ANATOMY |
the study of regional, systemic and surface anatomy |
|
|
WHAT IS MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY |
the study of cytology & histology |
|
|
PHYSIOLOGY |
study of the function of the body |
|
|
****PRINCIPLE OF COMPLEMENTARITY*** |
Anatomy and Physiology are inseparable. Function always reflects structure. What structure can do depends on its specific form |
|
|
TO STUDY ANATOMY |
Mastery of anatomical terms observation manipulation palpation ausculation |
|
|
HOW MANY SYSTEMS IN THE BODY |
11 systems |
|
|
LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION |
1. Chemical 2. Cellular 3. Tissue 4. Organ 5. Organ System 6. Organismal |
|
|
NESSESARY LIFE FUNCTIONS |
-Maintaining boundaries between internal and external enviroments -Movement -Responsiveness -Digestion -Metabolism -Excretion -Reprodution -Growth |
|
|
CATABOLIC |
Metabolism chemical reaction breaks things down |
|
|
ANABOLIC |
Metaboism chemical reaction synthesis |
|
|
A BODIES SURVIAL NEEDS |
-Nutrients -Oxygen -Water -Normal Body Temp -Appropriate atmospheric pressure |
|
|
HOMEOSTASIS |
Maitenance of a relatively stable internal enviroment despite continuos changes in the enviroment |
|
|
HOMEOSTATIC CONTROL MECHANISMS |
Communication necessary for monitoring and regulating homeostasis |
|
|
WHICH SYSTEMS PERFORM THE FUNCTIONS FOR HOMEOSTATIC COMMUNICATION |
Nervous and endocrine systems |
|
|
COMPONENTS OF A CONTROL MECHANISM |
-Receptor (sensor) travels the AFFERENT pathway -Control Center (BRAIN) travels the EFFERENT pathway to -Effector (muscles or glands)
|
|
|
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK |
Responses that reduce or shuts off orgininal stimulus examples: heart rate, breathing rate, thirst, regulation of body temp, regulation of blood volume by ADH |
|
|
REGULATION OF BLOOD VOLUME BY ADH |
-Receptors sense decreased blood volume -Control center in hypothalamus stimulates pituitary gland to release ADH -ADH causes kidneys (effectors) to return more water to the blood |
|
|
POSITIVE FEEDBACK |
response enhances original stimulus example: labor contractions, platelet plug formation and blood clotting |
|
|
HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE |
Disturbance of homeostasis increases risk of disease contributes to changes associated with aging |
|
|
SOLVENT |
disolved into |
|
|
VISCERA |
Organs |
|
|
AXIAL PART |
head, neck, trunk |
|
|
APPENDICULAR PART |
appendages or limbs |
|
|
DEEP |
away from the skin suface, more internal |
|
|
SUPERFICIAL |
toward or at body surface |
|
|
DISTAL |
farther from the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk. Example: The ankle is distal to the thigh. |
|
|
PROXIMAL |
Closer to the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk Example: The arm is proximal to the wrist. |
|
|
LATERAL |
on the outer side of |
|
|
MEDIAL |
on the inner side of |
|
|
DORSAL |
behind |
|
|
VENTRAL (ANTERIOR) |
in front of
|
|
|
SUPERIOR |
above |
|
|
ANATOMICAL POSTION |
The body is erect with feet slightly apart with palms facing forward |
|
|
CEPHALIC |
head |
|
|
FRONTAL |
forehead |
|
|
ORBITAL |
eyes |
|
|
NASAL |
nose |
|
|
ORAL |
mouth |
|
|
MENTAL |
chin |
|
|
INFERIOR |
below |
|
|
CERVICAL |
neck |
|
|
THORACIC |
chest |
|
|
STERNAL |
breastbone |
|
|
AXILLARY |
armpits |
|
|
MAMMARY |
breasts |
|
|
ABDOMINAL |
umbilical |
|
|
INGUINAL |
groin |
|
|
OTIC |
ear |
|
|
OCCIPITAL |
back of head |
|
|
ACROMIAL |
shoulder |
|
|
BRACHIAL |
arm |
|
|
ANTECUBITAL |
front of elbow |
|
|
OLECRANAL |
elbow |
|
|
ANTEBRACHIAL |
forearm |
|
|
CARPAL |
wrist |
|
|
MANUS |
hand |
|
|
POLLEX |
thumb |
|
|
METACARPAL |
top of hand |
|
|
PALMAR |
palm of hand |
|
|
DIGITAL |
fingers |
|
|
COXAL |
hip |
|
|
FEMORAL |
thigh |
|
|
PATELLAR |
knee |
|
|
POPLITEAL |
behind knee |
|
|
CRURAL |
leg |
|
|
SURAL |
calf |
|
|
FIBULAR |
side of calf |
|
|
PEDAL |
foot |
|
|
TARSAL |
ankle |
|
|
METATRSAL |
top of foot |
|
|
HALLUX |
big toe |
|
|
DIGITAL |
toes |
|
|
PLANTAR |
bottom of foot |
|
|
CALCANEAL |
heal |
|
|
DORSAL |
back |
|
|
SCAPULAR |
shoulder blade |
|
|
VERTEBRAL |
spinal column |
|
|
LUMBAR |
lower back right next to spinal column |
|
|
SACRAL |
tailbone |
|
|
GLUTEAL |
posterior (butt) |
|
|
PERINEAL |
space between anus and external genitalia |
|
|
SAGITTAL PLANE |
vertical planes splitting a body into right and left |
|
|
FRONTAL PLANE |
vertical planes splitting a body into anterior and posterior parts |
|
|
CROSS SECTION |
horizontal plane splitting a body into superior and inferior parts |
|
|
TWO INTERNAL BODY CAVITIES |
dorsal and ventral cavities |
|
|
DORSAL BODY CAVITY |
Cranial cavity and Spinal cavity |
|
|
VENTRAL BODY CAVITY |
Thoracic cavity and Abominopelvic cavity |
|
|
THORACIC CAVITY |
Pleural cavity, Mediastinum cavity, Pericardial cavity |
|
|
PLEURAL CAVITY |
contains lungs |
|
|
MEDIASTINUM CAVITY |
medial of the pleural cavity |
|
|
PERICARDIAL CAVITY |
encloses the heart |
|
|
ABDOMINOPELVIC CAVITY |
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity |
|
|
ABDOMINAL CAVITY |
contains digestive viscera |
|
|
PELVIC CAVITY |
contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum |
|
|
SEROSA/SEROUS MEMBRANE |
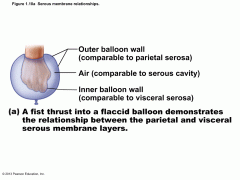
a thin double layer membrane covering the outer surfaces of the organs in the ventral body cavity |
|
|
PARIETAL SEROSA |
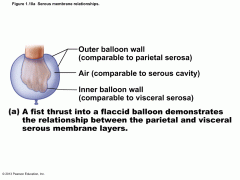
the membrane lining the cavity wall |
|
|
SEROUS FLUID |
fluid between the serous membranes |
|
|
PARIETAL & VISCERAL PERICARDIUM |
serous membranes around the heart |
|
|
PARIETAL & VISCERAL PLEURAE |
serous membranes around the lungs |
|
|
PARIETAL & VISCERAL PERITONEUM |
associated with the abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
MEDICAL QUADRANTS |
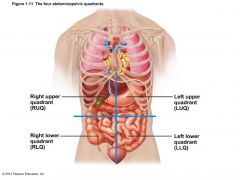
|
|
|
ANATOMISTS DIVISIONS |
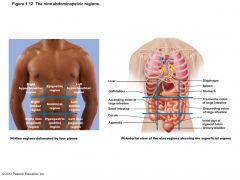
|
|
|
ORAL & DIGESTIVE CAVITIES |
contain the teeth and tongue. continuous with the cavity of the digestive organs, which opens to the body exterior at the anus |
|
|
NASAL CAVITY |
located within and posterior to the nose |
|
|
ORBITAL CAVITY |
in the skull; houses the eyes |
|
|
MIDDLE EAR CAVITY |
contain tiny bones that transmit sound vibrations to the hearing receptors in the inner ear |
|
|
SYNOVIAL CAVITIES |
joint cavities |

