![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The science of the shape and structure of organisms and their parts.
|
Anatomy
|
|
|
The biological study of the functions of living organisms and their parts.
|
Physiology
|
|
|
The study of the organs, parts, and structures of a body that are visible to the naked eye.
|
Gross, or Macroscopic, Anatomy
|
|
|
the study of microscopic structures of tissues and organs
|
Microscopic anatomy
|
|
|
The branch of biology that deals with the formation, structure, and function of cells.
|
Cytology
|
|
|
The anatomical study of the microscopic structure of animal and plant tissues.
|
Histology
|
|
|
Of, relating to, or in the region of the kidneys.
|
Renal
|
|
|
Of, relating to, or involving the heart and the blood vessels
|
Cardiovascular
|
|
|
Of or relating to a nerve or the nervous system.
|
Neural
|
|
|
The structure of a part of the body allows performance of certain functions.. The concept of "Structure determines function" is true in all of biology, for plants, animals, cells and organelles, even molecules!
|
Complementarity of structure and function
|
|
|
Levels of structural hierarchy, from smallest to largest
|
Chemical, Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organismal
|
|
|
The bodily system consisting of the skin and its associated structures, such as the hair, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands.
|
Integumentary System
|
|
|
The bodily system that consists of the bones, their associated cartilages, and the joints, and supports and protects the body, produces blood cells, and stores minerals.
|
Skeletal System
|
|
|
The bodily system that is composed of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue and functions in movement of the body or of materials through the body, maintenance of posture, and heat production.
|
Muscular System
|
|
|
The system of cells, tissues, and organs that regulates the body's responses to internal and external stimuli. In vertebrates it consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia, and parts of the receptor and effector organs
|
Nervous System
|
|
|
The bodily system that consists of the endocrine glands and functions to regulate body activities.
|
Endocrine system
|
|
|
The bodily system consisting of the heart, blood vessels, and blood that circulates blood throughout the body, delivers nutrients and other essential materials to cells, and removes waste products
|
Cardiovascular system
|
|
|
Another name for the cardiovascular system
|
Circulatory system
|
|
|
A network of vessels, tissues, and organs in vertebrate animals that helps the body regulate fluid balance and fight infection.
|
Lymphatic System
|
|
|
Another name of the lymphatic system
|
Immune system
|
|
|
The integrated system of organs involved in the intake and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and the environment.
|
Respiratory System
|
|
|
The alimentary canal together with the salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and other organs of digestion.
|
Digestive system
|
|
|
The bodily system consisting of the organs that produce, collect, and eliminate urine and including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
|
Urinary system
|
|
|
The bodily system of gonads, associated ducts, and external genitals concerned with sexual reproduction.
|
Reproductive System
|
|
|
Eight Neccessary Life Functions
|
Boundaries, Movement, Responsiveness, Digestion, Metabolism, Excretion, Reproduction, Growth
|
|
|
The ability or tendency of an organism or cell to maintain internal equilibrium by adjusting its physiological processes.
|
Homeostasis
|
|
|
A specialized cell or group of nerve endings that responds to sensory stimuli.
|
Receptor
|
|
|
A nerve ending that carries impulses to a muscle, gland, or organ and activates muscle contraction or glandular secretion.
|
Effector
|
|
|
Feedback that reduces the output of a system.
|
Negative Feedback
|
|
|
Effector enhances original stimulus
|
Positive Feedback
|
|
|
What is the anatomical position?
|
Human body erect, arms at sides, palms forward, feet together
|
|
|
Regional Terms:
head, neck and trunk |
Axial
|
|
|
Regional Terms:
Appendages or limbs |
Appendicular part
|
|
|
Nose
|
Nasal
|
|
|
Mouth
|
Oral
|
|
|
Neck
|
Cervical
|
|
|
Armpit
|
Axillary
|
|
|
Forehead
|
Frontal
|
|
|
Eye
|
Orbital
|
|
|
Cheek
|
Buccal
|
|
|
Breastbone
|
Sternal
|
|
|
Chest
|
Thoracic
|
|
|
Breast
|
Mammary
|
|
|
Abdomen
|
Abdominal
|
|
|
Arm
|
Brachial
|
|
|
Navel
|
Umbilical
|
|
|
Pelvis
|
Pelvic
|
|
|
Thigh
|
Femoral
|
|
|
Wrist
|
Carpal
|
|
|
Fingers
|
Digital
|
|
|
Hip
|
Coxal
|
|
|
Genital Region
|
Pubic
|
|
|
Anterior knee
|
Patellar
|
|
|
Foot
|
Pedal
|
|
|
Head
|
Cephalic
|
|
|
Ear
|
Otic
|
|
|
Between hips
|
Sacral
|
|
|
Base of the skull
|
Occipital
|
|
|
Spinal column
|
Vertebral
|
|
|
Shoulder blade
|
Scapular
|
|
|
Back
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
Buttock
|
Buttocks
|
|
|
Heel
|
Calcaneal
|
|
|
Sole
|
Plantar
|
|
|
Point of Shoulder
|
Acromial
|
|
|
Back of the knee
|
Popliteal
|
|
|
The serous membrane that surrounds the walls of an organ cavity
|
Parietal Serosa
|
|
|
The serous membrane that surrounds the organ itself
|
Visceral serosa
|
|
|
Thin watery fluid found in many body cavities, especially those lined with serous membrane
|
Serous fluid
|
|
|
Functions of Serous fluid
|
Prevents friction and infection
|
|
|
The membranous sac filled with serous fluid that encloses the heart and the roots of the aorta and other large blood vessels.
|
Pericardium
|
|
|
A thin serous membrane in mammals that envelops each lung and folds back to make a lining for the chest cavity.
|
Pleura
|
|
|
The serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal cavity and folds inward to enclose the viscera.
|
Peritoneum
|
|
|
Abdominal Regions
|
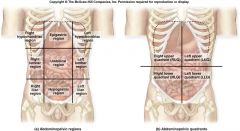
|

