![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what way does physiology depend on anatomy? |
Physiology depends on anotomy because the function will reflect the form. If physiology is good then then anotomy structure will work well (look and function) |
|
|
Would you be study in anotomy or physiology if you investigated how muscles shorten? If you explored the location of the lungs in the body? |
Investigating how the muscles shorten would be part of physiology. Exploring the location of lungs in the body would be part of anatomy. |
|
|
What is anatomy? |
Anatomy is the body part |
|
|
What is physiology |
Physiology is how the body part function. |
|
|
How is physiology and anatomy related? |
They are complimentary branches because anatomy depends on the physiology. Form = function |
|
|
What are the sundivisons of anatomy ? |
The subdivions on anatomy are •gross •microscopic anatomy • developmental anatomy |
|
|
How many subdivision does gross anatomy contain? |
3 |
|
|
What are the subdivision of gross anatomy ? |
•regional anatomy •systemic anatomy •surface anatomy |
|
|
What is regional anatomy? |
All the structures in a particular region of the body, like a leg or abdomen |
|
|
What is systemic anatomy? |
It is the study of system with system like the heart and the vessels. |
|
|
What is surface anatomy ? |
The study of internal structure as they relate to the overlying skin surface. Like when the nurse looks for the pulse in a vein and then draws out the blood. |
|
|
What is microscopic anatomy? |
The structure that are to small to be seen with the naked eye. |
|
|
What are the subdivision of microscopic anatomy? |
•cytology •histology |
|
|
What is cytology? |
The study of cells |
|
|
What is histology ? |
Histology is the study of tissue |
|
|
What is developmental anatomy ? |
Developmental anatomy is the study of how the structure changes through out the life spans. |
|
|
What is embryology? |
Embryology is the study of the structure before birth. |
|
|
What is pathology anatomy ? |
Changes caused by diseases. |
|
|
What is radiology anatomy? |
The study of structure through xrays |
|
|
What is palpation? |
Palpation is like feeling the organs with your hands |
|
|
What is auscultation? |
Studying the body parts through hearing (stethoscope) |
|
|
What is the principle of complimentary structure? |
The principle of complementary stated that form depends on structure which is that anatomy depends on physiology. So what a structure can do depends on its specific form. Function =Structure |
|
|
Levels of structural organization |

|
|
|
What are the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explains their relationships? |
•chemical level •cellular level •tissue level •organ level •organ system level •organismal level. |
|
|
What happens at the chemical level? |
Atoms . the smallest unit of life they form the organelles |
|
|
What happens at the cellular level. |
Cells have common functions But they vary in sizes and shapes. |
|
|
What happens at the tissue level? |
Is when similar cells come together because they have a common function. |
|
|
How many times of basic tissue types.? |
4 |
|
|
What are the 4 basic tissue types? |
•Epithelium •muscle •connective tissue •nervous tissue |
|
|
What is epithelium? |
Covers the body surface and lines cavities |
|
|
What are the muscles.? |
Provides movement |
|
|
What is connective tissue? |
Supports and protects organs? |
|
|
What is nervous tissue? |
Rapid internal communication. |
|
|
The levels of Structural Organization |

|
|
|
What level of structural organization is typical of a cytologists field of study? |
A cytologist would be at the cellular level of structural organization. |
|
|
What is the correct structural order for the following terms: tissue , organisms, organ , cell? |
Cell➡ tissue ➡organ➡organism |
|
|
Which organ system includes the bones and cartilage? Which includes the nasal cavity,lungs, and trachea? |
Bones and cartilage are part of the skeletal system. The nasal, cavity,lungs and trachea are part of the respiratory system organs |
|
|
What seperates living beings from non living objects? |
Living beings are able to maintain their boundaries. Movements, responsive, digestion,metabolism,excretion,reproduction,growth. While non living can have a few but not all of them. |
|
|
What name is given to all chemical reaction that occur within body cells? |
Metabolism |
|
|
Why is it neccesary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying 30,000 ft. |
The air is thin and gas exchange may be inadequate to support cellular metabolism |
|
|
What are the functional characteristics neccesary to maintain life in humans.? |
The functional characteristics necessary to maintain life in humans. •Maintain boundaries •Movement •responsiveness •digestion •metabolism •excretion •reproductive • growth.
|
|
|
What is the function of maintaining boundaries? |
Internal environments remain distinct from external environments. -all body cells are surrounded by selectively permeable membrane. -The body as a whole is enclosed by the integumentary system or skin |
|
|
What does the integumentary system do? |
Protect our internal organs from drying out. Bacteria. Damaging effects of heat. Sunlight. And unbelievable number of chemical in external environment. |
|
|
What does the movement function do ? |
Activities by the muscular systems. And the skeletal system the framework that the muscle pull on as they work. •blood, foodstuff,and urine propelled through internal organs of the cardiovascular, digestive, urinary system. |
|
|
What is contractility?
|
The muscle cells ability to move by shortening |
|
|
What does the responsiveness function do? |
The responsiveness function aka excitability. Is the ability to sense the changes in the environments and respond to them. •the nervous system is most involved in responsiveness. |
|
|
What does the digestion function do?
|
The digestion function breaks down the the ingested foodstuffs to simple molecules that can be absorbed into the blood. Then the nutrient rich blood distributed to all body cells by the cardiovascular system. |
|
|
What does the metabolism function do ? |
Includes all the chemical reactions that occur within body cells. Breaking down substances into simple building blocks. To synthesize more complex cellular structures. - depends on the digestive and respiratory system to make nutrients and oxygen available to the blood. -and on the cardiovascular system to distribute them through out the body. •regulated by hormones secreted on the endocrine system glands. |
|
|
What is the excretion function do? |
Removes the wastes, removes non useful substances produce during digestion and metabolism. •depends on the digestive system and urinary system |
|
|
Digestive system. |
Rids the body of indigesyive food |
|
|
Urinary system |
Dispose of nitrogen containing metabolic wastes . urea. And urine. And carbon dioxide by the cellular respiration. |
|
|
What does the reproduction function do? |
Cellular organism level • reproductive system directly responsible for offspring •regulated by hormones on the endocrine system |
|
|
What does the growth function do? |
Increase the size of body parts or organism as a whole . increase number of cells. |
|
|
What are the survival needs of the body? |
Nutrients Oxygen Water Temp Pressure |
|
|
Why do we need nutrients? |
Contain the chemical substances used for energy and cell building *carbohydrates are major part of energy fuel for body cells. |
|
|
Why do we need oxygen? |
20% of our air is oxygen Respiratory and cardiovascular make oxygen available to blood and body cells. |
|
|
Why do we need water? |
50- 60 % body weight is water -we get it form ingested food or liquids - loose it through evaporation from the lungs and skin and body excretions. |
|
|
Why is normal body temperatures needed.? |
If it drops to less than 98. 6 metabolic reactions become slower .if its too high proteins loose their shape. Muscular system generates most of the heat. |
|
|
Why is appropriate atmospheric pressure necessary. |
Breathing and gas changes in lungs depends on appropriate atmospheric pressure. If your too high up the air is thinner harder to breahe |
|
|
What process allows us to adjust to either extreme heat or extreme cold. |
The negative feedback mechanism allows us to adjust o either extreme hot or extreme cold. |
|
|
When we being to get dehydrated . we usually get thirsty which causes us to drink fluids . is thirst part of the negative or a positive feedback control? |
It is part of the negative feedback mevhanish as it makes us thirsty that cause us to drink which end the thirst stimulus . |
|

Why is the control system shown in this figure called a positive feedback mechanism?. What event ends it? |
It is positive because it enhance the change . the event ends when the plug is formed. |
|
|
What is homeostasis |
It is the process of keeping the balance in the body so everything functions well. |
|
|
Negative feedback mechanism |
Out put shuts off the oeigal stimuli or reduces its intensity . (Like the furnace) All negative feedback mechanism goal is to : prevent severe changes within the body. |
|
|
Positive feedback mechanism |
Enhances original stimuli so its accelerated . proceed in the same direction as initial change. "Cascades" Blood clots. And birth contractions. |
|
|
Describe the relationship between homeostatic imbalance a and disease? |
When homeostasis decrease the negative feed back mechanism does too sometimes causing destructive positive feed back mechanism to take over . Heart failure. Happens as we age. |
|
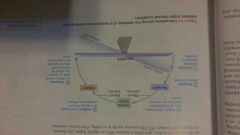
Homeostatic control system |
Figure |
|
|
What is the anatomical position? Why is it important?
|

The anatomical position is at attention just the palms face forward. It is important because it is regards to this position always. |
|
|
The axillary and acromial regions are both in the general area of the shoulder . where specifically is each located? |
Axillary is the armpit. Accromial is tip of shoulder |
|
|
What type of cut would separate the brain into anterior and posterior? |
The frontal plane |
|
|
What are the regional terms? |
Axial and appendicular |
|
|
What are the axial parts |
Head Neck Trunk |
|
|
What are the appendicular parts. |
Are the appendages or limbs attached to the body axis |
|
|
What are the planes |
Sagittal Frontal Transverse planes |
|
|
What is the sagittal plane ? |

Vertical plane. Divide into right and left Aka as midline median plate midsagittal |
|
|
What are Frontal Planes |

It is vertical Divide into anterior and posterior. Aka coronal plate |
|
|
What is a transverse or horizontal plate.? |

Runs horizontal Cuts from superior to inferior |
|
|
What are oblique sections? |
Cuts diagnolly between horizontal and vertical planes confusing so we Dont use them |
|
|
Joe went to the emergency room complaining or severenpains in the lower right quadrant of his abdome what could it be? |

It could be appendicitis |
|
|
Of the uterus , small intestines . spinal cord. And heart which one is in the dorsal cavity? |
Spinal cord is in the dorsal cavity |
|
|
When you rub your cold hands together the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands . why doesn't warming friction happen during the movement of the heart . lungs and digestive organs? |
Because the serous fluid seperates the organs so the won't create friction. Serous allows the serous membranes to glide easily over one another |
|
|
How many sets of internal cavities? |
2 |
|
|
What are the internal body cavities |
Dorsal cavities Ventral cavities |
|
|
What is Dorsal body cavity ? |
Protect the nervous systems organs 2 subdivisions |
|
|
What are the 2 subdivision of dorsal body cavities? |
Cranial cavity Vertebral cavity |
|
|
What is a cranial cavity? |
It is skull encases brain |
|
|
What is the vertebral or spinal cavity ? |
Encloses the delicate spinal cord. |
|
|
What are mennings . |
Membrane that covers the brain and spinal. |
|
|
What is the ventral body cavities? |
It is the more anterior and larger enclosed cavities. 2 major subdivision |
|
|
What are the subdivision of ventral body cavities. |
Thoracic cavity Abdomenopelvic cavity |
|
|
What is the thoracic cavity? |
It is superior . ribs muscles of chest. Subdivided into lateral Mediastinum Pericordial cavity which enclosed the heart and thoriac organs |
|
|
What is the abdominopelvic cavity? |
Its by the diaphragm . it is dome shaped important to breathing. It has 2 parts the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity. |
|
|
What is the abdominal cavity? |
Stomach . intestines. Spleens . liver and other organs |
|
|
The pelvic cavity? |
Inferior bony pelvis. Urinary bladder reproductive organs and rectum |
|
|
The four abdominopelvic quadrants |

|
|
|
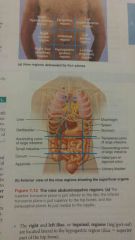
The nine region deliniated by four planes |

|
|
|
Nine regions showing the superficial organs. |
|

