![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 Categories to project life cycles |
|
|
|
Predictive Cycle / Fully Plan Driven Approach / Waterfall |
|
|
|
Iterative and Incremental Life Cycle |
|
|
|
Adaptive LIfe Cycles / Agile Methods / Change driven methods |
|
|
|
Chances of project success are lowest during: |
Initiating Phase |
|
|
Changes of project success are highest during: |
Closing phase |
|
|
Chances of risks occurring are higher during: |
Initiating, Planning processes Risk occurrence is reduced as the project progresses |
|
|
The impact of risk is greater during: |
the later processes of the project (Executing, Monitoring/Controlling, Closing) |
|
|
Stakeholders have the greatest influence during: |
Initiating, Planning processes and less and less as the project progresses. |
|
|
The process of going back through the process groups: |
an iterative process |
|
|
another opportunity to make a go or no go decision |
During the iterative process of reviewing various process groups and during the close out of each process group |
|
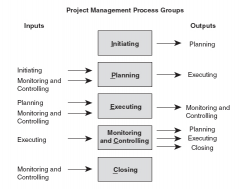
|
Examples of process groups and their inputs and outputs |
|
|
IPECC |
|
|
|
Tools and techniques |
Require action of some sort: measuring, applying some skill or technique, planning or using expert judgment |
|
|
Outputs |
Take the form of a deliverable: Results or outcomes that can be verified. |
|
|
Level of authority a project manager has is determined by: |
|
|
|
OPM |
Organizational Project Management (framework) |
|
|
3 types of PMO |
|

