![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bony thorax |
Chest Anatomy protective framework |
|
|
|
Respiratory system |
Lungs and Airways |
|
|
|
Mediastinum |
Space between lungs |
|
|
|
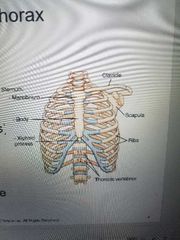
Sternum (breastbone) |
Manubrium. Body. Xiphoid process. |
|
|
|
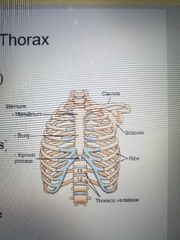
Bony thorax |
Sternum. Clavicles. Scapula. 12 pairs of ribs. 12 thoracic vertebrae. |
|
|
|
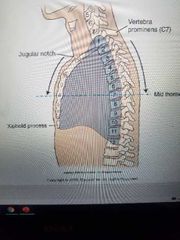
Bony thorax Positioning landmarks |
|
|
|
|
Between T2 and T3 |
Where is the jugular notch located using vertebrae |
|
|
|
C7 |
Where is the vertebra prominens? |
|
|
|
Respiratory system |
Exchange of gaseous substances between air and blood |
|
|
|
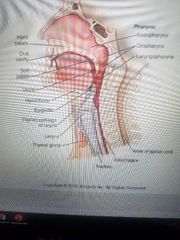
Respiratory system |
Four divisions are Pharynx. Trachea.
Bronchi.
Lungs. |
|
|
|
Anterior |
The trachea is anterior or posterior to the esophagus? |
|
|
|
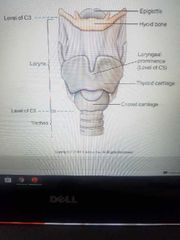
C5 |
Where is the Adam's apple located? |
|
|
|
Larynx (voice box) |
|
|
|
|
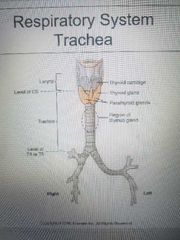
T4 or t4 |
Where is the trachea bifurcation? |
|
|
|
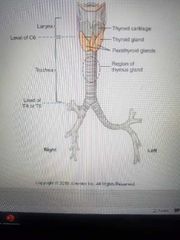
Trachea |
|
|
|
|
Are in the trachea |

What is the Blackness that the arrows are pointing to? |
|
|
|
Attenuate |
Bone _____ more x-rays than air |
|
|
|
Air, fluid or tissue, bone |
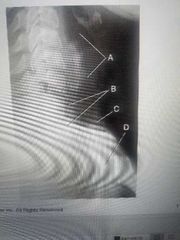
A, B, D |
|
|
|
Bronchi |
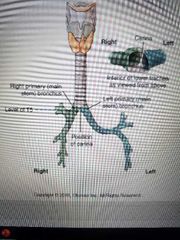
|
|
|
|
Left primary bronchus |
|
|
|
|
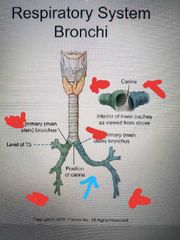
Position of carina at level of T5 |
what is the arrow pointing to and what level is it at |
|
|
|
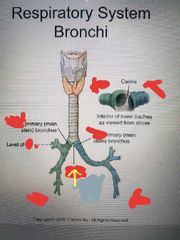
Secondary bronchi |
The right primary bronchi has 3 _____, while the left only has two |
|
|
|
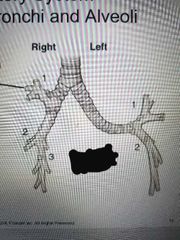
Alveoli |
Very small air sacs in the lungs that oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the blood through the thin wall of these Gas exchange |
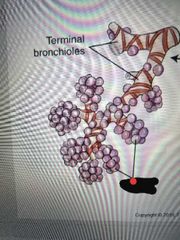
|
|
|
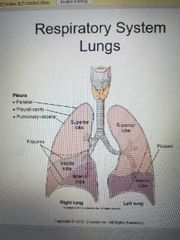
2 |
How many lobes are in the left lung |
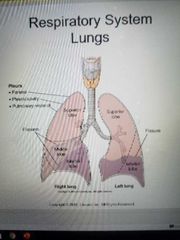
|
|
|
3 |
How many lobes are in the right lung |
|
|
|
Pleura |
The lungs are covered in what |
|
|
|
Right lung |
Superior lobe middle lobe inferior lobe |
|
|
|
Left lung |
Superior lobe
Inferior lobe |
|
|
|
Pleural cavity |
The potential space between the double-walled pleura |
|
|
|
Pneumothorax |
Air or gas present in the pleural cavity results in a condition called |
|
|
|
Hemothorax |
Accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity creates a condition called a |
|
|
|
Pleusrisy |
accumulation of fluid in pleural cavity |
|
|
|
Trachea |
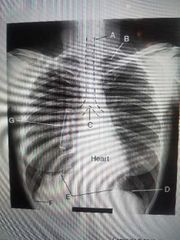
A? |
|
|
|
Carnia |
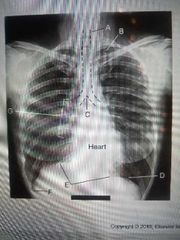
C? |
|
|
|
Diaphragm |
E? |
|
|
|
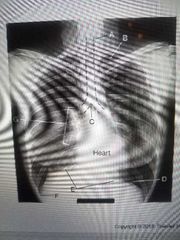
Apex & air in the lungs |
B? |
|
|
|
Costophrenic angle |
F? |
|
|
|
Hilum |
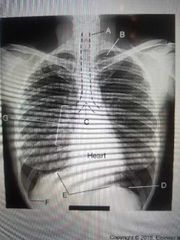
G? |
|
|
|
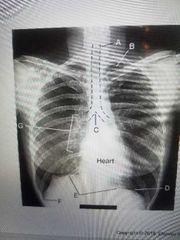
Apex |
B |
|
|
|
Base of lung |
D |
|
|
|
Costophrenic angle |
F |
|
|
|
Base of lung |
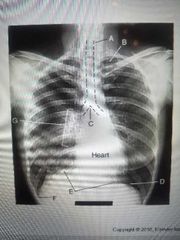
D |
|
|
|
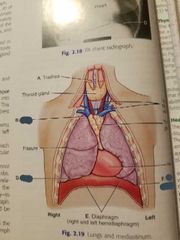
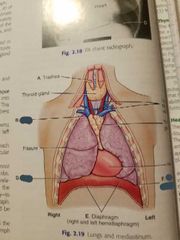
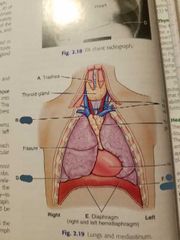
Lungs and mediastinum |
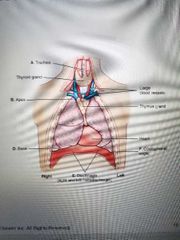
|
|
|
|
4 structures inside the mediastinum |
Trachea.
Esophagus. Thymus gland.
Heart and great vessels. |
|
|
|
Mediastinum |
Medial portion of thoracic cavity between lungs |
|
|
|
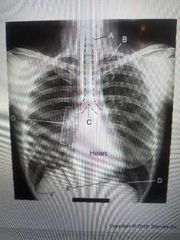
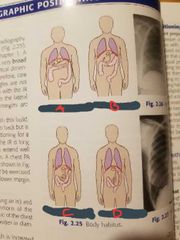
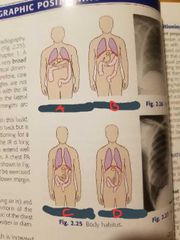
Hypersthenic |
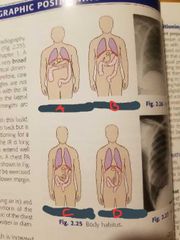
A |
|
|
|
Sthenic |
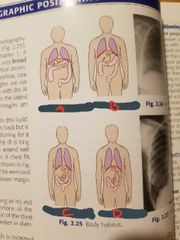
B |
|
|
|
Hyposthenic |
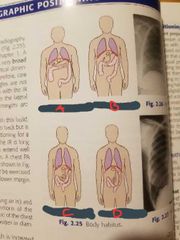
C |
|
|
|
Asthenic |
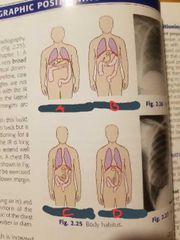
D |
|
|
|
5% |
A% |
|
|
|
50% |
B% |
|
|
|
35% |
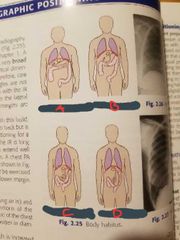
C% |
|
|
|
10% |
D% |
|
|
|
Up |
When you breathe out during expiration your diaphragm goes __ |
|
|
|
Inspiration |
Your diaphragm goes down during ____, when you breathe in |
|
|
|
Vertical (diaphragm downward), transverse, AP dimension |
During inspiration, the lungs increase in three dimensions. They are.. |
|
|
|
10 |
You should be able to see at least ____ ribs when doing a chest x-ray |
|
|
Patient preparation |
Removal of opaque objects.
Closing artifacts.
Long hair fastener.
O2 lines and pacemaker leads not in lung fields |
|
|

Radiation protection |
Limited repeat exposures.
Collimation.
Gonadal shielding.
Backscatter protection. |
|
|
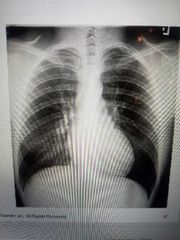
Technical factors |
High KV (110 to 125) Grid High mA, short exposure time |
|
|
|
Patient identification |
Patient ID.
Anatomic side marker. |
|
|
Breathing instructions |
Inspiration.
Clear, concise instructions. Exposure upon second full breath. 10 posterior ribs above diaphragm (ideal) |
|

