![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
CONCRETE |

IS COMPOSED OF CEMENT, FINE AGGREGATE, COARSE AGGREGATE MIXED WITH WATER. Portland cement is the commonly used type of cement for production of concrete. |
|
|
|
CEMENT |

a powdery substance made with calcined lime and clay. It is mixed with water to form mortar or mixed with sand, gravel, and water to make concrete. |
|
|
|
FINE AGGREGATE |

generally consist of natural sand or crushed stone with most particles passing through a 3/8-inch sieve. |
|
|
|
COARSE AGGREGATE |

are any particles greater than 0.19 inch, but generally range between 3/8 and 1.5 inches in diameter. |
|
|
|
LIME AND GYPSUM |

A material similar to concrete was first developed by the Egyptians, consisting of_________. |
|
|
|
TYPES OF CEMENT |
PORTLAND CEMENT AND POZZOLANA CEMENT. |
|
|
|
PORTLAND CEMENT |

cement that is manufactured from limestone and clay and that hardens under water. |
|
|
|
POZZOLANA CEMENT |

is a kind of Blended Cement which is produced by either intergrinding of OPC clinker along with gypsum and pozzolanic materials in certain proportions. Its is cheaper |
|
|
|
BENEFIT OF CONCRETE |
is a relatively cheap material and has a relatively long life with few maintenance requirements.It is strong in compression.Before it hardens it is a very pliable substance that can easily be shaped.It is non-combustible.
|
|
|
|
LIMITATIONS OF CONCRETE |
Relatively low tensile strength when compared to other building materials.Low ductility.Low strength-to-weight ratio.It is susceptible to cracking.
|
|
|
|
FORMWORK |

is a temporary mould into which concrete is poured and formed. It is fabricated using timber, but it can also be constructed from steel, glass fibre, reinforced plastics and other materials. |
|
|
|
COMPOSITION OF FORMWORK |
CEMENT, WATER, AGGRIGATES ( 3/4" INCH - DIAMETER ). |
|
|
|
SCAFFOLDING |

a temporary structure on the outside of a building, made usually of wooden planks and metal poles, used by workers while building, repairing, or cleaning the building. |
|
|
|
RE - BAR |

a steel reinforcing rod in concrete. |
REINFORCEMENT |
|
|
3/8" (10mm ) |

WALL, SLAB, STIRRUPS |
|
|
|
1/2" ( 12mm ) |

SLAB, BEAM, FOOTING |
|
|
|
5/8" ( 16mm ) |

COLUMN, BEAM |
|
|
|
3/4" ( 20mm ) |

COLUMN, BEAM |
|
|
|
1" ( 25 mm ) |

COLUMN, BEAM |
|
|
|
1 1/4" ( 32 mm ) |

COLUMN, BEAM |
|
|
|
ADMIXTURES |

materials in the form of powder or fluids that are added to the concrete to give it certain characteristics not obtainable with plain concrete mixes. In normal use, dosages are less than 5% by mass of cement and are added to the concrete at the time of batching/mixing. |
|
|
|
ACCELERATORS |

speed up the hydration (hardening) of the concrete. Typical materials used are CaCl. It is especially useful for modifying the properties of concrete in cold weather. |
|
|
|
RETARDERS |

slow the hydration of concrete and are used in large or difficult pours where partial setting before the pour is complete is undesirable. |
|
|
|
AIR ENTRAINING AGENTS |

add and entrain tiny air bubbles in the concrete, which reduces damage during freeze-thaw cycles, increasing durability. However, it entails a trade off with strength, as each 1% of air may decrease compressive strength by 5%. Prevent honey comb. |
|
|
|
PLASTICIZERS |

increase the workability of plastic, or "fresh", concrete, allowing it to be placed more easily, with less consolidating effort. It can be used to reduce the water content of a concrete while maintaining workability and are sometimes called water-reducers due to this use. Such treatment improves its strength and durability characteristics. |
|
|
|
PIGMENTS |

can be used to change the color of concrete, for aesthetics. |
|
|
|
CORROSION INHIBITORS |

are used to minimize the corrosion of steel and steel bars in concrete. |
|
|
|
BONDING AGENTS |

are used to create a bond between old and new concrete (typically a type of polymer) with wide temperature tolerance and corrosion resistance. |
|
|
|
PUMPING AIDS |

improve pumpability, thicken the paste and reduce separation and bleeding. |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

1. Selecting quantities of materials for selected mix proportion. |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

2. Mixing |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

3. Checking of workability |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

4. Transportation |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

5. Pouring in formwork for casting |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

6. Vibrating for proper compaction |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

7. Removal of formwork after suitable time. ( MIN. 7 DAYS TRIAL PERIOD TO MAX 28 DAYS ) |
|
|
|
STEPS IN CONCRETE CONSTRUCTION |

8. Curing member with suitable methods and required time. |
|
|
|
TYPES OF CONCRETE TESTING |
SLUMP TEST AND COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH TEST |
|
|
|
SLUMP TEST |
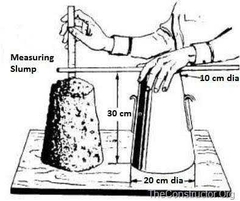
The consistency of the concrete determines how well the concrete will pour, handle and compact. The measurement used to gauge the consistency of concrete is called slump. Problems with consolidation and mortar loss can occur if your slump is too low (runny) or too high (thick). |
|
|
|
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH TEST |

lets you know the strength of your concrete once it hardens. It is performed by assessing the force needed to break concrete cylinders in varying levels of hardness. |
IF FAILED IN 7 DAYS TRY AGAIN. |
|
|
FINE AGGREGATE SIZES |

Coarse Sand(2.0mm – 0.5mm). Medium sand(0.5mm – 0.25mm). Fine sand(0.25mm – 0.06mm). Silt(0.06mm – 0.002mm). Clay(<0.002).
|
|
|
|
COARSE AGGREGATE SIZES |

Fine gravel (4mm – 8mm). Medium gravel (8mm – 16mm). Coarse gravel (16mm – 64mm). Cobbles (64mm – 256mm). Boulders(>256mm).
|
|
|
|
CONCRETE PROPORTION MIXTURE CLASS |
CLASS AA, CLASS A, CLASS B, CLASS C, CLASS D, CLASS E. |
|
|
|
CLASS AA |
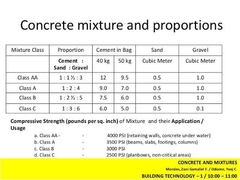
(1 : 1 1/2 : 3). BEAMS, SLAB, COLUMNS, ALL MEMBERS SUBJECTED TO BENDING. |
CEMENT IN BAG 40kg (12) / 50kg (9.5). SAND cu.m (0.5). GRAVEL cu.m (1.0). |
|
|
CLASS A |
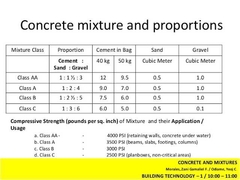
(1 : 2 : 4). BEAMS, SLAB, COLUMNS, ALL MEMBERS SUBJECTED TO BENDING. |
CEMENT IN BAG 40kg (9) / 50kg (7). SAND cu.m (0.5). GRAVEL cu.m (1.0). |
|
|
CLASS B |
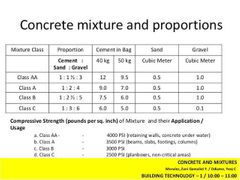
(1 : 2 1/2 : 5). NOT REINFORCED BY BENDING STRESS. |
CEMENT IN BAG 40kg (7.5) / 50kg (6). SAND cu.m (0.5). GRAVEL cu.m (1.0). |
|
|
CLASS C |
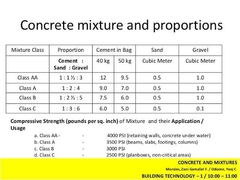
(1 : 3 : 6). FOOTING. |
CEMENT IN BAG 40kg (6) / 50kg (5). SAND cu.m (0.5). GRAVEL cu.m (1.0). |
|
|
CLASS D |
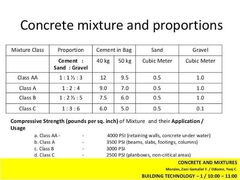
(1 : 4). WALLS |
|
|
|
CLASS E |
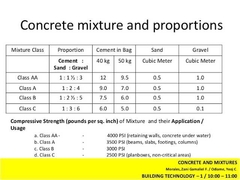
(1 : 2). |
|
|
|
PROPORTION OF CONCRETE |

6% AIR, 11% PORTLAND CEMENT, 41% GRAVEL ( COARSE AGGREGATE ), 26% SAND ( FINE AGGREGATE ), 16% WATER. |
|
|
|
RECOMMENDED CONCRETE MIX PROPORTIONS |

CEMENT CONTENT: (10% - 15%). AGGREGATES AND PEDDLES: ( 60% - 75% ). WATER ( 15% - 20% ). ENTRAINED AIR: ( 5% - 8% ). |
|
|
|
ADHESIVE |

also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non metallic substance applied to one surface, or both surfaces, of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation. |
|
|
|
SUPER GLUE |

a very strong quick-setting adhesive, based on cyanoacrylates or similar polymers. Used on Smooth surfaces, but most standard cyanoacrylate adhesives do not bond well with smooth glass. |
|
|
|
PVA GLUE |

Poly is an aliphatic rubbery synthetic polymer with the formula ₙ. uses and properties including sealing timber, sealing plaster, waterproofing plaster, render and mortar and as a wood glue for DIY and joinery. in its simplest form, a glue for sticking pieces of paper together. |
|
|
|
EPOXY RESIN |

any of a class of adhesives, plastics, or other materials that are polymers of epoxides. used as a secondary adhesive to reinforce the wood glue, used to laminate plywood with fiberglass, Used for coating bar tops and other frequently wet wooden surfaces. |
|
|
|
TILE ADHESIVE |

Use for floor and wall bonding of all types of ceramic tiles, mosaic and decorative bricks on cementitious renders, cementitious screeds and concrete. |
|
|
|
FILLER ADHESIVE |

It is used in an adhesive or sealant formulation, it is typically meant to take up space. |
|
|
|
WOOD ADHESIVE |

is an adhesive used to tightly bond pieces of wood together. |
|
|
|
SYNTHETIC |

made by chemical synthesis, especially to imitate a natural product. |
|
|
|
CERAMIC |

made of clay and hardened by heat. |
|
|
|
TILE GROUT |

is a dense fluid which is used to fill gaps or used as reinforcement in existing structures. It is generally a mixture of water, cement, and sand. |
|
|
|
SEALANTS |

material used for sealing something so as to make it airtight or watertight. |
|
|
|
SILICONE SEALANTS |

A flexible and waterproof substance normally used as a sealant for sealing joins around baths, sinks or other plumbing fixtures. It can withstand very high temperatures, making it ideal for applications that suffer high heat exposure. |
|
|
|
EPOXY |

Contains an artificial substance which sets hard when it is heated or when pressure is applied to it. |
|
|
|
ELASTIC SEALANT |

A sealant made of a flexible material in a plastic state during forming or application. A common elastometric sealant, polysulfide, is a high - polysulfide polymer or rubber. |
|
|
|
THERMOPLASTIC SEALANT |

Sealants that are soft when they are heated and hard when cooled. |
|
|
|
BUTYL SEALANT |

Achieve durable, long - lasting seals between all types of masonry, steel, glass and other common construction materials. |
|
|
|
BITUMINOUS SEALANT |

Ideal for sealing leaks and making repairs, even on wet surfaces. |
|

