![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
Semipermeable outer boundary of the cell's protoplasm that helps regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
If covered with ribosomes, this organelle is involved in the synthesis, secretion, or storage of proteins. If few or no ribosomes are present, it is involved with lipid secretion. |
Endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Contains the cell's generic material and is vital to the regulation of all cell functions |
Nucleus |
|
|
Primarily serves as a storage space for cell sap and dissolved substances, it can also aid in the recycling of cell materials and breakdown of organelles. |
Vacuole |
|
|
Composed of microtubules and microfilaments, facilitates movement within the cell |
Cytoskeleton |
|
|
Morphology varies based on what kind of is (e.g. chloroplast, chromoplast, leucoplast), responsibility is the same-manufacture and store carbohydrates |
Plastid |
|
|
Small, spherical organelles contain enzyme that can perform specialized functions, like convert days to carbohydrates |
Microbodies |
|
|
Tiny bodies that are the does of protein synthesis, or the lining of amino acids together into chains that will eventually form large, complex protein molecules |
Ribosomes |
|
|
Can modify and/or assemble substances and then package them for transport to locations inside and outside the cell |
Dictyosome |
|
|
Called the"powerhouse of the cell" where energy is released from organic molecules through the process of cellular respiration |
Mitochondrion |
|
|
Increases girth of roots and stems as they create new tissue |
Lateral meristems |
|
|
Two main types of lateral meristems |
Vascular cambium and cork cambium |
|
|
Produces secondary xylem and phloem |
Vascular cambium |
|
|
Produces outer bark |
Cork cambium |
|
|
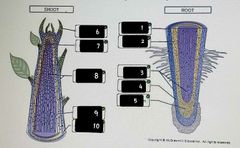
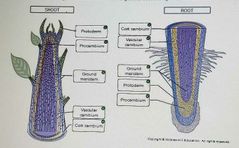
Located at or near the tip of the plant shoots and roots. Exhibit primary growth (length) |
Apical meristems |
|
|
Three types of primary meristems |
Protoderm (epidermis), procambium (primary xylem), ground meristem (all other primary tissues) |
|
|
Unique to grasses. Located at nodes, add to stem length |
Intercalary meristems |
|
|
|
|
|
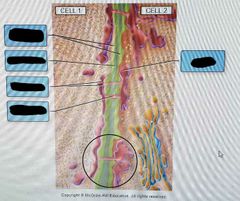
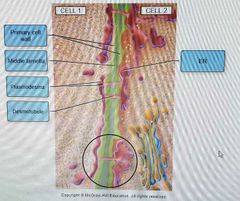
Simple tissues |
Made up of 1 cell type, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma |
|
|
Complex tissue |
Made up of two or more cell types, xylem, phloem, epidermis, periderm |
|
|
Root Cap |
Area that perceives perceives gravity and protects the root tip from damage by soil. Made up of parenchyma cells. |
|
|
Region of Cell Division |
Area of actively dividing cells (produces the root cap). Made up of apical meristem. |
|
|
Region of Elongation. |
Area where cells grow in width and length. Vacuoles occupy over 90% of its cells' volume. |
|
|
Region of Maturation |
Area where cells mature and differentiate into different types. Site of numerous, hairlike protuberances called root hairs. |
|
|
Aerial Roots |
Appear in many forms (velamen roots of orchids, prop roots of corn), and serve a variety of purposes. |
|
|
Parasitic Roots |
Some chlorophyll-lacking plants possess these roots so that they can steal food from other plants. (they penetrate another plant) |
|
|
Water Storage roots |
Common in Cucurbitaceae (pumpkin) species growing in arid regions, these roots store water for later use. |
|
|
Mycorrhizae |
"Fungus-roots" or mutualistic relationship between fungi and plant roots. |
|
|
Contractile Roots |
Found in plants like lilies and dandelions, these roots pull plants deeper into soil. |
|
|
Food-Storage Roots |
Found in plants like sweet potatoes, these roots store large amounts of carbohydrates (e.g. starch) |
|
|
Pneumatophores |
Unique to some swamp plants, these spongy roots increase gas exchange between the atmosphere and the water-submerged roots they are connected to. |
|
|
Buttress Roots |
These roots provide increased stability to tropical trees growing in shallow soil. |
|
|
Propagative Roots |
These roots are found at the base of aerial stems that developed. (adventitious buds) id. cherries,apples, pears. "suckers" can be separated. |

