![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structures comprise the brainstem? What is the overall function of the brainstem?
|
Brainstem: contains lots of nerve tracts for essential functions (respiration, heartbeat)
Made up of: Medulla Pons Midbrain Nuclei for cranial nerves |
|
|
What is a nucleus?
|
Collection of neuron cell bodies in CNS; similar to ganglia
|
|
|
What is a nerve tract?
|
Bundles of nerves in CNS; connect SC to brain
|
|
|
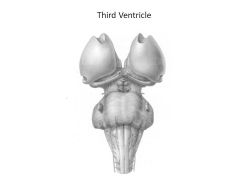
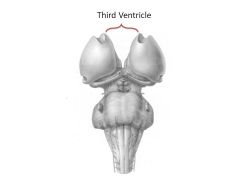
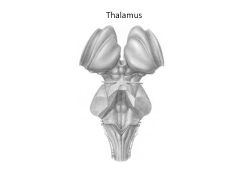
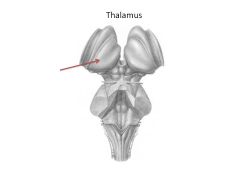
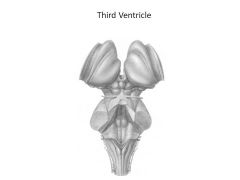
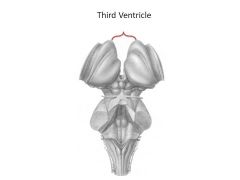
What structures comprise the diencephalon?
|
Thalamic nuclei:
Hypothalamus Thalamus Epithalamus |
|
|
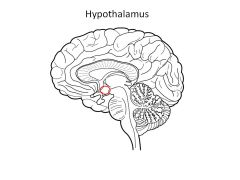
Function of hypothalamus
|
master control for ANS and endocrine
|
|
|
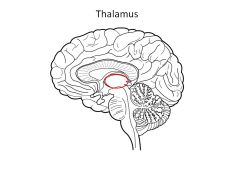
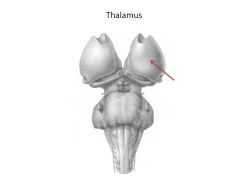
Function of thalamus
|
filter and relay all sensory input (except smell)
|
|
|
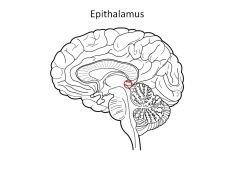
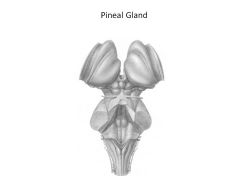
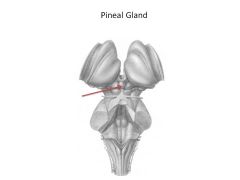
Function of epithalamus
|
Comprised of:
Pineal gland--releases melatonin; regulates circadian rhythms Habenular Nucleus: visceral/emotional response to odors |
|
|
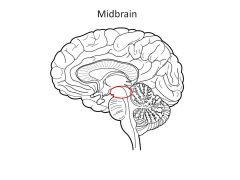
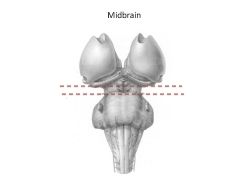
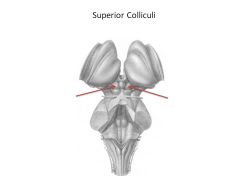
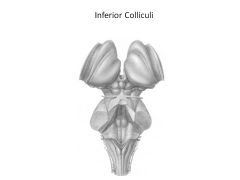
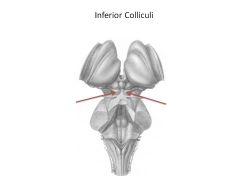
Function of midbrain
Components? |
Subconscious control of voluntary motor actions (substantia nigra)
Auditory and visual reflexes, e.g., looking at something when you hear it, following something with your eye (superior and inferior colliculi) |
|
|
How does PD arise? What does it result in and why?
|
lack of DA production in Substantia Nigra; patients have trouble initiating movement; difficult to overcome postural muscles, because DA allows inhibition of postural muscles
|
|
|
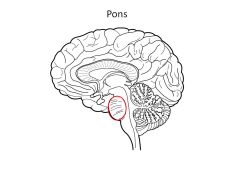
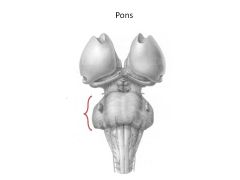
Function of Pons
|
mostly nerve tracts; connections to cerebellum
Contains a RESPIRATORY CENTER (works with medulla) |
|
|
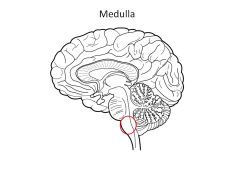
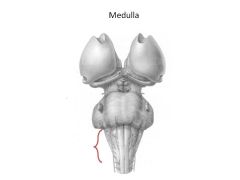
What is the function of the medulla?
|
Essential functions:
Cardiac (heart rate) Respiratory (resp rate) Vasomotor nuclei (centers)-->output to smoth muscle of BV's to moderate BP Reflex centers for salivation, swallowing, coughing, gagging, vomiting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
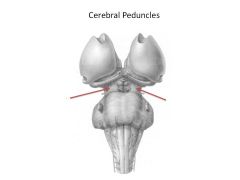
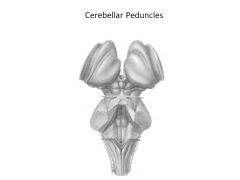
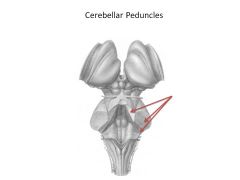
What is a peduncle? Give 2 examples.
|
Peduncle = nerve tract connections to a structure; ex: Cerebral peduncles, cerebellar peduncles
|
|
|
What are the superior and inferior colliculi collectively known as?
|
Corpora quadrigenema
|
|
|
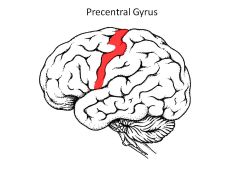
Where is the primary motor cortex located? Role?
|
Primary Motor Cortex is in Precentral Gyrus
Contains "upper MN's" that simulate "lower MN's" of spinal cord |
|
|
What distinguishes the higher centers of the brain from the lower centers?
What regions of the brain qualify as higher centers? |
Higher centers have extra layer of gray matter
Higher centers composed of CEREBRUM and CEREBELLUM |
|
|
Central Sulcus AKA?
|
Rolandic Fissure
|
|
|
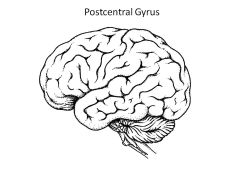
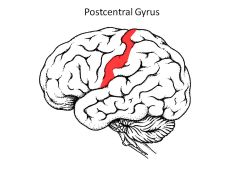
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex located? Role?
|
Primary Somatosensory Cortex is in postcentral gyrus
Receives sensory information from thalamus and determines type of pain/sensation |
|
|
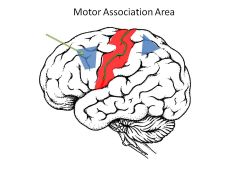
Function of motor association area?
|
Intermediate planning
|
|
|
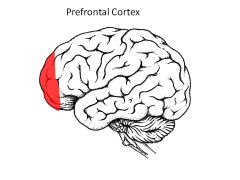
What is the function of the prefrontal cortex?
|
Judgment, forethought, long-term planning, motivation
|
|
|
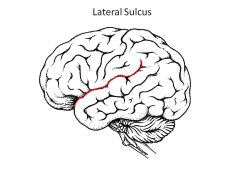
Lateral Sulcus AKA?
|
Sylvian Fissure
|
|
|
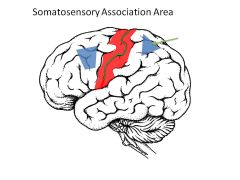
What is the function of the somatosensory association area?
|
Compares stimuli to things you've felt before to determine what sensation is
|
|
|
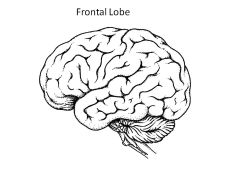
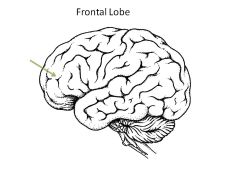
Role of Frontal Lobe?
|
motor, personality, judgment
|
|
|
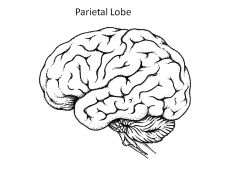
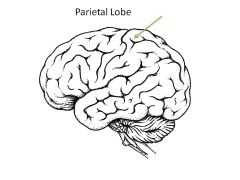
Role of Parietal Lobe?
|
Somatosensory (sensations you're aware of)
|
|
|
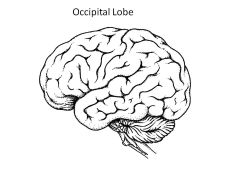
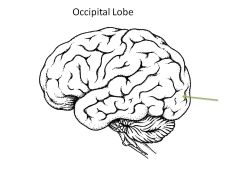
Role of occipital lobe?
|
Vision
|
|
|
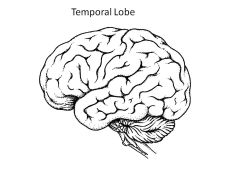
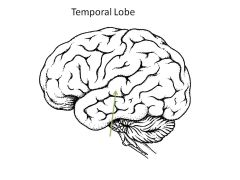
Role of temporal lobe?
|
Hearing
|
|
|
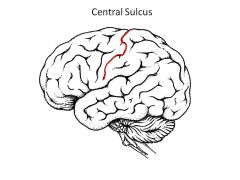
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

