![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Beginning with the neural plate, describe the formation of the dorsal hollow nerve tube (neurulation).
|
Thickening of the nueral plate (ECTODERM) into the neural fold
Accomplished by notochord releasing chemical messengers to INDUCE formation of neural tube Thickening of neural plate forms neural folds Neural folds then fuse to create neural tube (hollow) |
|
|
In formation of the spinal cord, what step occurs after formation of the neural tube?
|
Single neural tube layer divides to form multiple (PSEUDOSTRATIFIED) layers
|
|
|
What becomes of the notochord?
|
Becomes vertebral bodies
|
|
|
What is the role of the neuroepithelium?
|
Neuroepithelium AKA VENTRICULAR LAYER serves as germinal cells for entire CNS
|
|
|
What is the difference between gray and white matter?
|
Gray matter: Unmyelinated cell bodies
White matter: Myalinated axons |
|
|
Dorsal horn: neuron/info type, what forms it
|
Sensory information to interneurons
ALAR plate |
|
|
Lateral Horn: neuron/info type
|
Preganglionic sympathetic MN's
|
|
|
Ventral Horn: neuron/info type, what forms it
|
Somatic MN's: Basal plate
|
|
|
Mantle Zone vs Marginal Zone
|
Made up of neuroblast cell bodies to become gray matter; neuroblast cells are globe-shaped and most peripheral, will go on to form neurons of CNS; will dx/dy into neuroepithelium
Marginal Zone goes on to form white matter |
|
|
What does the spinal nerve split into?
|
Dorsal Ramus (muscles and skin) and Ventral Ramus (body wall, limbs)
|
|
|
What do oligodendrocytes form from?
|
Ventricular layer (CNS)
|
|
|
What do Schwann cells form from?
|
NCC, along with any neuron with soma in PNS
|
|
|
What are the DR and DRG formed from?
|
NCC
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
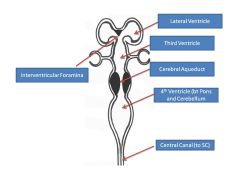
How many primary vesicles are there? Names and order (cranial to ventral)? What structure do they form from?
What does each vesicle go on to form? |
3 Primary Vesicles form from dorsal hollow nerve tube:
Cranial-->Ventral: 1) Prosencephalon (Forebrain) 2) Mesencephalon (Midbrain) 3) Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain and 2º vesicles) |
|
|
Name the secondary vesicles. Provide their numbering. What does each form?
|
Forebrtain:
1A) Telencephalon: cerebrum, basal ganglia; grows to cover structures deep to it (it's the cerebrum) 1B) Diencephalon: thalamic nuclei Midbrain: 2) Mesencephalon: midbrain Hindbrain: 3A) Metencephalon: cerebellulm, pons 3B) Myencephalon: medulla |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|

