![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an Antibiotic? |
A medicine that inhibits the growth of or destroys microorganisms. |
|
|
Explain how bacteria can develop resistance to an antibiotic. |
Through natural selection. |
|
|
What are the four ways disease can be spread? |
Airborne- dust anddroplets in air, coughing and sneezing. Common vehicle- through water Contact- touching skin to skin Vector borne- through saliva or eg. mosquito |
|
|
what are thetypes of micro-organisms that can cause disease. |
Fungi, bacteria, protozoa, virus |
|
|
Describe 4 ways our body prevents disease from entering the blood stream. |
saliva, mucous, skin, tears |
|
|
Explain how vaccination prevents the onset of a disease. |
The administration of antigenic material to stimulate an individual's immune system to develop adaptive immunity to a pathogen.
|
|
|
State 3 ways disease can spread |
Air borne Contact Water borne |
|
|
Draw a labelled diagram of a virus particle. |
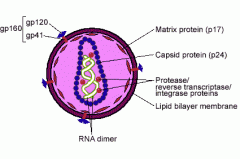
|
|
|
Describe the work of B cells. |
Produce antibodies Antibodies can bind to antigens on the pathogens surface to either make the pathogen harmless, attract phagocytes. Allow quick response to the same infection in the future
|
|
|
Describe the work of T cells |
Eliminate infected body cells These are the deadliest of all immune cells |
|
|
Describe the work of an Antigen. |
A toxin or other foreign substance which induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies |
|
|
Be able to write a Letter to the Editor inresponse to an article on public health |
Attention, address, city, state, postal code, dear editor (state your reason for writing), state your case, include a call to action, end with a statement to support your case. |
|
|
Understandwhy the spread of emerging diseases can occur so rapidly in today’s world (e.g.densely populated cities and increased global travel) |
Human population growth, technological advances, and changing social behaviors lead to the selection of new microbial pathogens. |
|
|
Know that some diseases can be transmitted byvector. |
|
|
|
Know whatvaccinations are and how they work |
the application of small doses used to provide immunity against one or several diseases. |
|
|
describe the first line of defense. |
Saliva, Tears, skin, mucous linings, stomach acid. |
|
|
describe the second line of defense. |
Pathogen gets in the blood stream the ingestion of invading organisms by certain types of white blood cells( called phagocytes) The white blood cells are the most important part of our immune system. There are no other ways that our body's immune system fights off infection Inflammatory response; blood flow is increased to infected areas Histamine release; increase blood flow. |
|
|
describe the third line of defense. |
Neutrophils- Short life span (2-3 days). Can destroy up to 25 bacteria before death Macrophages Bigger tougher and stronger than neutrophils Longer living Can destroy up to 100 bacteria before death. |
|
|
what is the link between the second and third lone of defense. |
The phagocyte takes the antigen to the helper T cell. |
|
|
Know whatan antibody is and how they help to eliminate pathogens from the body. |
Used by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the harmful agent, called an antigen, via the variable region. |
|
|
Know whatan antigen is and how it helps to stimulate an immune response. |
An antigen is any substance that causes your immune system to produce antibodies against it. |
|
|
Know thecomponents (cells) of the immune system and how they work together to overcomeinvasion by pathogens. |
Tonsils, lymph nodes and vessels, bone marrow, spleen, thymus |
|
|
Be able to assess the validity and reliabliity of anexperimental investigation minor. |
validity- how well does the experiment test the question at hand. reliability- the ability of your results to be repeatable. |
|
|
Know thesources of emerging diseases. |
Newly emerging- diseases that arerecognized in the human host for the first time. Reemerging- diseases that historicallyhave infected humans, but continue to appear. |
|
|
Define Antiseptics |
Antiseptics are something you apply to your skinif you have a cut or graze and it will repair it. |
|
|
Define disinfectants. |
A disinfectant is something you apply to solidsurfaces to clean them. |

