![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Photosynthesis |
A chemical reaction which occurs in every green plant, produces food in the the form of glucose so the plant can grow |
|
|
Photosynthesis word equation |
Carbon Dioxide + Water --> Glucose + Oxygen |
|
|
Photosynthesis Symbol Equation |
6 CO2 + 6 H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 |
|
|
What 4 things are needed for photosynthesis |
Sunlight Chlorophyll Water Carbon Dioxide |
|
|
Why is sunlight needed? |
It is a source of energy and absorbed by chlorophyll |
|
|
How is water taken? |
Travels up from the roots |
|
|
How is carbon dioxide taken? |
Diffuses in through the stomata into spaces between spongy mesophyll in leaves. |
|
|
Leaf Diagram |

|
|
|
Example of a leaf mutation |
Variagated Leaf - chlorophyll only in some parts |
|
|
Bits with Chlorophyll contain what? |
starch and is needed so photosynthesis can occur |
|
|
What happens to glucose after it has been synthesised? |
Soluble Glucose is converted into Insoluble starch Some starch is then stored in leaves, bulbs and tuber (for winter) Rest is used immediately for respiration |
|
|
Starch |
Chain of Glucose Molecules |
|
|
Why Insoluble Starch? |
If soluble glucose --> affects water concentration in cells Dont move away from storage areas |
|
|
5 uses of glucose from phorosynthesis |
Respiration Fats and Oils Amino Acids Insoluble Starch Cellulose |
|
|
Respiration (use of glucose) |
Needed to release energy for chemical reactions |
|
|
Fats and Oils ( use of glucose) |
Production of fats and oils for storage |
|
|
Amino Acids (use of glucose) |
Glucose combines with nitrates to make proteins and amino acids for growth |
|
|
Insoluble starch (use of glucose) |
Producing insoluble starch in leaves and storage organs for later use |
|
|
Cellulose (use of glucose) |
Cellulose needed for structural growth, make new cell walls and increase biomass |
|
|
Energy and Photosynthesis |
Energy used to power the reaction and breaks apart chemical bonds Extra energy stored in the bonds of the product |
|
|
Where is the energy? (Reactant and Product) |
Little Energy - in reactant
Greater Energy - in product |
|
|
Is photosynthesis exothermic or endothermic? |
Photosynthesis is endothermic because it takes in light energy |
|
|
4 limiting factors of photosynthesis |
Light Intensity Concentration of Carbon Dioxide Temperature Availability of Chlorophyll |
|
|
Light intensity graph |
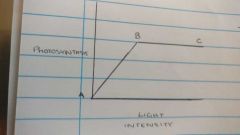
|
|
|
Light intensity relationship |
Increase in light means increase in rate of photosynthesis (increase till optimum then no effect |
|
|
Carbon dioxide relationship |
Increase in CO2 increase in rate of photosynthesis |
|
|
CO2 Graph |
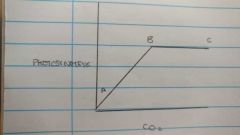
|
|
|
Temperature Relationship |
Varies in different countries (adaptation) unless optimum it is the limiting factor |
|
|
Temperature Graph |
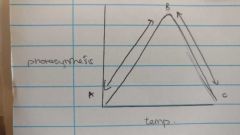
|
|
|
How do farmers maximise growth in a green house? |
Use paraffin lamps which is more light and produce more CO2 when burning and heat |

