![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is biology?
|
The study of life
|
|
|
What is the scientific method
|
State the problem
Gather information Form a hypothesis Perform Experiment Analyze data Draw conclusions Revise and Repeat -------------------------- answers may vary |
|
|
Define control group
|
A group that does not change in an experiment. They are used to compare to the experimental group.
|
|
|
Define Experimental group
|
A group in an experiment that changes
|
|
|
What is an atom?
|
The smallest building block of life
|
|
|
What are the four main types of carbon compounds?
|
Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbohydrates
|
|
|
what is a Chemical Compound?
|
A substance formed from two or more elements
|
|
|
Define molecule
|
two or more atoms bonded together being the smallest unit of a Chemical compound
|
|
|
Carbon has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic mass of 12. What does a model of a carbon look like?
|

|
|
|
what is an Ionic bond?
|
a magnetic attraction between two atoms
|
|
|
What is a covalent bond?
|
When two or more atoms share electrons
|
|
|
What is a hydrogen bond?
|
an intermolecular attraction between the hydrogen of on molecule and another atom of another molecule
|
|
|
What does a PH scale look like?
|
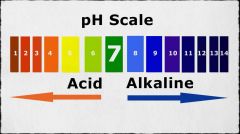
|
|
|
What elements are found in proteins, carbohydrates and lipids?
|
hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, oxygen
|
|
|
what are the monomers of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
|
protein- amino acid
lipids- fatty acids and glycerol carbohydrates- glucose nucleic acid- nucleotides |
|
|
Who devised the cell theory
|
schleiden schwann
|
|
|
who first used a simple microscope?
|
vahn leeywenhook
|

