![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
187 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What macromolecules are sugars and starches? |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
What are the 3 types of carbohydrates? |
Mono Di Poly |
|
|
What are the types of carbohydrates based on? |
The number of sugar units |
|
|
Simple sugars are what type of carb? |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
What type of monosaccharide is the most common? |
Glucose |
|
|
What type of form do monosaccharides take? |
Ring or chain |
|
|
Why is glucose important? |
Metabolism |
|
|
What type of sugar is found in milk? |
Galactose |
|
|
What does tri in triose mean? |
It is a 3 carbon sugar |
|
|
What are 2 important pentose sugars? |
Ribose Deoxyribose |
|
|
Deoxyribose is important in what molecule? |
DNA |
|
|
What important sugar is in RNA? |
Ribose |
|
|
What is a disaccharide? |
2 monosaccharides joined together |
|
|
What are the 3 types of starch? |
Amylose Amylopectin Glycogen |
|
|
Which 2 starches are branched chains? |
Glycogen and amylopectin |
|
|
What starch is nonbranching? |
Amylose |
|
|
What 2 starches are found in plants? |
Amylose and amylopectin |
|
|
What starch is found in animals? |
Glycogen |
|
|
What is important about polysaccharides? |
They form important structural components in plants and animals |
|
|
What is the main component of the cell wall in plants? |
Cellulose |
|
|
Why is cellulose a good structural component? |
It is insoluble and tough to digest |
|
|
What is important in the structure of outer coverings of insects, crabs, and lobsters? |
Chitin |
|
|
Chitin doesn't include what subunit? |
Glucose |
|
|
The link between 2 monosaccharides that forms a disaccharide is formed during what? |
Dehydration synthesis |
|
|
What is the main nonpolar component of cells? |
Lipids |
|
|
What is the main function of lipids? |
Energy storage and cell membrane structure |
|
|
What happens during dehydration synthesis? |
A molecule of H2O is removed |
|
|
What is the link called between 2 monosaccharides when they become a disaccharide? |
Dehydration linkage |
|
|
What are 3 examples of disaccharides? |
Maltose Sucrose Lactose |
|
|
2 glucose make what type of disaccharide? |
Maltose |
|
|
What 2 monosaccharides compose sucrose? |
Glucose and fructose |
|
|
What 2 monosaccharides make up lactose? |
Glucose and galactose |
|
|
What type of form do polysaccharides take? |
Long chains |
|
|
What is starch? |
A polysaccharide made of glucose |
|
|
Why are all lipids insoluble in water? |
They repel water |
|
|
Why do lipids serve as components of the cell membrane? |
They repel water and are insoluble |
|
|
What are 3 types of lipids? |
Phospholipids Fats Steroids |
|
|
What is the function of phospholipids? |
They form the cell membrane |
|
|
What is the function of steroids? |
Signaling, tells target cells what to do |
|
|
What is the composition of fat? |
A glycerol head and 3 fatty acid chain tails |
|
|
What is the composition of phospholipids? |
Glycerol, phosphate group, 2 fatty acid chains |
|
|
What is the composition of steroids? |
4 hydrocarbon rings |
|
|
Are lipids polymers? |
No |
|
|
Are lipids macromolecules? |
No |
|
|
What is the formation of fatty acids? |
Long hydrocarbon chains with an acid group at the end |
|
|
What is glycerol composed of? |
3 carbon carbohydrate 3 alcohol groups (-OH) |
|
|
What is an ester linkage? |
An oxygen atom bonded to 2 carbon atoms and linking 2 other molecules |
|
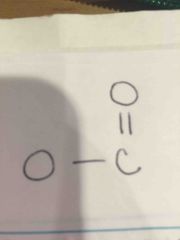
What type of link is shown here? |
Ester linkage |
|
|
What type of fats have double bonds? |
Unsaturated |
|
|
What type of fat is oil? |
Unsaturated |
|
|
What type of fat has only single bonds? |
Saturated fat |
|
|
What type of fat is solid? |
Saturated |
|
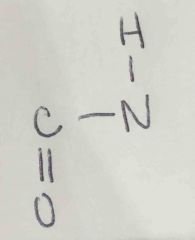
What type of bond is this? |
Peptide |
|
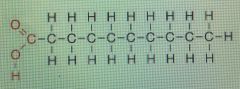
What is this picture showing? |
A saturated fatty acid chain |
|
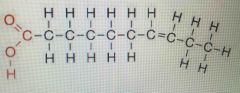
What is this picture showing? |
Unsaturated fatty acid chain |
|

What is this picture showing? |
A triacylglycerol fat molecule |
|
|
Are phospholipids polar or nonpolar? |
Highly polar |
|
|
What does the sandwich structure refer to? |
The phospholipid bilayer as the cell membrane |
|
|
What is this the basic shape of? |
Steroid |
|
|
What is cholesterol? |
A type of steroid |
|
|
Along with phospholipids, what is another essential component of the cell membrane? |
Cholesterol |
|
|
What is the relationship between yogurt and cholesterol? |
Yogurt absorbs cholesterol which helps us digest it |
|
|
What are all lipids? |
Hydrophobic |
|
|
What is this most important type of macromolecule? |
Protein |
|
|
What is the most versatile macromolecule? |
Protein |
|
|
Fatty acid chains with many carbon carbon double bonds are said to be what? |
Polyunsaturated |
|
|
What configuration does unsaturated fat prefer? |
Cis |
|
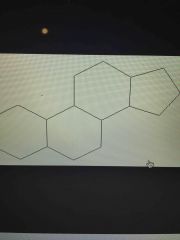
What is this the basic shape of? |
Steroid |
|
|
What is the energy storage for carbs? |
4 kcal/g |
|
|
What is the energy storage for proteins? |
4 kcal/g |
|
|
What is the energy storage for fats? |
9 kcal/g |
|
|
How much harder is it to give up fat than other molecules? |
2 times |
|
|
What fat is the main component of the cell membrane? |
Phospholipid |
|
|
What type of link is found between phospholipids? |
Ester |
|
|
What is the charge of phospholipids? |
Negative |
|
|
Enzymes are what type of molecule? |
Protein |
|
|
What makes the amino acid unique to others? |
The side chain |
|
|
What type of bond is a peptide bond? |
Covalent |
|
|
Why are proteins called polypeptides? |
They are made of long chains of amino acids |
|
|
What holds amino acids together in proteins? |
Peptide bonds |
|
|
What protein is found in hair, nails, and skin? |
Keratin |
|
|
Other than keratin, what type of protein is found in the skin? |
Collagen |
|
|
What type of protein is found in the eye? |
Crystallin |
|
|
What is the structure of an amino acid? |
Amino group and carboxyl group |
|
|
About how many amino acids are naturally occurring? |
20 |
|
|
What are the 5 parts of an amino acid? |
Central carbon (alpha carbon) Hydrogen Amino group Carboxyl group Side chain |
|
|
What do we categorize amino acids by? |
The side chain |
|
|
How is a peptide bond formed? |
dehydration synthesis |
|
|
What is the exact sequence of amino acids called? |
primary structure |
|
|
What determines the structure of an amino acid in a chain? |
primary structure |
|
|
What is at the end of an amino acid chain? |
carboxyl group |
|
|
The folding of an amino acid chain refers to what? |
the secondary structure |
|
|
What are the 2 types of folding associated with the secondary structure of an amino acid chain? |
alpha helix or beta sheet |
|
|
Of the 2 folding types in an amino acid chain, which is more flexible? |
helix |
|
|
What type of amino acid chain folding do you find in enzymes? |
helix |
|
|
The pleated sheet folding in an animo acid chain is primarily used for what? |
structure |
|
|
What are lipids mostly made of? |
Hydrocarbons |
|
|
What type of linkage holds together the hydrophilic shell of a tertiary structure? |
Hydrogen bonds why |
|
|
Why isn't the quaternary structure present in all proteins? |
There has to be more than 1 chain present |
|
|
What are the 4 types of bonds present in the tertiary structure? |
Disulfide bond Ionic bond Hydrogen bond Van der waals force |
|
|
What is the function of nucleic acids? |
Records genetic info |
|
|
Are nucleic acids polymers? |
Yes |
|
|
What makes up a nucleic acid? |
Monosaccharide sugar Phosphate group Nitrogenous base |
|
|
What are the 2 types of nucleic acid? |
DNA and RNAWHT |
|
|
What are the monomers of nucleic acids? |
Nucleotides |
|
|
How are nucleotides linked together? |
What ar |
|
|
What are the four bases of DNA? |
TAGC |
|
|
What is the function of enzymes? |
Catalyze all metabolic functions, Speed up reaction time |
|
|
What are the four bases of RNA? |
TGUCWHT |
|
|
What bases pair together in DNA and RNA? |
TA or AU GC |
|
|
What are purines? |
Guanine and adenine in nucleic acids |
|
|
What are pyridmidines? |
Cytosine and thymine or uracil in nucleic acids |
|
|
How is oxygen in the blood transported via protein? |
Carried by hemoglobin |
|
|
How is oxygen in muscles transported via proteins? |
Carried by myoglobin |
|
|
What is another name for the side chain of an amino acid? |
R group |
|
|
What is the tertiary structure of a protein? |
The secondary structure folded into a 3D shape |
|
|
What are the domains of the tertiary structure? |
Hydrophobic and hydrophilic, they alternate |
|
|
What is the tertiary structure core made of? |
Hydrophobic domain |
|
|
What is the shell made of in the tertiary structure? |
Hydrophilic sections |
|
|
What type of linkage holds together the hydrophobic core in the tertiary structure? |
Van der waals force |
|
|
What is the smallest size distinguished by the naked eye? |
1 millimeter |
|
|
What part of the nucleus holds RNA? |
Nucleolus |
|
|
What is the cloudy material outside the nucleolus? |
Chromatin |
|
|
When chromatin forms into shapes what is it called? |
Chromosome |
|
|
What is the function of ribosomes? |
Protein synthesis |
|
|
What are the 2 subunits of ribosomes? |
RNA and protein |
|
|
What is the function of the large part of ribosomes? |
Links amino acids |
|
|
What is the function of the small part of ribosomes? |
Reads RNA sequence |
|
|
What are bound ribosomes? |
Ribosomes attached to rough ER |
|
|
What is the function of bound ribosomes? |
Produces ribosomes for export |
|
|
What makes up the endomembrane system 1? |
Both ERs |
|
|
What |
1 micrometer |
|
|
What is the function of rough ER? |
Makes polypeptides to be secreted from cells and makes secretory proteins |
|
|
What is the function of smooth ER? |
Lipid and carb synthesis and detoxification |
|
|
What is the endomembrane system 2? |
Golgi apparatus |
|
|
What receives products from the ER? |
Golgi apparatus |
|
|
What is the shipping side of the Golgi apparatus? |
W |
|
|
What is the receiving side of the Golgi apparatus? |
Cis |
|
|
What is the sequence of the ER, Trans, and Cis? |
ER > Cis > Trans |
|
|
What is the function of lysosomes? |
Intracellular digestion |
|
|
What are some things that lysosomes digest? |
Bacteria, food, foreign debris, worn out organelles |
|
|
What do lysosomes hydrolyze? |
Macromolecules |
|
|
What are 2 types of prokaryotic cells? |
Bacteria and Cyanobacteria |
|
|
What is glycoslysation? |
The Golgi apparatus making proteins out of sugar |
|
|
What is a nuclear envelope? |
The double membrane that bounds the nucleus |
|
|
What is the function of nuclear pores? |
Holes that allow larger molecules to pass |
|
|
What is the most prominent structure in eukaryotic cells? |
Nucleus |
|
|
What is the function of nuclear pores? |
Controls what gets in and out |
|
|
What happens to DNA in the nucleus? |
Protected, replicated, and transcripted |
|
|
Since ribosomes are attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus, what does that say! |
Protein production is present |
|
|
What is transported out of nuclear pores? |
RNA |
|
|
What is the function of vacuoles? |
Storage |
|
|
What is the function of chloroplasts? |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Why are chloroplasts considered symbionts? |
It has its own circular DNA and ribosomes |
|
|
Why are the 2 chloroplast membranes transparent? |
To absorb light efficiently for photosynthesis |
|
|
What does the inside of a chloroplast contain? |
Flattened disks called thylakoids and liquid |
|
|
What is the liquid of chloroplasts called? |
Stroma |
|
|
What are stacks of thylakoids called? |
What do |
|
|
What is plasmodesmata? |
Exocellular sticky stuff that connects plant cells |
|
|
What does endosymbiosis refer to? |
Chloroplasts and mitochondria being similar to prokaryotes |
|
|
What are 3 types of cytoskeleton? |
Microtubule Intermediate filament Microfilament |
|
|
What does the cytoskeleton assist in? |
Cell movement |
|
|
What is the function of the large central vacuole? |
Storage and maintains shape |
|
|
Microtubules have a unique role in what? |
What doe |
|
|
What are microtubules compared to? |
Train tracks bc they assist in the movement of vesicles |
|
|
What do microtubules have to do with centrosomes? |
9 Microtubule triplets make up 1 centriole, and 2 centrioles make up a centrosome |
|
|
what is the function of microfilaments? |
They assist in muscle contraction and structure |
|
|
What is the function of intermediate filaments? |
Permanent support |
|
|
What is the extra cellular matrix of animal cells made of? |
Collagen, fibronectin, proteoglycan, and fluid the |
|
|
The extracellular matrix of animals cells is similar to what plant cell feature? |
Plasmodesmata |
|
|
What are the 3 types of animal cell junctions? |
Tight Gap Anchoring |
|
|
What is the function of a tight junction? |
Very close connection, nothing passes through |
|
|
What is the function of an anchoring junction? |
Allows small molecules to go through |
|
|
What is the function of contractile vacuole? |
Removes water from cell to prevent it from bursting, found in protists |
|
|
What is the function of a gap junction? |
Channels between cells, molecules can get through but not too large |
|
|
What are the 3 functions of the cell membrane? |
Communication Keep cell contents together Control of movement in and out of cell |
|
|
About how thick is the phospholipid bilayer? |
7-10 mm thick |
|
|
What type of microscope do you need to view the phospholipid bilayer? |
Electromicroscope |
|
|
Phospholipids are said to be what? |
Amphipathic |
|
|
What does Amphipathic mean? |
Molecule has a polar and non polar side, hydrophobic and hydrophilic sides |
|
|
What is the function of food vacuole? |
Storage |
|
|
What do you get more DNA from your mom than your dad? |
The mitochondria is DNA carrying and is maternally inherited |
|
|
What is the function of the mitochondria? |
Energy production (ATP) |
|
|
What is the shape of DNA found in the mitochondria? |
Circular |
|
|
Why is mitochondria considered a symbiont? |
It has its own DNA |
|
|
What is the inner membrane of mitochondria called? |
Cristae |
|
|
What is the liquid in mitochondria called? |
Matrix |

