![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diagram for feedback loop |
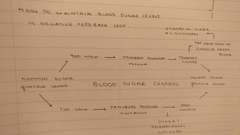
|
|
|
Glucose |
A sugar found in the body (blood sugar), comes from the digestive system or from stored supplies in the liver and major muscles |
|
|
Use of glucose |
Used as a respiratory substrate and used to synthesise other molecules or into glycogen and stored |
|
|
5 Reasons for Glucose |
Cellular Respiration Cell division (mitosis) Muscle Contraction Copying DNA Neurones need energy to carry signals |
|
|
Glycogen |
A branched storage of carbohydrate found in liver and muscles, and can be stored |
|
|
Regulated by two hormones |
Insulin Glucagon |
|
|
Glucagon |
Produced in the pancreas |
|
|
Insulin |
Controls storage of glycogen in the liver Glucose to glycogen |
|
|
Glucagon |
Breaks down glycogen on the liver Glycogen to glucose |
|
|
Glucose or Glycogen |
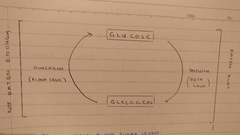
|
|
|
Type 1 Diabetes |
Affects children and young adults Dont produce insulin and cells are destroyed and due to unknown causes. Immune systems attacks w/ antibodies. Blood sugar conc rises to harmful levels Insulin injections to help reduce blood sugar and reduce sugar in diet and exercise regularly |
|
|
Type 2 Diabetes |
Affects older people Insulin receptors change over time and liver and muscle cells dont respond which prevents conversion of glucose into glycogen and conc. remains high Symptoms : feel thirsty, urinate more often and frequently too tired. Exercise, eat healthy and stay not obese |

