![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thermoregulatory Centre Diagram |
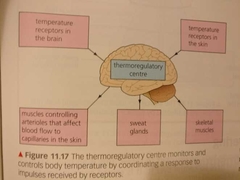
|
|
|
Optimum temp for most of your enzymes |
36.5 and 37.5° |
|
|
How to detect body temp change |
Receptors communicates with centre via electrical impulses sent along your nerves. The centre then coordinates a return towards a normal temp using three mechanisms |
|
|
What controls your body temperature |
Thermoregulatory centre |
|
|
Three mechanisms |
Sweat glands Skeletal muscles Controlling the blood that reaches the surface of your skin |
|
|
Sweating |
Too hot, sweat glands produce sweats. Maximum if several litres per hour. Sweat is mainly water, salts and urea. Sweat evaporates from your skin and transfers heat energy and cools you |
|
|
Shivering |
Too cold - shiver, involuntary movement and have no control. Caused by skeletal muscles quickly contracting and relaxing and generate heat to warm up Use glucose in respiration and you can not shiver for long period of time without becoming tired |
|
|
Vasodilation |
The increase in size of blood vessels to increase the flow of blood to the surface of the skin and therefore increase heat loss. Cools you down when temp is too high |
|
|
Vasoconstriction |
The reduction in size of blood vessels to reduce the flow of blood to the surface of the skin and therefore reduce heat loss Too cold |
|
|
Blushing |
When hot - because of vasodilation |
|
|
Hypothermia |
Below 35°, shivering and mentally confused. Causes organs to fail and is followed by death |
|
|
Hyperthermia |
Above 38.5°, happens during heat stroke and during allergic reactions to drugs. Headaches, nausea and vomiting are symptoms. Organ failure and death |

