![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
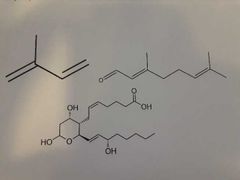
|
Thromboxanes |
|
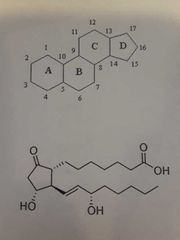
|
Prostaglandins |
|
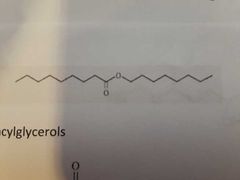
|
Waxes |
|
|
Contains RCOOH |
Fatty acids |
|
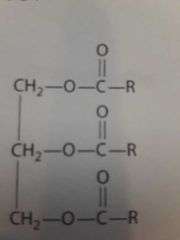
|
Triacylglycerol |
|

|
Phosphoacylglycerols |
|

|
Ceramide |
|
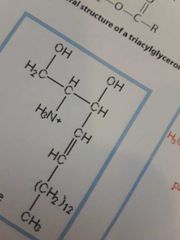
|
Sphingosine |
|

|
Sphingomyelin |
|

|
Cerebroside (steroid) |
|
|
What is/are the negative effects of Hexokinase of glycolysis? |
G-6-P |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of PFK1 of glycolysis? |
Positive: AMP, F-2,6-BP Negative: ATP, citrate |
|
|
What is the negative effector of enolase of glycolysis? |
F- |
|
|
What are the negative and positive effectors of Pyruvate Kinase of glycolysis? |
Positive: AMP, F-1,6-BP Negative: ATP ACoA |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of PDHC E2 of the pre TCA cycle? |
Positive: CoA Negative: ACoA |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of PDHC E3 of the pre TCA cycle? |
Positive: NAD+ Negative: NADH |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of citrate synthase? |
Negative: ATP, NADH, succinyl, CoA, citrate Positive: ADP |
|
|
What are the negative effectors of aconitase of the tca cycle |
Fluotoacetate/citrate |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of iso citrate dehydrogenase in the tca cycle |
Positive: ADP, Ca++, NAD+ Negative: ATP, NADH |
|
|
What are the positive and negative effectors of alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex of the tca cycle? |
Positive: Ca++ Negative: NADH, succinyl CoA |
|
|
What is the negative effector of succinate dehydrogenase of the tca cycle? |
Malonate |
|
|
T or F: The more unsaturated the fatty acid is, the lower it's melting point? |
True |
|
|
What is facilitated diffusion? |
Something that helps a molecule across a membrane. It is a passive process. |
|
|
What is primary active transport? |
Uses energy directly when transferring something across a membrane. |
|
|
What is secondary active transport? |
The molecule is moved by a gradient difference |
|
|
What does uniport mean |
1 thing is taken through |
|
|
What is co transport? |
2 solutes are carried |
|
|
What is symport? Antiport? |
Symport- same direction Antiport- opposite directions |
|
|
Does the malate aspartate shuttle cost any energy to use? |
No it doesn't |
|

Identify protein level structure and type of force or bond responsible for the stabilization |
2o beta sheets H bonding in backbone by carbonyl and amines |
|

Level if protein structure and type of bond responsible for the stabilization |
4o disulfide bridge using hydrophobic interactions |
|

Level of protein structure and bond responsible for the stabilization of the structure |
1o peptide bonds between aas |
|

Level of protein structure and type of bond responsible for the stabilization |
3o dipole dipole |
|

|

|
|

|
Thromboxane |
|

|
Sphingomyelin |
|

|
Fatty acid |
|

|
Steroid |
|

|
Cerebroside |
|

|
Phosphatidyl choline |
|

|
A wax |
|
|
Glycogen phosphorylase degrades glycogen and must be phosphorylated to be active Glycogen synthase synthesizes glycogen and is inactive when phosphorylated. How do insulin and glucagon regulate these |
Glucagon triggers phosphorylation so it increases degradation and decreases synthesis Insulin triggers the activation of phosphatases that remove phosphates turning synthesis on and degradation off, reversing the effect if glucagon |
|
|
Gel filtration separates by what |
Separates by weight. The heavier stuff will come out first |
|
|
How does an anion exchange colum separate out stuff if the pH is 7.4 |
Those with a pI lower than the pH will be filtered out first, than as increasing pH |
|
|
If I is a heterotrimer alpha1 beta 2 (a is 250 kD, b is 120kD) and they are held together by disulfide bridges, draw a picture of the stained SDS page gel that will result if the mixture is run in the presence and absence of a reducing agent |

|

