![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
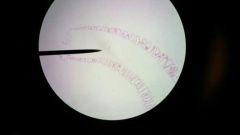
1) phylum? 2) identify: osculum & function 3) identify: ostia & function |

Phylum Porifera
H2o is absorbed thru the ostia
h2o current leaves the sponge through the osculum |
|

Identify these 3 different sponge skeletons |
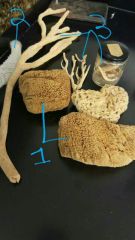
1) spongin 2) spicule silica (lace) 3) spicule calcium carbonate (hard, tough) |
|
|
What is the function of a spongocoel/choanocyte? |
Generates an h2o current across the microvilli, who then filter nutrients through the current
Used by porifera |
|
|
Sponges and Cnidarians: energy obtaining patterns |
chemoheterotrophs |
|
|
Sponges and cnidaria: diploblastic |
Contain 2 cell layers during embryonic development: endoderm, ectoderm |
|
|
Porifera reproduction |
Mostly asexual, some sexual |
|
|
Polyp |
Young cnidarian (ex. Coral) asexual and sessile (fixed in one place) |
|
|
Medusa |
Middle aged cnidaria (ex. Jellyfish) Sexual reproduction Free floating |
|
|
Larval |
Older cnidaria Free-swimming stage |
|
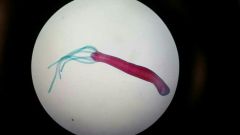
1) Phylum? 2) Class? |
1) cnidaria 2) hydrozoa Alternate between polyp/medusa |
|
|
Cnidodytes |
Associated w/ hydrozoa "Stinging cell" protection mechanism and helps to capture prey |
|
|
Feeding polyp vs reproductive polyp (picture) Phylum? Class? |

Phylum cnidaria Class obelia |
|
|
Class Scyphozoa |
Belong to phylum cnidaria Medusa dominant: True jellyfish |
|
|
Class Anthozoa |
Belong to phylum cnidaria Polyp dominant: Coral, sea anemones Hard exoskeleton of CaCO3 |

