![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitosis & the Cell Cycle |
-new cells produced in meristems -produces genetically identical cells -similar to meiosis |
|
|
Mitosis - What has to happen? |
-genetic material must be replicated and divided -cytoplasmic organelles must be divided |
|
|
Steps of Cell Cycle |
-Interphase -> Mitosis -> Cytokinesis *Interphase -> DNA replicated, cell volume & organelles increase in size & number *Mitosis -> IP MAT *Cytokinesis -> cell wall forms to divide cytoplasm of two daughter cells |
|
|
Important things to know: Cell Cycle |
-site of division -> meristem, many other places hold potential -not dividing = interphase -dividing = passing through cell cycle rapidly |
|
|
Interphase |
-can be divided into stages: G1 ->increase in size/number of organelles, formation of material needed to replicate S -> DNA replication G2 -> formation of materials needed during mitosis |
|
|
Mitosis |
-IP MAT *Interphase (previous) *Prophase *Metaphase *Anaphase *Telophase *interphase & cytokinesis not considered stages of mitosis |
|
|
Beginning Mitosis - Interphase |
*normal cell -nuclear envelope is intact, nucleoli can be seen inside the nucleus, chromosomes are indistinct |
|
|
Stages of Mitosis - Prophase |
*chromosomes visible -nuclear envelope disintegrated, nucleoli beginning to disappear, chromosomes have condensed -- look like a plateful of thick black noodles |
|
|
Stages of Mitosis - Metaphase |
*no nucleus, chromosomes center of cell -mitotic spindle formed and chromosomes lie midway between two poles of spindle |
|
|
Stages of Mitosis - Anaphase |
*chromosomes split, head to ends of cell -sister chromtids separate, begin to move to opposite poles of spindle |
|
|
Stages of Mitosis - Telophase |
*starts to divide, nucleus begins appearing -chromosomes have complete separation, begin to elongate and become thinner |
|
|
Ending Mitosis - Cytokinesis |
*cell wall begins to appear, cells split -cell-plate begins to form, when completely formed, two new daughter cells are result *telophase & cytokinesis often occur simulatneously |
|
|
Cell Cycle Image |
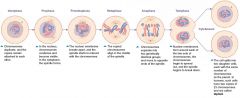
image: http://publications.nigms.nih.gov/insidethecell/images/ch4_phases_allbig.jpg |
|
|
Cell Water Movement |
*diffusion & osmosis account for most of the passive (non-energy requiring) movement of molecules into and out of cells |
|
|
Cell Water Movement - Diffusion |
-movement of molecules from area of higher concentration to lower concentration *move down a concentration gradient *temperature effect -> cool move slowly, warm, more energy, diffusion increases -can occur across cell membrane into or out of cell |
|
|
Cell Water Movement - Osmosis |
-specialized diffusion through selectively permeable membrane -greater water concentration to lesser water concentration *cell membrane -> selectively permeable *solute -> particle dissolved in solution *solvent -> liquid of solution |
|
|
Cell Water Movement - Osmosis (Cont.) |
*hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic -> compare solutions using solute concentrations -hypotonic -> lower solute concentration -hypertonic -> higher solute concentration -isotonic -> same solute concentration |
|
|
Osmosis & Water Potential |
-tendency of water to move by osmosis affected by *amount of solute present *if water under pressure water potential = solute potential + pressure potential |
|
|
Solute Potential |
-effect of solute concentration -as solute added, water concentration less -> water potential declines |
|
|
Pressure Potential |
-pressure exerted on rigid cell wall by water inside -pressure potential occurs in a closed container -pressure raises cell water potential |
|
|
Cellular Energy |
-revolves around carbohydrates & ATP -carbohydrates -> long term energy storage -ATP -> immediate energy source *Respiration converts carbohydrates to CO2 and ATP *Photosynthesis converts CO2 into carbohydrates *using* ATP |
|
|
Respiration Equation |

*produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy |
|
|
Photosynthesis Equation |
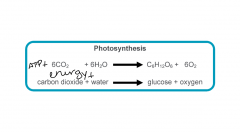
*produces glucose (sugar) and oxygen |
|
|
Mendelian Genetics |
-genes often found on different chromosomes are segregated independently (non-reliant on each other) -dominance vs recessiveness -punnet squares -> RR x rr, RR x Rr, Rr X Rr, etc. |
|
|
Monohybrid Cross |
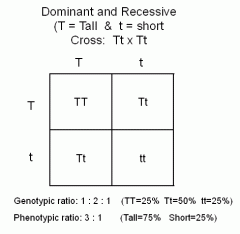
phenotype ratio: 3:1 genotype ratio: 1:2:1 |
|
|
Dihybrid Cross |
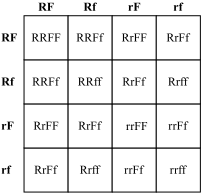
phenotype ratio: 15:1 geneotype ratio: 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 |

