![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Asexual reproduction |
produces offspring genetically identical to the parent |
|
|
Asexual reproduction occurs during |
mitosis |
|
|
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that |
sister chromatids separate during anaphase |
|
|
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is |
a sperm |
|
|
Define genome |
the complete set of an organism's genes and other DNA sequences |
|
|
Quaking aspen can send out underground stems for asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is not as common, but when it does happen, the haploid gametes have 19 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in the cells of the underground stems? |
38 |
|
|
How are sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes different from each other? |
Homologous chromosomes contain the same gene loci but may have different alleles of a particular gene. Sister chromatids are identical copies of each other produced during DNA replication. |
|
|
Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during |
meiosis I |
|
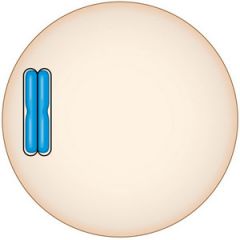
This chromosome has two chromatids, joined at the centromere. What process led to the formation of the two chromatids? |
The two chromatids were formed by duplication of a chromosome. |
|
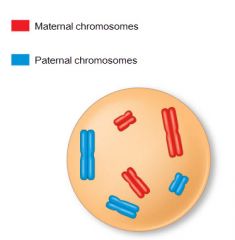
Is the cell diploid or haploid |
Diploid |
|
|
In a plant's sexual life cycle what do gametophytes produce? |
Gametes |
|
|
Diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte). What is this an example of? |
alternation of generations |
|
|
Identify all possible products of meiosis in plant and animal life cycles |
Spores Gametes |
|
|
If a horticulturist breeding gardenias succeeds in having a single plant with a particularly desirable set of traits, which of the following would be her most probable and efficient route to establishing a line of such plants? |
Clone the plant |
|
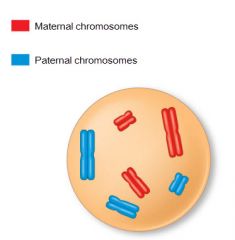
What is the best evidence telling you whether this cell is diploid or haploid? |
The cell is diploid because it contains two sets of chromosomes. |
|
|
What is a karyotype |
organized images of a cells chromosomes |
|
|
What number and types of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell? |
44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes |
|
|
Homologous chromosomes purpose |
carry information for the same traits |
|
|
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be |
2x |
|
|
What is crossing over? |
the exchange of homologous portions of nonsister chromatids |
|
|
Mitosis results in the formation of how many cells; meiosis results in the formation of how many cells |
two diploid cells ... four haploid cells |
|
|
In alternation of generations, what is the diploid stage of a plant that follows fertilization called? |
sporophyte |
|
|
For what purposes might a karyotype be prepared? |
for prenatal screening, to determine if a fetus has the correct number of chromosomes to determine whether a fetus is male or female to detect the possible presence of chromosomal abnormalities such as deletions, inversions, or translocations |
|
|
Meiosis I produces _____ cells, each of which is _____ |
two ... haploid |
|
|
Meiosis II typically produces _____ cells, each of which is _____ |
four ... haploid |
|
What takes place here? |
prophase II |
|
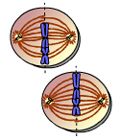
What takes place here? |
anaphase II |
|
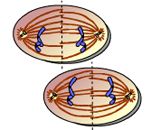
What takes place here? |
telophase II and cytokinesis |
|
|
During _____ sister chromatids separate |
anaphase II |
|

What take place here? |
telophase I and cytokinesis |
|
|
At the end of _____ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids |
telophase I |
|
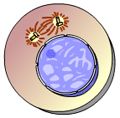
What takes place here? |
prophase I |
|
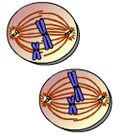
What takes place here? |
metaphase II |
|
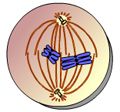
What takes place here? |
metaphase I |
|
|
Synapsis occurs during _____ |
prophase I |
|
|
Homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles during _____ |
anaphase I |
|
|
During _____ chromosomes align single file along the equator of a haploid cell |
metaphase II |
|
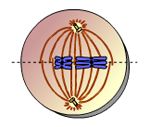
What takes place here? |
metaphase I |
|
|
At the end of _____ and cytokinesis there are four haploid cells |
telophase II |
|
|
During _____ a spindle forms in a haploid cell |
prophase II |
|
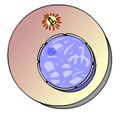
What takes place here? |
interphase |
|
|
Human gametes are produced by |
meiosis |
|
|
Normal human gametes carry _____ chromosomes |
23 |
|
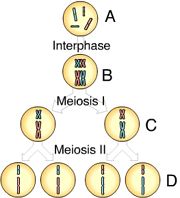
Which of these cells are haploid? |
C and D |
|
|
A diploid organism whose somatic cells each contain 32 chromosomes produces gametes containing _____ chromosomes |
16 |

