![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Most everything is regulated by
|
Isoleucine
|
|
|
What happens in allosteric inhibition?
|
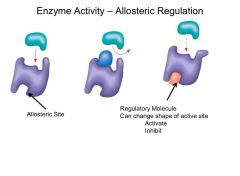
Active site changes shape
---> substrate cannot bind |
|
|
What is an allosteric site?
|
Additional site on enzyme where ONLY a regulatory molecule can bind
(NOT AN ACTIVE SITE) |
|
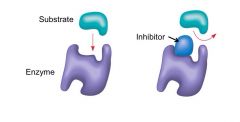
What happens to the substrate when the inhibitor binds to the active site?
|
Substrate cannot bind (competitive inhibition)
|
|
|
What term means the reaction does not occur?
|
Inhibit
|
|
|
Non protein, organic molecules
- often carrier/ transport molecules (vitamins) |
Coenzyme
|
|
|
What 2 factors affect enzyme function?
|
Temperature
pH |
|
|
Non protein enzyme helpers
- usually inorganic (iron) |
Cofactor
|
|
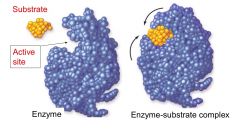
When shape changes to hold substrate?
|
Induced fit
|
|
|
An induced fit where the enzyme changes shape after substrate binds
|
Active site
|
|
|
How do enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions?
|
Hold reactant in position that reaction is most likely to occur
|
|
|
How do enzymes catalyze reactions?
|
Decrease amount of NRG needed, lower course of reaction
|
|
|
Free NRG needed to start a reaction
|
Activation energy
|
|
|
Chemical reaction
Anabolic (small to big) Needs NRG NON-SPONTANEOUS |
Endergonic reaction
|
|
|
Chemical reaction with +🔺G
|
Endergonic
|
|
|
Chemical reaction
Catabolic (big to small) Gives NRG SPONTANEOUS |
Exergonic (NRG is EXiting)
|
|
|
Chemical reaction with -🔺G
|
Exergonic
|
|
|
Processes with a positive 🔺G are
|
Non spontaneous
|
|
|
Processes with a negative 🔺G are
|
Spontaneous
|
|
|
What does 🔺G stand for?
What is it's formula? |
Gibbs Free Energy
G(products) - G(reactants) |
|
|
This occurs with NRG in a chemical reaction (requires NRG)
|
Non spontaneous processes
|
|
|
This occurs without NRG input and increased entropy... a chemical reaction
|
Spontaneous processes
|
|
|
What is entropy (s)?
|
Disorder/ randomness
|
|
|
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
|
Transformation of NRG increases entropy of the universe
|
|
|
In the first law of thermodynamics:
Energy can _______ Energy cannot______ |
NRG can transfer
NRG cannot be created/ destroyed |
|
|
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
|
Total NRG in the universe is constant
|
|
|
Study of NRG and it's transformations
|
Thermodynamics
|
|
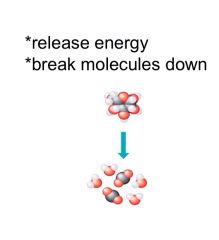
Big to small
|
Catabolic pathways
|
|
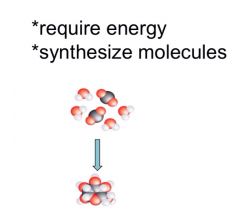
Small to big
|
Anabolic pathways
|
|
|
Proteins that catalyze a reaction
|
Enzyme
|

