![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are genes? |
Units of inheritance that determine the traits passed from 1 generation to the next
|
|
|
What are alleles? |
Variants of a gene Ex: genes that determine pea pod shape |
|
|
What is a genome? |
The entire collection of all genetic material in a microbe |
|
|
2 DNA strands intertwine to form a ______ _____. |
Double Helix * each strand is equal & anti-parallel |
|
|
A always binds to ____ in DNA. C always binds to ____ in DNA.
|
A - T C - G |
|
|
What is Chargaff's Rule? |
%A = %T %C = %G |
|
|
Where does DNA carry the genetic information? |
In its sequence |
|
|
Where do eukaryotic cells keep chromosomes? |
Condensed & packaged into the nucleus |
|
|
What kind of chromosomes do prokaryotes have? |
Single, circular chromosomes |
|
|
What are plasmids? |
- Small circular extra-chromosomal DNA - Carries genes with non-essential functions (like antibiotic resistance) |
|
|
What is the central dogma of biology? |
DNA (genes) --> RNA (message) --> Protein (product) |
|
|
What is replication? |
DNA copying itself |
|
|
What is transcription? |
DNA makes RNA |
|
|
What is translation? |
RNA makes protein |
|
|
What is semiconservative replication? |
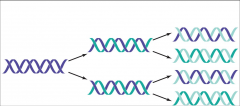
Each strand serves as a template for replication |
|
|
What does helices do? |
unzips DNA (replication fork forms) |
|
|
What is DNA polymerase (DNAP)? |
the replicating enzyme |
|
|
DNA synthesis occurs ___' to ___' |
5' to 3' |
|
|
2 types of strands formed during replication? |
Lagging & Leading |
|
|
What why does DNAP move? |
towards the helices |
|
|
The _______ strand is fragmented because it has to go back every time DNA unzips |
Lagging strand |
|
|
What is the origin (oriC)? |
A specific DNA sequence at which replication begins |
|
|
What is the terminus (terC)? |
A DNA region at which each replication fork ends during replication |
|
|
How does replication initiate? |
DNA polymerase and helicase bind to DNA at oriC & begin replication |
|
|
Replication is _____________? |
Bidirectional: 2 complexes of DNA polymerase set off in opposite directions (looks like greek letter theta) |
|
|
Where do both copies of replicated DNA reside? |
in its own new daughter cell |
|
|
Describe RNA synthesis (transcription). |
1. DNA sends messages to ribosomes 2. mRNA message is made by RNA polymerase 3. Promoters control transcription |
|
|
________+_______= RNA polymerase |
Core + Sigma |
|
|
What is the core responsible for? |
assembling RNA |
|
|
What is sigma responsible for? |
- Finding promoters on the DNA strands where the RNA polymerase can bind - each sigma recognizes a specific promoter sequence & determines which messages get sent |
|
|
What are promoters? |
DNA sequences that indicate where to start transcription (start the message) |
|
|
What 2 things are part of a promoter? |
-35 box & -10 box |
|
|
Promoter sequences are NOT ______? |
identical |
|
|
How do you determine the consensus sequence for sigma? |
average all the promoter sequences |
|
|
Stronger promoters are closer to _________. |
consensus |
|
|
What are 2 things strong promoters do? |
- call over lots of RNA polymerases - microorganism will create lots of messages (lots of protein later on) |
|
|
What do RNA nucleotides base pair with? |
complementary DNA |

