![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Origin of keratinocytes? |
Ectoderm |
|
|
Where are the stem cells for keratinocytes found? |
interfollicular basal layer, bulge region of hair follicles |
|
|
How many days does it take for a keratinocyte to moved from the basal layer to the stratum corneum? Through the stratum corneum? |
14 days
14 days |
|
|
Do all keratinocytes in the basal layer migrate to the top? |
NO- some cells are stem cells and remain in the basal layer (this was a Merz question) |
|
|
What signal is neccesary to maintain the proliferative state of the basal layer stem cells? |
p63
suppresses cell cycle inhibitors |
|
|
What promoted terminal differentiation of basal deratinocytes and spinous layer development? |
notch |
|
|
Which ion is necessary for keratinocyte differentiation? |
CALCIUM |
|
|
Acidic vs basic keratins (both epithelial and hair).
type and which chromosome? |
Acidic: K9- K28 (epithelial), K 31-K 40 (hair), chromosome 17 (17 year olds drop acid, small dog (K9) drinking acid), low molecular weight
Basic: K1-K8, K 71-80 (epithelial bookends!), K 81-86, chromosome 12 |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K1, K 10 |
suprabasalar layer, NO PALM
EHK, epidermolytic icthyosis |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K1, K9 |
palmoplantar suprabasal layer
vorner epidermolytic PPK |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K2e, K10 |
Granular layer
Icthyosis bullosa of Siemens (Sie - 2ie) |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K3, K12 |
Cornea
Meesmann corneal dystrophy |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K4, K13 |
non keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
white sponge nevus |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K5, K14 |
Basal layer
EBS multiple types, dowling degos, naegeli franschetti jadassohn, dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K6a, K16 |
ORS, hyperproliferative states, UVR, wound healing
Pachyonychia congenita 1 (Jadassohn–Lewandowsky syndrome)- oral leukokeratosis |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K6b, K17 |
nail bed
Pachyonychia congenita 2 (Jackson Lawler syndrome)- EICs, prenatal teeth, steatocystoma |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K8, K18 |
simple endothelium
IBD, cryptogenic cirrhosis |
|
|
K20 |
Merkel cells |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K 75 |
hair medulla, PFB
|
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K81, 83, 86 |
hair cortex, monolethrix |
|
|
Location and associated disease?
K74 |
hair IRS, wooly hair |
|
|
4 types of cells in the basal layer? |
melanocytes, keratinocytes, merkel cells, langerhans cells |
|
|
What keratins do basal keratinocytes make/express? |
K5/14 |
|
|
What keratins are made in the stratum spinosum? |
Produce 1/10
express, but don't produce 5/14 (this is made in the basal layer) |
|
|
In what layer do lamellar granules start to form? |
stratum spinosum |
|
|
What is contained within the lamellar granules (odland bodies)? Decreased numbers of lamellar granules are associated with what? |
Lamellar granules - ceramide, FFA, cholesterol (these start to form in the stratum spinosum, in the upper granulosum, enzymes degrade lamella granules to release their contents --> cornified lipid envelop formation)
decreased number of LG in Flege's disease, Harlequin icthyosis |
|
|
Normal number, but structurally abnormal lamellar granules seen in what disease? |
congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma |
|
|
What keratins are expressed in the stratum granulosum? |
Express K1/10 (made in stratum spinosum) --> K2/11 |
|
|
Keratohyaline granules start forming in what layer? |
Stratum granulosum |
|
|
what is in the keratohyaline granules? |
F granules- contain profilaggrin
L granules- contain loricrin |
|
|
Which component of the cornified envelop is decrease in psoriasis? |
decreased loricrin, increased involucrin |
|
|
What common condition has decreased profillagrin? |
ichthyosis vulgaris |
|
|
This filaggrin degradation produce blocks UV and forms NMF? |
urocanic acid |
|
|
Where is the cornified envelope formed? |
Initiated in the upper spinosum, completed in the SC
Contains LIP Loricrin (80%) Involucrin Profillagrin (cleaves to fillagrin) |
|
|
What are the 5 components of the desmosome junction? |
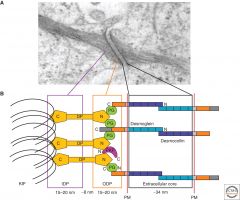
1. Desmoglein (transmembrane, Ca2+ dependent cadherin) 2. Desmocollin (transmembrane, Ca2+ dependent cadherin) 3. Desmoplakin DP (link btw cadherin and keratin) 4. Plakoglobin PG (link btw cadherin and keratin) 5. Plakophilin PKP (link btw cadherin and keratin)
|
|
|
What are the cadherins? |
Desmolgein
Desmocollin |
|
|
Which member of the plakin family is found in both desmosomes and adherens junctions? |
Plakoglobin |
|
|
Associated disease?
Desmocollin 1? |
Desmocollin 1 (transmembrane cadherin)
subcorneal pustular dermatosis
|
|
|
Components of adherens junctions? |
aka zona adherens
classic cadherins (E, P, N) plakoglobin alpha catenin beta catenin |
|
|
Associated disease?
Desmoglein 1 |
Desmoglein 1- Pemphigus foliaceous, bullous impetigo, SSSS, striate PPK |
|
|
Associated disease?
Desmoglein 3 |
Desmoglein 3- pemphigus vulgaris |
|
|
Associated disease?
Desmoplakin |
striate PPK, carvajal syndrome, wooly hair syndrome |
|
|
What are the cutaneous effects of EGFR inhibitors? |
PRIDE!!!
papulopustules/paronychia, regulatory abnormalities of hair growth, itching, dryness, EGFRi |
|
|
What therapies are best used to manage EGFR inhibitor side effects? |
ORAL TETRACYCLINES
remember, examples of EGFR inhibitors include gefitinib, erlotinib, afatinib, and icotinib for lung cancer, and cetuximab for colon cancer. |
|
|
Which antimicrobial proteins are expressed constitutively in keratinocytes? Stimulated? |
Constitutive expression: B definsins, leukocytes protease inhibitors
Stimulated: HBD2, LL37, TLR, STAT3
**remember, AD has decreased expression of LL37 and HBD2
** psoriasis has increased expression of LL37 and HBD2
This is why there are so many more infections in AD!!!! |
|
|
Inheritance patterns of EBS? |
All are AD except EBS with muscular dystrophy |
|
|
Defect in EBS? |
K5/14 |
|
|
Presentation of Dowling Degos disease? Mutation? |
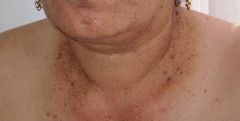
AD mutation in keratin 5
Black/brown macules in reticular distrubution in axillae, neck, inframmary, can be a/w perianal SCC |
|
|
Presentation of bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma? Mutation? |
EHK- BCIE
AD mutation in K1, 10
newborn- widespread bulla, erythroderma infant to adult- corrugated hyperkeratosis prominent in flexures, malodorous, macerated intertriginous regions |
|
|
Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens presentation? Mutation? |
AD mutation in K2e, 10
similar to EHK, but with milder blistering
fragile blisters early in life (Mauserung phenomenon- superficial molting in neonates) |
|
|
Diffuse PPK presentations of Unna-Thost and Vorner? Mutation? |
Unna- Thost (U --> non epidermolytic), AD mutation in K1 (one, UNO thost), hyperkeratosis over pressure areas
Vorner (epidermolytic), AD mutation in K9 >K1 (9ER, vornER), hyperkeratosis over pressure areas |
|
|
Pachyonychia congenita 1 vs 2? |
PC1 (Jadassohn Lewandowsky)- defect in K6a/16, oral leukokeratosis (ONE tongue)
PC2 (Jackson Lawler)- defect in K6b, 17, natal teeth (TWO teeth), steatocystoma multiplex, velus hair cysts |
|

mutation? |
Monilethrix, AD mutation in K81/86 (hHb1/6)
Hair findings- short, fragile, dry, lusterless, breaking internodal
Cutaneous/other- KP, brittle nails, tooth abnormalities, cataracts, MR |
|
|
White sponge nevus of Cannon has a mutation in what? |
AD mutation in K4/13
white fissured, spongy plaques on oral mucosa, esophagus, vagina, rectum |
|
|
Which keratin pair is expressed in a hyperproliferative epidermis?
1/10 3/12 5/14 6/16 8/18 |
6/16 |
|
|
Type I (acidic) hair keratins?
Type II (basic) hair keratins? |
I: 31-40 II: 81-86 |
|
|
Just read this... |
Keratinocyte adhesion:
Desmosomal cadherins- desmosomes Classic cadherins- adherens junctions Catenins- desmosomes and adherens Claudins- tight junctions Connexins- gap junctions |
|
|
All of the following pertain to odland bodies except:
a. contain squalene b. are found intracellularly in the upper level of keratinocytes c. discharge their contents into the extracellular space at the junction of the granular and cornified layers d. establish a barrier to water loss e. mediate stratum corneum adhesion in conjunction with filaggrin |
odland bodies (lamellar granules) do NOT contain squalene |
|
|
Odland bodies:
a. contain keratins b. are found intracellularly in the basal cell layer c. are exclusively intracellular d. crosslink with K5/14 e. are secretory granules with features of lysosomes |
Odland bodies (lamellar granules) are secretory granules with features of lysosomes |
|
|
What is the major lipid barrier of the skin? |
ceramide |
|
|
What is the major component of the cornified envelop which surrounds corneocytes? |
loricrin (80%) |
|
|
What component of the stratum corneum blocks UV light? |
urocanic acid |
|
|
At what estimated gestational age are all layers of the keratinized epidermis identifiable?
8w 12w 16w 20w 24w |
24 weeks!!
mature epidermis complete with interfollicular keratinization |
|
|
Epidermal stratification occurs at what EGA?
4w 8w 12w 16w 20w |
8 weeks, remember p63 is responsible for this!!! |
|
|
Once a keratinocyte leaves the basal layer, how long until it is shed? |
28 days (14 days to get to the corneum, 14 days to get through) |
|
|
T/F, not all basal cells have the potential to divide |
TRUE |

