![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coxsackie A virus is mostly responsible for... |
A16
HFM Disease |
|
|
Coxsackie B virus is mostly responsible for... |
myocarditis, pericarditis, meningitis |
|
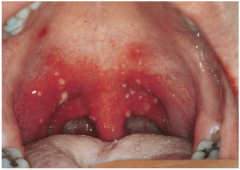
Cause? |
Coxsackie A and B
painful vesicles and erosions on the soft palate, uvula, tonsils, pharynx, buccal mucosa |
|
|
Progression/characteristics of measles? Incubation period? |
paramyxoviridae virus
incubation about 2 weeks prior to development of exanthem
3-4 days prior to exanthem, prodrome of cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, photophobia, high fever, malaise, swelling of eyelids
1-2 days prior to exanthem, development of koplik's spots
erythematous macules and papules in a cephalocaudad spread |
|
|
Koplik's spots are pathomneumonic of... |
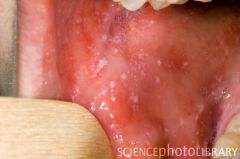
measles |
|
|
Forcheimer's spots are pathomneumonic for... |
Rubella (Togaviridae)
petechial macules on the soft palate |
|
|
Difference between rubeola and rubella? |
Rubeola --> measles --> paramyxoviridae
Rubella --> German measles --> togaviridae
Rubella has tender LAN and Forcheimer's spots, Rubeola has Koplik's spots |
|
|
Specific complications of Rubella? |
Arthralgias and arthritis in postpubertal girls, women
Less often- hepatitis, myocarditis, pericarditis, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, encephalitis |
|
|
Triad of congenital rubella? |
MC from infection during first 16 weeks of pregnancy, about 20% chance of damage to the fetus
Triad of: cataracts, deafness, congenital heart defects (PDA, VSD) |
|
|
Progression of the exanthem of Erythema Infectiosum? |
Erythema Infectiosum --> Fifth's Disease
Human parvovirus B19
Parvoviridae (ssDNA)
1. Bright red macular erythema of cheeks (1-4d) 2. Lacy reticular rash on trunk, neck, extensor extremities (7-10d) 3. Periodic recurence of lacy rash with heat, sunlight, activity |
|
|
Complications of Fifths disease? |
1. Patients with decreased RBC survival time ---> (hemoglobinopathies, hemolytic disease) --> aplastic crisis, prolonged viral shedding
2. Immunocompromised --> severe chronic anemia, viral shedding
3. Pregnant --> fetal infection, anemia, miscarriage/stillbirth, hydrops fetalis (greatest risk of infection acquired before 20 weeks) |
|
|
Human parvovirus B19 structure? Causes what? |
single stranded DNA
Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), papular purpuric gloves and socks syndrome |
|
|
Smallpox/variola, cause? Characteristics? |
Smallpox (variola), d/t orthopoxvirus of poxviridae family
high fever for 1-4 days prior to rash onset, plus malaise, HA, backache, lesions consentrated on face and limbs (somewhat spare trunk)
SYNCHRONOUS LESIONS ie all the lesions are in the same stage of development
Patients are contagious until the last crust falls off |
|
|
What is vaccinia? What is variola? |
Vaccinia is an orthoposxvirus used as a vaccine for smallpox in humans --> papules at vaccination site --> vesiculates --> crust
Variola is small pox |
|
|
Not only is the smallpox vaccine effective against smallpox, it can also protect against... |
monkey pox
primarily in Africa (rodents and monkeys) |
|

Disease? Who is at risk? |
Orf (ecthyma contagiosum, sore mouth, scabby mouth)
shepherds, vets, butchers at risk --> typically on hands following contact with infected animal: will get a papule --> nodule --> ulcerates/crusts
Heals in 4-8 weeks |
|
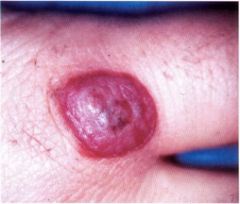
this guy is a dairy farmer. |
Milkers nodule
pseudocowpox
lesions on hands virtually identical to ORF |
|
|
Most common molluscum contagiosum in kids? HIV? |
Kids: MCV 1
HIV: MCV 2 |
|

Vector for disease in South America? Phases of disease? |
Dengue Fever!
Aedes aegypti can also transmit Chikungunya (Africa)
Acute phase- fever 2-7 days, HA, muscle/bone pain, vomiting, epistaxis, gingival bleeding
Critical phase- defervescence, abd pain, vomiting, mucosal bleeding, increase in HCT with decrease in platelets
Convalescent phase- white isles in sea of red, hypervolemia |
|
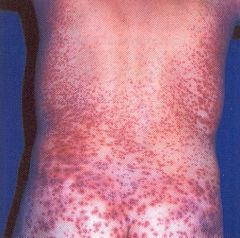
Patient from Caribbean presents with a high fever, gingival bleeding, pulmonary edema |
Dengue fever
Classic convalescent phase of 'white isles in a sea of red' |
|
|
Clinical presentation of Chikungunya? Vector? |
Togaviridae, transmitted by aedes aegypti (same as dengue fever)
fever, HA, myalgias, arthralgias, acral edema and erythema, genital ulcers, PIH |
|
|
Diagnosis of Rabies in animals? |
brain tissue from two locations |
|
|
Skin biopsies looking for rabies should be taken from where? |
posterior neck |
|
|
Post exposure prophylaxis for rabies? |
Wound cleaning
RIG
Vaccine (days 1, 3, 7, 14) |
|
|
Forchheimer's spots?
Koplik spots? |
Forchheimer's spots- petechiae on soft palate in Rubella
Koplik spots- gray-white papules on buccal mucosa in Measles |
|
|
Adjunctive treatment for measles? |
high dose vit A 200,000 IU x 2, 24 hours apart |
|
|
Pathogenesis of parvovirus? |
ssDNA
globoside (P antigen) on RBC is the receptor, parvo virus infects them and lyses them
some people lack the P antigen, and thus are not susceptible |
|
|
Diseases related to HHV6? |
PR DRESS ** Rosai-Dorfman (sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy) Accelerates progression of HIVv MS Chronic fatigue syndrome |
|
|
What is Eczema vaccinatum? |
Vaccinia (small pox) virus superimposed on dermatitic skin (AD, dariers, nethertons) --> systemic illness with 30-40% mortality rate in untreated patients |
|
|
On the BX of Orf, what is secreted to cause the vascular proliferation? |
VEGF |
|
|
Dengue fever is also known as 'break bone fever', why? |
Severe back pain!
remember, Grandpa had this!!
remember, white isles in a sea of red |
|
|
How do we diagnose dengue fever? |
Lab triad: increased LFT, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia
Will see evidence of plasma leakage, hematocrit will be more than 20% of normal with a more than 20% drop in hct after fluid replacement
positive tourniquet test, petechiae, ecchymoses, purpura, bleeding mucosa
will see white isles in a sea of red |
|
|
Chikungunya fever also has severe myalgias and arthralgias, just like Dengue fever... pathogenesis difference? |
Chikungunya has actual VIRAL infection of the synovium |

